Review Q's Week 1 Flashcards
1. Anatomy of the heart (1-59) 2. Physiology humoral n nonhumoral factors (60-85) 3. seminar (86-128) 4. pathology of hypertension (129-145) 5. patho lab of hypertension (146-153) 6. renin system pharma (154-174) 7. vasculation of heart anatomy (175-222) 8. clinical aspects of hypertension (223-245)
What produces the second heart sound?
In ventricular diastole, when the pressure is low in the ventricle and high in aorta and pulmonary trunk. The blood wants to backflow, but instead the close the semilunar valves are shut. This shutting is what causes the dub
What is the third elevation called?

incisura (or dicrotic notch)
Which grade of hypertensive retinopathy causes papilloedema?
Grade 4
What causes the double peak in systole in bispheriens pulse?
anterior motion of mitral valve
What is a potential issue that may develop after endothelial destruction?
Atherosclerosis
Which vegal branch supplies the superficial cardiac plexus?
inferior branch of left vagus
(the rest supply the deep cardiac plexus)
Which body reflex prevents pulmonary edema?
the atrial mechanoreceptor reflex
(AKA Bainbridge reflex or cardiopulmonary reflex)
What structure allows from communication between atria and ventricles?
atrioventricular orifice
(protected by the tricuspid valve on the left side and the bicuspid valve on the right)
Which of the following has two cusps?
a. aortic valve
b. pulmonary valve
c. both
d. neither
d. neither
Which is most likely?
a. Primary hypertension
b. Accelerated hypertension
c. Secondary hypertension
d. Essential hypertension

b. Accelerated hypertension
Which is located anteriorly in the sulcus between the ventricles?
a. small cardiac vein
b. middle cardiac vein
c. great cardiac vein
c. great cardiac vein
Describe the diastolic pressure if the heart rate and vascular resistance are low.
diastolic pressure would be low. The low heart rate would give the blood plenty of time to run off to the periphery; the vascular resistance is also low, so it would make it easier for the blood to run off into the circulation. -> low diastole
Where does blood flow during arterial septal defects? Why?
flows from left to right (at the beginning) because the left has higher pressure
Which two of the following adrenergic receptors does norepinephrine have a higher affinity for?
a. alpha 1
b. alpha 2
c. beta 1
d. beta 2
a. alpha 1
+
c. beta 1
Which is associated with Watson’s water hammer?
a. aortic stenosis
b. aortic insufficiency
b. aortic insufficiency
(Watson’s water hammer AKA bounding pulse AKA Corrigan’s pulse)
Which of the following increases calcium by releasing Ca from intracellular stores?
a. DAG
b. IP3
b. IP3
The aortic pressure is described as rising in a “tardus” manner, what does this mean? What condition could this be an indicator or?
tardus means slow; the pressure of the aorta would be rising slowly, which could indicate aortic stenosis
A patient comes in with weakness, dizziness, and perspiration. He compains of pain in his chest and left arm. Which nerves are conveying the pain? What can you give the patient to relief symptoms?
Pain sensation conveyed through sympathetic nerves of the heart (T1-T5 segment of the spinal cord)
Sublingual nitroglycerin is placed under the tongue (rapid absorption) to dilate the coronary arteries.
How does angiotensin 2 affect blood pressure? explain.
it increases BP by vasoconstriction and helping release aldosterone and vasopressin/ADH which then reabsorb Na and water
(it also indirectly enhances sympathetic activity by increasing NA release and by increasing reactivity to adrenergic stimulation)
Give me four vasodilators/activators of NO synthase.
Acetylcholine (usually)
Adenosine
Bradykinin
Substance-P
What three structures bring blood to the right atrium?
IVC, SVC, coronary sinus
Where do each of the following types of hemorrhages occur?

intercerebral is associated with hypertension
epidural is due to trauma
Which two of the following adrenergic receptors does epinephrine have a higher affinity for?
a. alpha 1
b. alpha 2
c. beta 1
d. beta 2
c. beta 1
+
d. beta 2
T/F: beta blockers are initiating drugs of hypertension treatment
False; beta blockers were used as initiating drugs, now we only use them in special circumstances
(ex/ angina and heart failure, and in heart failure we use a specific beta blocker)
During high blood pressure, how will baroreceptors act on vasopressin, sympathetic, and parasympathetic activity?
decrease vasopressin
decrease sympathetic activity
increase parasympathetic activity
What degrades natriuretic peptides?
Neprilysin
Which drugs reduce arteriolar and ventricular remodeling?
losartan + valsartan
(Angiotensin receptor blockers)
What two things separate the heart from the lungs?
pericardium and pleura
Describe the location of the small cardiac vein. What is it adjacent to?
between the right atrium and ventricle

