Restrictive Pulmonary Disease Flashcards
____________________ are a heterogeneous group of diseases characterized by dyspnea and reduced total lung capacity (TLC).
Chronic Interstitial/Restrictive Lung Diseases
What makes up the interstitial layer of the lung?
• specify the tissues.
Interstitial compartement = area of the lung between the epithelial and capillary endothelial basement membranes
Tissue: (basically just connective tissue with some endothelial cells)
• Basement membrane of endothelial and epithelial cells
• Collagen fibers
• Elastic Tissues
• Fibroblasts
What 3 or maybe 4 diseases fit into the category of fibrosing restictive lung disease?
DIC-P = Firbrosising Diseases
- Drug/Radiation acquired Fibrosis
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Collagen vascular disease
- Pneumonocioses
Tom presents with a progressive lung disease that results in dyspnea on exertion with a chronic dry cough. Chest CT shows a progressing crushed glass appearance. He has no history of using pneumotoxic drugs or exposure to raditation?
• Most likely diagnosis?
• Keys to Dx?
• What causes this disease?
Dx:
• Ideopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) - cause is unknown, but appears to be from repeated injury by an unknown agent.
Key Symptoms/factors:
• Presents insidiously as dyspnea on exertion
• Dry cough
• Must rule out drugs and radiation as causes before this becomes the Dx.
Tom presents with a progressive lung disease that results in dyspnea on exertion with a chronic dry cough. Chest CT shows a progressing crushed glass appearance. He has no history of using pneumotoxic drugs or exposure to raditation.
• What is his Px?
• Treatment options?
Px:
• Poor prognosis with Ideopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, No great drugs available
Tom presents with a progressive lung disease that results in dyspnea on exertion with a chronic dry cough. Chest CT shows a progressing crushed glass appearance. He has no history of using pneumotoxic drugs or exposure to raditation.
• Given his likely Dx what specifically do you suspect you would see on CT and/or autopsy?
• What are some key characteristics to differentiate this disease from others?
This guy has IPF (ideopathic pulmonary fibrosis)
CT or Gross Exam:
• Patchy Interstitial fibrosis that has Space and Time differences, LOWER LOBES are typically affected first and the disease works OUTWARDS to INWARDS starting with a SUBPLEURAL distribution
Gross Exam ONLY:
• SHRUNKEN HobnailedPleura
Tom presents with a progressive lung disease that results in dyspnea on exertion with a chronic dry cough. Chest CT shows a progressing crushed glass appearance. He has no history of using pneumotoxic drugs or exposure to raditation.
• What microscopic 5 key microscopic findings are you likely to see?
• What umbrella term covers 4 or the 5?
Key Microscopic Findings:
USUAL INTERSTIAL PNEUMONIA:
• Fibroblast Foci
• Collagenized areas
• Intervening areas of Normal Lung
• Honeycombing in Advanced stages
5th not part of UIP:
• MILD LYMPHOCYTIC INFLAMMATION
**What chemical mediator is likely responible for this CT. Note that the pathologist has also returned results that indicated this guy has signs of UIP (usual interstitial pneumonia). There is no known etiologic agent.
• what cells secrete this mediator?
• what are some Key features to notice on this Chest CT?

- White lines at periphery of lung aka NET-LIKE reticulations = areas of fibrosis
- Starting Out and Moving In is a sign of Ideopathic pulmonary fibrosis IPF
TGF-ß - comes from injured pneumocytes
**What disease do you suspect? Why?

Ideopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis - (right) Lower Lobes seem to be more involved than the upper lobes. (left) the disease is starting from OUTSIDE and Moving In = HOBNAILED appearance
**What are the changes in this tissue indicative of?

• tissue changes = Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP) - histologically you can see patchy areas of interstitial fibrosis
*Also note the arrows are showing that it is starting from outside and moving in.
**What is the association between this image and Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (remember this is just the histologic term for tissue that has changes indicative of Ideopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis)?

- Notice Lymphocytic Infiltrate (left)
- 3 arrows point out a Fibroblast Foci - believed to be a site of recent injury
**What are some key features to notice on this tissue?
• what disease is this indicative of?

