BSCE II Flashcards
(81 cards)
Voluntary opening of the upper eyelid is produced by motor innervation from which nerve?
Oculomotor (CN III)
- eyelid opening via levetor palpebrae
- Also does eye movement (SR, IR, MR, IO), pupil constriction, accomodation
Describe rhematoid factor
IgM autoantibody against IgG Fc region
-it’s directed against determinants on the immunoglobulin molecules gamma chain
What does it mean if P value = 0.01
If P value ≤ 0.05 –> reject the null
- Null is that there is no sig diff bw groups
- if you reject null –> means there is a sig difference
Which types of parasides have indirect life cycle, why?
Indirect life cycles
- req 2 host stages
- Definitive host
- Where repro and adult life phase take place
- Intermediate host
- Where development occurs and then transmitted back to definitive host
- Definitive host
- Facilitates disease transmission in the form of vectors
- Ex) mosquitos, plasmodium, leishmania

How long do panic attacks last
they peak in 10 mins
-does not last for days at all
Which cell responsible for the regeneration of peripheral axons?
Schwann cells
- each schwann cell myelinates only 1 PNS axon
- injured in GBS

What describes the therapeutic result of cognitive behavioral therpay
Cognitive restructuring
-(Not extinction– that is from discontinuing + or - reinforcement which eventually eliminates the behavior)- in operant conditioning
By what age should a baby develop object permanence
Beta-hCG is structurally similar to which other hormones..and therefore has the activity of those hormones
- FSH
- LH –> stim progesterone secr from corpus luteum
- TSH
The denaturation of proteins always leads to (rev/irrev) loss of secondary and tertiaty structure?
rev
The stability of quaternary structure in proteins is d/t what type of bonds holding the subunits together?
Non-covalent

Which type of bonds stabilize the alpha helix?
H-bonds
-alpha helix and beta sheets are secondary xtures

In a P/A xray of wrist
-which bone is superimposed on the other?
Pisiform is superimposed on the triquetrium

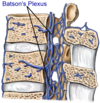
Venous plexus of batson
serves as conduit for cancer cells to travel from one part of body to another
-particular prostatic adenocarcinoma
The confluence of dural sinus is assoc with which bone
occipital

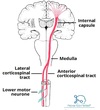
A lesion in the corticospinal tract would product what?
UMN syndrome
Which zone is affected most by hypoxia

Zone III = hepatocytes closest to the central vein
-hepatocytes closest to the portal triad are least susceptible
Where are ketone bodies synthesizes?
Liver

Which nerves responsible for erection?
pelvic sphanchnic nerves (S2-S4)
- NO –> vasodiltion –> proerectile
- NE is anti erectile
- erection is parasymp

Which xture can interact to produce leucine zipper xture
alpha helix (not beta sheet)

Which N is big toe pain
L5 dermatome

What is initial product of FA synth?
Palmitate 16c

stab would in left 5th intercostal space just lat to sternum would hit what?
Right ventricle

What does a nucleosome consist of?
8 histone core
DNA looped around
H1