Find the Posterior vein of the left ventricle


What are Lacunar Infarcts? Where are they common?
They are small noncortical infarcts caused by occlusion of a single penetrating branch of a large cerebral artery.
Most common in basal ganglia, deep white matter, and brain stem.
Which part of the interventricular septum is more likely to be defective?
membranous part (not muscular part)
When a patient is lying supine, at which vertebral level is the heart situated in?
a. T5-T7
b. T5-T8
c. T6-T8
d. T6-T9
b. T5-T8
Aortic stenosis results in? (3 things)
reduces stroke volume
a slow rising arterial waveform
late peaks in systole
Which of the following peaks in systole and diastole?
a. bispheriens pulse
b. dicrotic pulse
c. both
d. neither
b. dicrotic pulse
identify the black arrow

Right marginal artery
(aka acute marginal artery)
What’s a branch of the circumflex artery?
left marginal artery (or obtuse marginal artery)

Beta-blockers to give in heart failure patients are
carvedilol
metoprolol succinate
bisoprolol or nebivolol
The arterial pressure slope of the descending limb is determined by
systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
What are the four ways the sympathetic fibers stimulate the action of the heart?
↑ heart rate
↑ impulse conduction
↑ contraction force
↑ blood flow
A patient has a blood pressure of 169/90. Which hypertension grade is he in?
grade 2 (if one value crosses the threshold, thats enough to move into the stage)
grade 1 is 140/90 to 159/99
grade 2 is 160/100 to 179/109
grade 3 is 180/110 or higher
musculi pectinati originates from which of the following?
a. limbus fossa ovalis
b. Sulcus terminalis
c. fossa ovalis
d. crista terminalis
d. crista terminalis
Describe the diastolic pressure if the heart rate and vascular resistance are high.
diastolic pressure would be high. The high heart rate wouldn’t give enough time for the blood to run off to the periphery; the vascular resistance is also high, so it would make it hard for the blood to run off into the circulation. -> high diastole
What causes transient tachycardia that’s caused by norepinephrine release?
activation of beta 1 adrenergic receptors
How does the anacrotic notch affect arterial blood pressure?
distorts the pressure upstroke
What structure is found in “a”?

SA node
What’s found laterally to the heart?
lungs
Which is more effective in reducing blood pressure and ventricular hypertrophy?
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril +captopril
c. valsaratan + losartan
a. aliskiren
what causes disc edema with splinter hemorrhages?
severe hypertension
(disc edema=Papilledema; and the splinter hemorrhage is in picture)

What are two syndromes associated with aortic dissection?
Marfan and Turner syndrome
identify

sinoatrial nodal artery
Which of the following is used to perform ligation in surgery?
a. transverse pericardial sinus
b. oblique pericardial sinus
a. transverse pericardial sinus
How can we reduce mortality in heart failure patients?
sacubitril (neprilysin inhibitor) and valsartan (angiotension II receptor blocker)
** this combo is called ARNI
How do you tell the difference between pathological and physiological hypertrophy of the heart?
pathological hypertrophy is usually when the patient is obese and the heart enlarges so it can pump efficiently to the body
physiological hypertrophy is then the person is an athlete (Athletic heart syndrome)
in pathological hypertrophy the heart rate is high but in physiological hypertrophy, the resting heart rate is low
Which grade of Hypertensive Retinopathy is this?