Key Features:
• White arrows: Dense Collagen Deposition
• Asterisks: Metaplastic Bronchiolar Epithelium
• BLUE = Lymphocytic Infiltrate
Is UPF (usual interstitial pneumonia) diagnostic of IPF (ideopathic pulmonary fibrosis)?
• why or why not?
• NO - Collagen Vascular diseases often show UIP histologically - IPF is a diagnosis of EXCLUSION
What are some diseases you should consider if you see UPF in a patient?
1 consider Collagen Vascular Diseases:
• Rheumatoid Arthritis
• Systemic Lupus Erthematous
• Sjogren’s
• Systemic Sclerosis
• Inflammatory Myopathies
• Mixed CT diorders
**What are changes here indicative of?

Usual Interstitial Pneumonia - note this biopsy was taken from someone with a collagen vascular disease
What are the key changes seen in Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia (COP)?
• What lung tissues are affected?
• Is treatment available?
COP:
• Intraalveolar Process - NOT interstitial
KEY FEATURES:
• Polypoid plugs of loose organizing Connective Tissue in bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli
• ALL ORGANIZING CT is the SAME AGE and underlying architecture is preserved.
Tx:
• STEROID treatment is effective here.
Are the changes of Polypoid plugs of loose organizing CT seen in Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia specific to this disease? why or why not?
NO these changes are not specific to COP, these changes are also seen in resolving acute lung injury/infection, DISTAL to the obstruction
How do you tell the difference between Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia and a resolving infection?
CLINICAL Hx.
What are changes seen here indicative of?
• Key features of this specimen?
• what is in your differential?

Changes:
• Intraalveolar plugs of Loose Fibroconnective tissue - see white arrows
• KEY is that its INTRAalveolar not in the interstitium
DDx:
• Could be Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia or a Resolving Infection or Injury
**What is seen on this lung specimen?
• what’s in you DDx?
Loose organizing CT found INSIDE alveoli, not the interstitium, this is indicative of COP (cryptogenic organizing pneumonia) or a resolving lung injury or infection
*this patient had ARDS
Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP)
• Mean age at onset
• Pace of onset
• Response to Steriods
• Ability to Recover

Desquamative Interstitial Pneumonia (DIP)
• Mean age at onset
• Pace of onset
• Response to Steriods
• Ability to Recover

Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia (COP)
• Mean age at onset
• Pace of onset
• Response to Steriods
• Ability to Recover

Are pneumoconioses neoplastic or non-neoplastic?
• what are some common causes?
NON-neoplastic
Common causes = Mineral Dust:
• Coal
• Beryllium
• Silica
• Asbestos
**Usually Chronic Exposure is required**
What is the pathogenesis of all pneumoconioses?
- Alveolar macrophages take in particulate matter
- Macrophages Migrate from Alveolus to the Respiratory Bronchiole
- Many Macrophages enter INTERSTITIAL tissue then MIGRATE THROUGH lymphatics
- Macrophages Die and their matter is dumped
- This tends to happen at specific foci: Division of Large Vessels, Under the Pleura, and in the Hilar Lymph nodes
What are the 3 stages of Coal Workers Pneumoconiosis (CWP)?
- Antracosis - carbon gets stuck in macrophages - NORMAL in urban ppl.
- Simple Coal Workers Pneumonoconiosis (CWP)
- Complicated CWP - Progressive Massive Fibrosis
Simple Coal Workers Pneumoconiosis:
• What parts of the lung are involved?
• How are these parts affected?
• What do you see on histology?
- *Upper Lobe** involvement with little or NO pulmonary dysfunction. May see:
1. Macules of coal dust - 1-2mm = just an accumulation of dust
2. Nodules of coal dust - 0.3-1cm = Carbon laden Macrophages
**What is seen here?

