Rheumatoid Arthritis - Investigations and Management Flashcards
How is RA mainly diagnosed?
Clinical symptoms
What bloods can be used to confirm?
CRP - Shows inflammation
ESR- shows inflammation but affected by many things
RF - Positive in majoirty but increases with age
Anti ccp - More specific but less sensitve
When is a CXR used in RA?
?Rheumatoid nodules
How can an US help?
Shows increased blood flow toward joint
What are the 4 types of treatment?
- Analgesia/NSAIDS
- Steroids
- DMARDs
- Biological
What are the NSAIDS and how do they work?
What should you be aware of?
Ibruprofen, Naproxen
Reduce inflammation but be awared of IHD and GI symptoms (bleeds and ulcers)
How do the steroids work?
Reduce immune response and can be given intra/peri articular
How do DMARDS work and whay are they?
Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs - They attempt to alter the course of the disease, not just mask symptoms.
Methotrexate - Inhibits T cells
Sulphasolazine - Suppresses TNF1 and Il1
Leflunomide - Inhibits lymphocyte production
What are the biological agents?
They also try and alter the course of the disease
infliximab and adalimumab are anti tnf
Etanercept is anti TNF
Risk of causing infection due to immune suppression
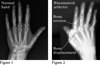
What are the five radiological signs of RA?
Joint space narrowing
Erosions
Subchondral osteopenia
Joint subluxation
Soft tissue swelling