grade 4, this is is papilloedema
The blood is pumped in the right ventricle to go to ___ via ___
the lungs via the pulmonary trunk
Which of the following are renin competitive inhibitors?
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril +captopril
c. valsaratan + losartan
a. aliskiren
Which of the following provides space for an enlarging heart?
a. transverse pericardial sinus
b. oblique pericardial sinus
b. oblique pericardial sinus
How do you locate the inferior border of the heart on a patient?
from the fifth intercostal space of the left side to the sixth costal cartilage
The smooth outflow part of the right ventricle is called
The smooth outflow part of the left ventricle is called
R-> the infundibulum
L-> Aortic vestibule
The outside portion of Crista terminalis is called?
Sulcus terminalis
Which second messenger does NO use to mediate vasodilation?
cGMP
The left coronary artery splits into
LAD (left anterior descending artery)
+
LCX (left circumflex artery)
Which of the following borders of the heart are mainly made up of the left atrium?
a. left border
b. right border
c. apex
d. superior border
e. inferior border
f. base of heart
d. superior border
+
f. base of heart
Where does the right coronary artery (RCA) originate?
Above the right cusp of the aortic valve
Where is the left auricle found? What is its function?
on the left atrium, it provides extra space for blood
What is this phenomenon? What causes it?

Fibrinoid Necrosis, occurs due to Malignant Hypertension
Where is the heart located?
a. superior mediastinum
b. middle mediastinum
c. inferior mediastinum
b. middle mediastinum
The image is indicative of
a. Benign nephrosclerosis
b. Malignant nephrosclerosis

Benign hypertension
Describe an anacrotic pulse
slow rise, later peak, and less stroke volume
Whats the diagnosis?

Intracerebral hemorrhage
What does it mean when the arterial pressure slope of the ascending limb is not steep (slowly rising pressure)?
high afterload (slow ejection ex/ arterial stenosis)
Which of the following sounds are classically heard in diastole?
a. S1
b. S2
c. S3
d. S4
b. S2
Which ventricle has a C shaped lumen?
the right ventricle
Which of the following is both sympathetic and parasympathetic activity activated?
a. brain ischemic reflex
b. crushing reflex
c. baroreceptor reflex
d. bainbridge reflex
e. atrial chemoreceptor reflex
e. atrial chemoreceptor reflex
What kind of pulse is this? What does it indicate?

Dicrotic pulse (2 peaks in once cycle, one in systole and one in diastole)
indicates heart failure /shock
Which cells produce nitric oxide? What stimulates their synthesis?
endothelial cells; blood flow shearing forces and NO-dependent vasodilators stimulate synthesis.
What is a high normal BP?
130-139/85-89

What is the incisura? (whats its other name?)
the incisura (aka the dicrotic notch) is a lowering in the arterial pressure due to the closure of the aortic valve (occurs at the beginning of diastole)
Which of the following is NOT a function of NO?
a. antiproliferative
b. antithrombotic
c. antiinflammatory
d. they’re all NO functions
d. they’re all NO functions
Which of the following is the diagram a representation of? explain.
a. bigeminal pulse
b. pulsus alternans

b. pulsus alternans
the pulses in pulsus alternans is regular while the pulses in bigeminal pulse occur irregularly (not the same distance between each pulse)
Describe the relationship between compliance and pressure
inversely proportional
How do you calculate Blood Pressure? (what’s the formula)
cardiac output X peripheral resistance
How does sleep apnea cause hypertension?
the body is afraid of hypoxia in sleep so it produces adrenaline, that leads to hypertension
Which artery accompanies the phrenic nerve?
pericardiacophrenic artery
Damage to which node is called heart block?
AV node (if defective, conductance will not reach the ventricles)
What kind of pulse is this? What does it indicate?

bispheriens pulse
occurs in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
What artery supplies the posterior third of the interventricular septum?
PDA posterior descending artery
Which of the following sounds is heard when both the mitral and tricuspid valves are closed?
a. S1
b. S2
c. S3
d. S4
a. S1
(at systole)
Which of the following does the transverse pericardial sinus lie anterior of?
a. aorta
b. vena cava
c. pulmonary trunk
b. vena cava
(it lies behind/posterior to the other two options)
How do you locate the superior border of the heart on a patient?
it’s from the second costal cartilage of the left side to the third costal cartilage of the right side
What is the ventriculo-aortic pressure gradient and what does it cause?
Its the pressure difference between the ventricle and the aorta, it causes the blood to move out of the ventricle and into the circulation.
Which of the following borders of the heart are mainly made up of the right atrium? (one or more)
a. left border
b. right border
c. apex
d. superior border
e. inferior border
f. base of heart
b. right border
How does vascular resistance affect the slope of the descending limb of the arterial pressure?
more vascular pressure, less steep slope
Which of the following has two anterior cusps
a. aortic valve
b. pulmonary valve
c. both
d. neither
a. aortic valve
Which bundle branch receives blood from the left coronary artery?
both bundle branches
(right bundle branch blood from both right & left coronary arteries, while the left only from the left coronary artery)
Which has a side effect of fetal anomalies?
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril +captopril
c. valsaratan + losartan
b. lisonopril +captopril
Which of the following peaks in systole?
a. bispheriens pulse
b. dicrotic pulse
c. both
d. neither
c. both
identify