Coal dust MACULE with adjacent airspaced - notice this is just dust and there are no macrophages or collagen deposition so its not a nodule
Billy presents with a fibrosing lung disease characterized by black scars in the lung full of dense pigment and collagen. Immunohistochemical staining rules out pneumonia. He has a 40 year history of working in coal mines.
• What is his dx?
• What were key clues to the Dx?
• What stages were there in the development of this disease?
• What other medical conditions could have put him at a higher risk of developing this disease?
COMPLICATED Coal Workers Pneumoconiosis (CWP)
Keys:
• Coal working
• BLACK SCARScomposed of pigment andCollagen
Stages:
• He progressed from antracosis => SIMPLE CWP => COMPLICATED CWP
Risks:
• Rheumatoid Arthritis - puts you at a higher risk
**What is shown here?

This Complicated CWP aka Black Lung - extensive fibrosis and nodules means that this is complicaed CWP and not simple CWP
**Remember RA is a risk factor for developing this
Who usually gets silicosis and where are the lesions associated with this disease often found?
Who:
• Sandblasters, Mine workers, Stone cutters - this takes decades to develop
Primarily the upper lobes are affected - causes a NODULAR FIBROSIS
Why does Silicosis take on a different morphology from Complicated CWP?
• what should you look for when doing microscopy of suspected silica nodule?
Silica induces release of Fibrogenic mediators from macrophages. Look for birefringence in these nodules
What might you want to screen your patient for if he is diagnosed with Silicosis?
• why?
People with Silicosis are at increased risk of getting TB because they have impaired macrophage function
**What is shown in these two pictures? (left = high magnification, right = lower magnification)
- key features?
- Where in the lung were these biopsies taken?

Silicosis is shown here - key features: birefringence and nodules created by the silica induced activation of macrophages
• biopsies are probably from the upper lobes because this is where silicosis manifests itself
Name 4 non-neoplastic asbestos-related diseases.
Non-neoplastic Asbesto-Related Diseases:
• Diffuse Pleural Fibrosis
• Benign Pleural Effusions
• Pleural Plaques
• Parenchymal Interstitial Fibrosis (Asbestosis)
**What is shown here? Which is more pathogenic?

Both are asbestos - the curly flexible fiber (left) are less pathogenic than the straight stiff fibers (right)
**What type of pneumonoconiosis would lead to the formation the structures shown on the lung pleura?

• Pleural plaques are caused by Asbestosis
What are some symptoms of Asbestosis?
• what type of exposure is required to cause this disease?
• How long does it typically take for the disease to develop?
Patients usually experience slowly progressive dyspnea, the latency period after heavy prolonged asbestos exposure is typically around 20 years.
What leads to the formation of the structures shown in this picture?
• What are these caused by?
Asbestos bodies are seen here, these form as a result of macrophages attempting to destroy asbestos fibers and they get coated with iron. ADDITIONALLY, FIBROSIS is also everywhere from macrophages releasing fibrinolytic substances in trying to break down the fiber.
**What is seen here?
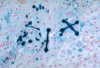
Asbestos bodies that have been stained with Prussian Blue stain
**How long does is the latency period of this disease?

Shown here is asbestosis - it has a latency period of ~20 years
What is the most common cancer for someone who gets exposed to asbestos to get?
• what conditions are you most likely to get with exposure to asbestos? and what symptoms are they associated with?
Lung caner is more likely to result from asbestos exposure than mesothelioma
Asbestosis and Pleural Plaques are the most commmon complications of exposure, asbestosis may result in dyspnea and cough while plaques may be asymptomatic
What condition shown here is the result of some chemotherapy drugs acting in the lung?
•**key features**?

Drug induced pneumonitis is shown here.
Key Features:
• Interstitial Fibrosis accompanied by Lymphocytic inflammation and type II pneumocyte hyperplasia
**The biopsy shown here was taken from a man who worked for several years in the ceramic tile industry.
• what other occupations would put this man at risk for getting this disease?
• what other disease (besides fibrosis) is this man at risk for?

This guy is at increased risk of CANCER because he has Berylliosis. He could have been exposed to beryllium as a beryllium miner or as a worker in the space industry.

