Rx misses Flashcards
Why does isoniazid cause peripheral neuropathy (numbnes & tingling)
- Isoniazid creates a functional pyridoxine deficiency (B6)
- prevented or reversed with vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) supplementation
Diag?
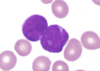
Name of cell on histo? Cells stain pos for what?

Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)– this is subtype of AML
Histo – Auer rods (purple needles in cyto),
-Stain pos for Myeloperoxidase
What type of cell?

Spherocytes (small round RBCs w/ no central pallor)
What are the signs of hypocalcemia
- Chvosteks sign = tapping facial nerve (tap the Cheek) –> contraction of facial muscles
- Trousseaus sign = carpal spasm upon bp cuff inflation
- Tetany
- Seizure
- QT prolongation
- Twitching
Diag?

Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome
= acute primary renal insufficiency d/t hemorrhage. Assoc w/ septicemia (N. meningitidis), DIC, shock
-Image shows sack of blood adrenal ***
Which nerve injury causes Trendelenburg sign?
Superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
-lesion is contralat to side of hip that drops. But lesion is ipsilat to the leg pt stands on
Which antiepileptic causes life threatening rash
Lamotrigene
- Life threatening rash = stevens-johnsons syndrome
- MOA: block voltage gated Na+ channels –> inh release of glutamate
Which heart condition are pts with Turners at risk for developing?
Coarctation of aorta
Schizoaffecive disorder diag
Schizophrenia + major mood disorder (MDD or bipolar) w/ psychotic features
- Schizophrenia: ≥2 sx for ≥1 mo (delusion, hallucination, disorganized speech, catatonic behavior, flattening, avolition, anhedonia asocial, alogia)- 1 sx must be first three.
- Major mood disorder
- Must have Psychotic features > 2 wks w/o mood episode
What does histo show?
What conditions do you see this in?

Caseating granuloma (has central necrosis), epithelioid histiocyte aggregation
- See this in TB & fungal infections
Which diseases assoc w/ HLA-B27
- Psoriatic arthritis (NOT RA)
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- IBD-associated arthritis (Chrons & UC)
- Reactive arthritis
PAIR
Organisms associated with IV drug abuse
- S. aureus
- Tricuspid valve Endocarditis
- Pnemonia
- Osteomyelitis
S.pneumoniae
- Pneumonia
- Candida albicans
- Tricuspid valve endocarditis
- Osteomyelitis
Pseudomonas
- Tricuspid valve endocarditis
- Osteomyelitis
HTLV –>Adult T cell lymphoma (neoplasma of mature T cells)
A 50-yo f
- generalized malaise and a nagging cough w/ hemoptysis. Today dark urine.
- PE: Diminished air entry in the lungs B/L and an ulcerated lesion of the mucosa of the right naris.
- No hx asthma or allergies.
- Urinalysis: (+) blood
- Cr= 1.7 mg/dL. (normal 0.6-1.2)
Granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis (Wegener)
- –> leads to RPGN (crescentic)
- Nephritic = azotemia (incr Cr), hematuria
- PR3/C ANCA in serum (vs eosinophilic granulomatosis w/ polyangiitis- churg-strauss- has Eosinophils in urine and has hx asthma/allergies but has ANCA)
- Lung and nose involvement (vs microscopic polyangiitis- very similar sx but no nose/upper resp)
- Focal necrotizing vasculitis
What is DLco in pulmonary function measurements?
= Diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) –(measures the general diffusion capacity)
- This indicates a reduced ability of the lungs to transfer gases from the alveolar sacs to the pulmonary capillaries and visa versa.
- Will be decr in COPD (emphysema)
- Will be incr in polycythemia, asthma, and increased pulmonary bl vol as occurs in exercise.
- 57-yo m, asymptomatic
- A blood smear shows neutrophils in all stages of maturity with an especially large number of immature myelocytes and segmented neutrophils compared to mature cells.
Laboratory results and blood smear are shown below:
Diag?

CML
-tx w/ tyrosine kinase inhibitors (imatinib, dasatinib)
A 45-yo obese f
- 2-day hx of intermittent ab pain, N/V.
- Sx worse after eating a hamburger & fries @ bbq yesterday.
- Smoker
- Fmhx HCC
diag?
Cholelithiasis
(4 Fs- fat, f, forty, fertile)
- 7-yo son
- bouts of perianal itching, which occur at night and disrupt his sleep.
- PE: mild erythema around the anus.
- physician instructs the mother to apply cellophane tape to the child’s anal area at night when the itching occurs and bring tape back for analysis.
The pediatrician observes the findings in image
Diag?

Enterobius vermicularis (pinworm)
Pneumonia in an IC pt is prob caused by which organism?
pneumocystis jirovecii
UTI
(-) nitrite
(+) leukocyte esterase
Foley catheter
Pt in hospital
Which organism caused UTI?
Enterococcus: bc (-) nitrite and nosocomial (HA) and catheter
- E.coli is most common cause but has (+) nitrite. Also klebsiella, serratia
- Staph sapro don’t see in nosocomial (HA) or catheter
CML tx
tyrosine kinase inhibitors (imatinib, dasatinib)
What does this histo show?
what conditions do you see this in?

- Non caseating granuloma (lack central necrosis-heach histiocyte has nu)
- Histo: big aggregate of epithelioid histiocytes (this makes it a granuloma). multinucleated giant cells inside, surrounded by lots of lymphocytes
- Conditions:
- Reactional to foreign material (ex- ruptured breast implant–> material leaks out)
- Sarcoidosis
- Beryllium exposure
- Chrons disease
- Catscratch disease– granulomas are stellate shaped
A 24-yo fintellectually disabled
- Having MI
- PE: tall, lanky body and lenses that are displaced both downward and inward.
Homocystinuria
- Sx
- Intellectual disability
- Marfanoid habitus– tall lanky body
- Down and inward eye lenses– lens subluxation
- Cardiac problems – MI
- Pathogenesis
- def cystathione synthase (B6 as cofactor) –> incr homocystine
- or def methionine synthase (B12 as cofactor) –> incr homocystine
What test to confirm c diff infection
Toxin assay (gold std)
- Can also use ELISA (faster, but less sensitive)
- c diff has 2 protein exotoxins (A and B) that cause the colitis
- toxin producing strains able ot survive bc of disruption of normal GI flora (d/t ABX)
Congenital condition
Diag?

Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (bowel moves into thorax)