left circumflex artery (LCX)
Which cusp of the mitral valve has more surface area?
a. anterior
b. posterior
c. septal
b. posterior
Describe the systolic and diastolic pressure in aortic insufficiency/regurgitation
systolic pressure high and diastolic pressure low
(the aortic valve not closing means that blood can go in two directions- the circulation and back to the ventricle- and this causes the diastolic pressure to be lowered)
(the systolic pressure is high because more volume goes in the ventricle, causing it to stretch and eject blood harder)
The activation of which of the following causes vasodilation?
a. angiotensin type 1 receptor
b. angiotensin type 2 receptor
b. angiotensin type 2 receptor
Where does Kugels anastomotic artery arise from and where does it transverse?
Arises from the proximal left circumflex artery and ends up in the distal right coronary artery
What’s the only cause of pain of abdominal organs?
excessive destination
Which of the following does vasopressin use to increase systemic vascular resistance?
a. cAMP
b. IP3
b. IP3
(vasopressin uses cAMP to increase blood volume)
Which of the following makes the patient LESS susceptible to ischemia?
a. right dominant coronary circulation
b. left dominant coronary circulation
c. balanced coronary circulation
c. balanced coronary circulation
(if blockages happen they’re better off because they have a back up)
Which (one or more) of the following inhibits parasympathetic/ vagal activity?
a. brain ischemic reflex
b. crushing reflex
c. baroreceptor reflex
d. atrial mechanoreceptor reflex
e. atrial chemoreceptor reflex
d. atrial mechanoreceptor reflex
AKA bainbridge reflex
What is pulasus parvus?
its a small amplitude of arterial pressure
(Pulsus parvus et tardus is the physical exam finding in aortic valve stenosis-The term “parvus” means weak and “tardus” means late, thus the pulse is weak and late.)
A patient has a blood pressure of 159/90 and has two risk factors. What his risk of CVD death? How would you treat him?
moderate risk, treat with lifestyle changes for a few weeks then with drug if insufficient

What two (main) structures of the heart bring blood to the heart?
superior and inferior vena cava
compare and contrast the effect of epinephrine of high VS of low concentrations on diastolic and systolic pressure
at low concentrations= increases systolic + decrease diastolic
at high concentrations= increases systolic + increase diastolic
(because at high concentrations it also starts affecting the alpha receptors, not just the beta)
T/F: the lower the heart rate, the lower the diastolic pressure
true (lower heart rate gives more time for the blood to run off)
Which dermatomes are responsible for the pain in the medial side of the arm and the forearm?
T1 and T2
What provides blood to the left atrium?
the four pulmonary veins
Activation of which causes vasoconstriction?
a. angiotensin type 1 receptor
b. angiotensin type 2 receptor
a. angiotensin type 1 receptor
What two (main) structures take blood away from the heart?
pulmonary trunk and aorta
Which of the following occurs when the mitral valve is open?
a. systole
b. diastole
b. diastole
What identifies the first grade of hypertensive retinopathy?
arteriole thickening
What two nerves are the afferent pathway of baroreceptors?
CN X and IX
(CN X for the aortic arch and CN IX for the carotid sinus)
Which of the following has a greater side effect of coughing? explain the mechanism.
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril +captopril
c. valsaratan + losartan
b. lisonopril +captopril
(Decrease bradykinin degradation)
What causes the semilunar valves to open?
when ventricular pressure exceeds diastole pressure in pulmonary trunk and ascending aorta
When does blood enter arteries? What is the exception to the rule? explain.
blood enter arteries during systole, except the coronary arteries, which get blood during diastole. This is because the (right and left) coronary arteries are branches of the aorta, and during systole, blood rushes through it at a very high pressure and speed, so it doesn’t have time to turn perpendicularly and go to the branches of the aorta. When the aortic valve closes, the pressure decreases, allowing blood to go to the coronary arteries.
What’s the diagnosis?