What areas of the body are typically affected by Sarcoidosis?
• what are some typical symptoms?
Affected areas:
• Hilar Lymph nodes
• Lungs
• Skin
Symptoms:
• Insideous onset of shortness of breath, cough, and/or constitutional symptoms - remember this is a systemic disease.
Can sarcoidosis be treated?
Yes, treat sarcoidosis with steroids - disease is usually responsive to this
A bronchioalveolar lavage shows a mCD4:CD8 ratio that exceeds 2.5 is indicative of what disease?
• can you diagnose the disease on the basis of this?
CD4:CD8 ratio above 2.5 indicated sarcoidosis, but it is not diagnostic. Remember sarcoidosis is a diagnosis of exclusion, you must first rule out other causes like mycobacterial or fungal infections.
If just given histology, what can help you distinguish between something like berylliosus and sarcoidosis?

Sarcoidosis is most often distributed along the BROCHOVASCULAR BUNDLES and INTERLOBULAR SEPTA
What is this?

Non-caseating graulomas surrounding a bronchiole
**Epitheliod histiocytes and giant cells are typically well form and non-necrotizing**

**What is this?

Asteroid Body - inclusions found in sarcoidosis, but are not specfic to sarcoidosis
**What is this?

Schaumann Body - calcified concretion found in sarcoidosis, but is not specific to this disease
What is Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?
• how does this disease progress?
Type IV Hypersensitivity (T-cell mediated) response caused by exposure to inhaled organic dusts. If the stimulus is not removed it can progress to FIBROSIS.
Differentiate the events that happen in acute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis.
Acute:
• is more of an interstitial pneumonitis caused by preexisting antibodies binding to antigens and causing activation of complement and attraction of PMNs (C5a)
Subacute and Chonic:
• macrophages take up the antigen present it on MHC II to Tcells and there is Tcell infiltration of lung tissue
What are some bacterial antigens that can cause hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
• what about animal proteins?
• Fungal antigens?
Bacterial:
• Famer’s lung, Mushroom worker’s lung, Humidifier lung, Hot tub lung
Animal Proteins:
• Bird fancier’s lung, Mollusk shell HP
Fungal:
• Malt worker’s lung
• Cheese washer’s lung
• Paprika splitter’s lung
• Maple bark strippers lung
What characteristics of the histology shown here are indicative of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis?

Characteristics:
• Lymphocytic inflammation surrounding airways
• Loosely fomed ILL DEFINED GRANULOMAS
• INTERSTITIAL FIBROSIS and ORGANIZING PNEUMONIA

If people with hypersensitivy pneumonitis remain in persisitent contact with their allergic stimulus what will happen?
• how can this end stage disease be differentiated from usual Interstitial Pneumonia?
• What is the prognosis of late stage hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
- HONEYCOMB lung - predominantly in the UPPER LOBE additionally there are usually granulomas present too
- People with late stage disease that resembles usual interstitial pneumonia only have about 2 years to live
Are the changes in this radiograph more consistent with usual interstitial fibrosis/ideopathic PF or chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis?

Lower lobe, so this is most likely to Ideopathic pulmonary fibrosis
**What is shown here?


What is shown here?

**Not the grooves in these cells and the large amounts of eosinophils

What disease is caused by defects in GM-CSF or Macrophages?
• How do these defects arise?
• what does this cause?
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
Cause are either autoimmune, secondary, or hereditary.
Autoimmune - antibodies are made to GM-CSF
Secondary - diverse causes: malignancy, immunodeficiency
Genetic - neonates signaling GM-CSF is disrupted
A defect in ___________(a) causes ____________ (b) and leads to the appearance shown below.

Defect in GM-CSF (a) leads to Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (b) caused by accumulation of surfactant in the alveoli
What is the bug and what stain was used to stain it?

Pneumocystits jirovecii - stained with Gomori methenamine silver stain
This tissue biopsy was taken from an AIDS patient with a CD4 below 200. What is the most likely pathogen?
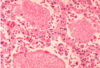
Pneumocystis Jirovecii - traditonally also stained with Gomori methenamine silver stain