aortic dissection
identify (black arrow)

left diagonal artery (branch of LAD)
What is this called?
a. anacrotic notch
b. dicrotic notch

a. anacrotic notch
The pericardial cavity is a space between which two structures?
between the parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium
What converts angiotensin I to angiotensin (1-7)?
neutral endopeptidases (NEP)

Which of the following are competitive antagonists of AT1- receptors?
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril +captopril
c. valsaratan + losartan
c. valsaratan + losartan
Describe the relationship between pressure and heart rate while undergoing the Valsalva maneuver (in a normal patient)
inversely proportional
(because high mean arterial pressure, the baroreceptors see this and decrease heart rate)
Which of the following makes the arterial pressure slope of the ascending limb LESS steep?
a. anemia
b. aortic insufficiency
c. aortic stenosis
c. aortic stenosis
What occurs if the BP cuff is slightly too tight for the patient? How will that affect the BP results?
if it was small it will give false high reading
describe the stroke volume and vascular resistance thats relates to a small and slow pulse.
stroke volume = low
vascular resistance = high
(small and slow pulse=Pulsus parvus et tardus=aortic stenosis- due to the stenosis the resistance is high and the stoke volume is low-blood cannot easily get through)
Describe the production of the first heart sound.
papillary muscle contracts tightens the chordae tendinae and drawing the cusps of AV valve together in order to close the mitral and tricuspid valves (lub)
identify (blue circle)

Left conus artery
(goes around the pulmonary trunk along with right conus artery)
identify the artery. Which artery does it arise from?

PDA posterior descending artery (aka posterior interventricular artery)
its a branch of the right coronary artery
What are three functions of the fibrous skeleton of the heart?
keeps orifices/valves intact (no dilation or contraction)
provides attachment of muscles
separates atria from ventricles
A patient has a blood pressure of 159/90 and has more than 3 risk factors. What his risk of CVD death? How would you treat him?
high risk, start with drugs and lifestyle changes

A 43 patient comes in with aortic dissection, what is it? and what is the likely cause?
an aortic dissection is an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta that allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. mostly caused by hypertension.
What’s found anteriorly to the heart?
sternum, muscles, ribs
identify

left anterior descending artery (LAD)
(aka anterior interventricular artery)
Which disease is characterized by low diastolic pressure, no incisura, and large stroke volume
aortic insufficiency also known as aortic regurgitation
(low diastolic pressure because the blood is leaking into wrong compartments. the large stroke volume because of the stretching due to the extra blood. incisura missing because the aortic valve isn’t closing)
What supplies blood to the left branch of the AV bundle?
Left coronary artery
What is the oval depression with a margin that is found on the left atria called?
fossa lunata
(indicates fossa ovalis on the right atria)
What’s the most common artery involved in MI?
LAD/anterior interventricular artery
Which of the following leads to hypertrophy?
a. valve incompetence
b. valve stenosis
b. valve stenosis
What artery goes around the pulmonary trunk?
right conus artery
aka annulus of vieussens
How do sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves control cardiac output?
by controlling the SA node (the pacemaker)
LVEPD (Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure) shows a change in blood pressure that’s known as an atrial kick. explain it.
the atrial kick occurs when the ventricle is 80% filled with blood and its relaxed. The rest of the 20% of blood is added in when the atrium contracts (forcing the blood in the relaxed ventricle). This is the atrial kick

What is used as a biomarker of heart failure? Why?
proteolytic fragments of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP)
(WHY? Natriuretic Peptides are high in heart failure. They’re r_eleased when the atrial pressure is high_ and its dilated, they act to reduce the BP- by natriuresis= the excretion of sodium by the kidneys)
Which grade of hypertensive retinopathy does this picture show?

Grade 3 (includes hemorrhages, cotton wool, and lipid deposition)
Which of the following borders of the heart are mainly made up of the left ventricle? (one or more)
a. left border
b. right border
c. apex
d. superior border
e. inferior border
f. base of heart
a. left border
+
c. apex
What is this phenomenon? What causes it?

The image shown onion skin thickening, its caused by malignant hypertension
T/F: aliskiren levels can be detectable in plasma for 3 weeks after treatment
false, its in the kidneys for 3 weeks, whereas its plasma levels become undetectable at an earlier time
Which vein carries blood from the pericardium to the brachiocephalic veins?
Pericariacophrenic veins
What is Malignant Hypertension?
extremely high blood pressure (diastolic 120mmHg+) that develops rapidly and causes some type of organ damage
Which of the following is best to use in hypertensive diabetic patients?
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril +captopril
c. valsaratan + losartan
b. lisonopril +captopril
During low blood pressure, how will baroreceptors act on vasopressin, sympathetic, and parasympathetic activity?
increase vasopressin
increase sympathetic activity
decrease parasympathetic activity
When do we use coronary angiography?
to localize the site of the coronary artery block
(catheter inserted though femoral to intect the dye)
A patient has fibroid necrosis and onion skin lesion. What’s most likely?

accelerated/malignant hypertension
Which of the following increases calcium by helping influx through calcium channels?
a. DAG
b. IP3
a. DAG
The left phrenic nerve senses pain near the heart, where is this pain referred to?
the skin of the supraclavicular region of the left side
malignant hypertension vs accelerated hypertension
Accelerated hypertension is defined by retinal damage, including hemorrhages, exudates and arteriolar narrowing. A recent significant increase over baseline BP that is associated with target organ damage.
The additional presence of papilloedema constitutes malignant hypertension, which is usually associated with diastolic blood pressure greater than 180/120mmHg
How many papillary muscles are in the right ventricle?
three (anterior, posterior and septal)
When does acetylcholine do vasoconstriction/dilation?
causes constriction when directly related to vascular smooth muscle
causes dilation when endothelium present
What is the “b” location called? What structure is also found there?

the triangle of Koch
AV bundle/bundle of His is located in it
What is the effect of the setpoint atrial blood pressure on sympathetic activity?
ABP at setpoint inhibits sympathetic activity
What prevents the prolapse of the cusps into atria during systole?
chordae tendinae
Patient has left coronary dominance, what supplies blood to the interventricular septum of the patient?
left coronary artery
Where is the deep cardiac plexus
in front of bifurcation of trachea and behind arch of aorta
What’s the location of the superficial cardiac plexus?
below the arch of aorta and in front of the right pulmonary artery
Which of the following prevents the conversion of angiotensin 1 to 2?
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril +captopril
c. valsaratan + losartan
b. lisonopril +captopril
What converts angiotensin II to angiotensin (1-7)?
ACE2
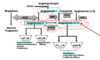
compare and contrast the effect of epinephrine and norepinephrine on systemic vascular resistance
norepinephrine has a high affinity to alpha 1, which causes constriction of vascular smooth muscles, and thus increases SVR
epinephrine (low concentration) has a high affinity to beta 2, which causes relaxation of vascular smooth muscles, and thus decreases SVR
epinephrine (high concentration) has a high affinity to alpha 1, which causes constriction of vascular smooth muscles, and thus increases SVR
Explain renovascular hypertension (aka renal artery stenosis)
This condition occurs when the blood flow to the kidney decreases (can be due to plaque build-up, atherosclerosis, etc.) When the kidneys receive low blood flow, they act as if the low flow is due to dehydration. So they respond by releasing hormones that stimulate the body to retain sodium and water (renin!) Blood vessels fill with additional fluid, and blood pressure goes up.
Which of the following mediates angiotensin II induced growth in the left ventricle and the arterial wall?
a. angiotensin type 1 receptor
b. angiotensin type 2 receptor
a. angiotensin type 1 receptor
Where are two locations that arterial baroreceptors are found?
aortic arch and carotid sinus (the wider area before the internal carotid artery splits)
Patient has BP of 150/111 what grade of hypertension is he in?
grade 3

What kind of pulse is this?

Bigeminal pulse
(rhythm of heart is disrupted, variable cycle length, and thus variable filling of the heart with blood)
The visceral pericardium is also known as
the serous pericardium OR the epicardium
When are diuretics contraindicated?

Which of the following is more likely to be caused by rheumatic fever?
a. pulmonary valve stenosis
b. aortic valve stenosis
b. aortic valve stenosis
Which artery is the yellow arrow pointing at?

left coronary artery
Which part of the right atrium is smooth? what is it called?
the posterior part called sinus venarum
posterior= smooth
anterior= rough
When are beta blockers contraindicated?

What is aliskiren metabolized by?
P450 enzyme 3A4
Which of the following is closest to the heart?
a. fibrous pericardium
b. parietal pericardium
c. visceral pericardium
c. visceral pericardium
What is “masked hypertension”?
a condition opposite of white coat, when BP is high at home but normal in the office
Which of the following has two posterior cusps
a. aortic valve
b. pulmonary valve
c. both
d. neither
b. pulmonary valve
When a patient is standing, at which vertebral level is the heart situated in?
a. T5-T7
b. T5-T8
c. T6-T8
d. T6-T9
d. T6-T9
This is a histology image of a brain, what happened?

Lacunar infarct caused liquefactive necrosis, this is the space that was resolved- the cystic space
(you can find hemosiderin in cases with hemorrage)
Which of the following are angiotensin receptor blockers?
a. aliskiren
b. lisonopril
c. captopril
d. valsaratan
e. losartan
d. valsaratan
+
e. losartan
identify

right coronary artery
Which of the following plays a greater role in cardiac hypertrophy?
a. angiotensin type 1 receptor
b. angiotensin type 2 receptor
b. angiotensin type 2 receptor
Which of the following protects the heart?
a. fibrous pericardium
b. parietal pericardium
c. visceral pericardium
a. fibrous pericardium
What’s found posteriorly to the heart?
aorta, esophagus, and the left pulmonary vein
How much does the blood pressure have to increase to double the risk of CVD death? (2 fold risk increase)
systole increases by 20 and the diastole increases by 10mmHg
T/F: blood pressure measurement are roughly equal no matter the location they are taken in
false; ambulatory/home measurements are less by 5mmHg. Some patients also have white coat hypertension, where their BP increases when encountering doctors.
Where is the coronary sinus?


A patient has a blood pressure of 181/90. What his risk of CVD death? How would you treat him?
high risk. immediately start with drugs and lifestyle changes.

What supplies blood to the majority of the hearts conducting system?
Right coronary artery
Which is located posteriorly in the groove between the ventricles?
a. small cardiac vein
b. middle cardiac vein
c. great cardiac vein
b. middle cardiac vein
Which of the following decreases diastolic pressure?
a. epinephrine
b. norepinephrine
a. epinephrine
Where is the crux of the heart?
“crux” meaning “cross”; it is the area on the lower back side of the heart where the coronary sulcus (the groove separating the atria from the ventricles) and the posterior interventricular sulcus (the groove separating the left from the right ventricle) meet.

T/F: angiotensin I is converted to angiotensin II only through angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
Cathepsin G + Chymase also convert it
Describe the shape of the heart muscle fibers?
in spirals resembling the number 8
What supplies the right ventricle at the anterior interventricular groove?
Left coronary artery
In which of the following can tachycardia be found? explain.
a. brain ischemic reflex
b. cushing reflex
a. brain ischemic reflex
(this reflex is associated with hypotension, so the tachycardia is used to compensate; the cushing reflex has hypertension, so the baroreceptor reflex is used to compensate)
the pericardiacophrenic artery is a branch of the
internal thoracic artery
When are ACE inhibitors contraindicated?

Which of the following borders of the heart are mainly made up of the right ventricle? (one or more)
a. left border
b. right border
c. apex
d. superior border
e. inferior border
f. base of heart
e. inferior border
Describe the hearts position in comparison to the midline.
2/3 shift to the left (the rest of 1/3 to the right)
Which of the following patients experience a higher increase in heart rate after standing up after laying down?
a. normal patient
b. patient with autonomic dysfunction
c. patient with venous insufficiency
c. patient with venous insufficiency
(because they have a larger amount of blood pooling in the veins, so the compensation is greater)

When are ARBs contraindicated?

What occurs to angiotensin I if ACE inhibitors are applied?
levels increase and may be converted to angiotensin (1-7) via NEP pathway
Describe action potentials of baroreceptors during low pressure vs high pressure?
more firing during high pressure and less during low pressure
Which of the following is a muscular groove?
a. sulcus terminalis
b. crista terminalis
a. sulcus terminalis
(crista terminalis is a muscular ridge)
Which part of the right ventricle is rough and which is smooth?
posterior= rough
anterior= smooth
At what age does most of the new onset of hypertension occur?
between the age of 30&40
What causes dicrotic pulse?
low cardiac output and high vascular resistance
What kind of pulse is this? What does it indicate?

pulsus internans
found in aortic stenosis and is a sign of severe left ventricular dysfunction
What supplies the anterior 2/3rd of the interventricular septum?
The anterior interventricular artery (LAD artery)
risks and benefits of:
Monotherapy vs combination therapy of hypertension
Monotherapy is using one drug, it was found that it doesn’t have a good control on BP and increases the side effects of that drug.
this is why we preferably start with a single-pill combination of 2 drugs. (use one pill because it increases compliance)
T/F: the higher the slope of the arterial ascending limb pressure, the slower the heart rate
false, the opposite is true (higher slope with higher heart rate)
Describe the blood flow to the kidneys. What could this lead to?

bilateral renal artery stenosis (can be caused by hypertension leading to plaque build-up)
ischemic atrophy of kidneys can occur (smaller and granular)

Which of the following is the diagram a representation of? explain.
a. bigeminal pulse
b. pulsus alternans

a. bigeminal pulse
pulsus alternans is regular while the pulses in bigeminal pulse occur irregularly (not the same distance between each pulse)
Which part of the left ventricle is rough and which is smooth? explain.
posterior= rough
anterior= smooth
(the posterior part is rough because it has to diffuse the pressure that’s exerted by the blood pooling in from the atria)
What is this phenomenon?

Hyalinization within arterial wall
(Hyaline arteriosclerosis)
When do we use Monotherapy to treat hypertension?
when the patient has grade 1 hypertension, so we use
only ACEI or ARB alone
when patient is more than 80 yr old or fragile, so you don’t want to lower their BP significantly, so start with a single drug in a low dose
When are calcium antagonists contraindicated?
dihydropyridines VS diltiazem VS verapamil

Where is the oblique pericardial sinus located?
between the pulmonary veins (and the inferior vena cava)
How do ANP and BNP affect BP and how?
(atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP); B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP))
decrease BP by promoting vasodilation and natriuresis
Which of the following occurs when the aortic and pulmonary valves are open?
a. systole
b. diastole
a. systole
Which sympathetic chain branch supplies the superficial cardiac plexus?
left superior cervical ganglion
(the rest supply the deep cardiac plexus)
During pulmonary congestion, how will baroreceptors act on vasopressin, sympathetic, and parasympathetic activity?
decrease vasopressin
increase sympathetic activity
decrease parasympathetic activity
(Atrial mechanoreceptor reflex)
Find the Oblique vein of the left atrium

*gets microscope out to see this tiny vein*

Describe the relationship between blood pressure and volume?
a. directly proportional
b. inversely proportional
a. directly proportional
Which grade of Hypertensive Retinopathy is this?

Grade 2, the image shows Arteriovenous nicking (in our slides he put “AV nipping”)
AV nicking is when an arteriole is seen crossing a venule, resulting in the compression of the vein with bulging on either side of the crossing

Which of the following may activate baroreceptors?
a. epinephrine
b. norepinephrine
b. norepinephrine
(it has a high affinity to alpha one receptors, they increase the vascular resistance, increasing both systolic and diastolic pressure, this leads to an increase in mean arterial pressure, which baroreceptors compensate for)
What is the only cause of heart pain?
ischemic injury
Which side of the body is the apex of the heart pointing towards?
to the left
Why is the flow of blood to the body continuous if the heart ejects blood in a pulsatile manner?
The elastic recoil of the aorta is what makes blood flow smooth. It stretches to accommodate the blood then pushes it out continuously until the next pulse occurs.
Which coronary artery is larger?
left coronary artery
The arterial pressure slope of the ascending limb is determined by
the ejection speed (the stroke volume)
How do thrombocytes work?
they circulate and check if there’s endothelial damage. if damage is present, they’re activated and cause thrombosis.
(** NO acts to counteract this, so if NO is not present, the thrombosis is uncontrolled)
A patients father died at 60 due to CVD and his mother at the age of 70. Does this mean he has a family history of premature CVD?
no.
(tafree’3= if someone’s father got heart attack at the age of 50 he is considered to have family history of premature cvd. if someone’s father got heart attack at the age of 60 he is not considered to have premature cvd. if someone’s mother had heart attack at the age of 60 this is premature cvd for women because they usually get heart attacks 10 years after men.)


