Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis Flashcards
pH Equation
pH = 6.1 + log HCO3/(0.03*pCO2)
Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis
Respiratory Acidosis and Alkalosis
- pH = 6.1 + log HCO3/pCO2

Metabolic compensation to respiratory alkalosis and acidosis:
Metabolic compensation to respiratory alkalosis and acidosis:
the kidneys slowly alter the HCO3 in an attempt to return the pH to normal.

Rules for acid base disturbances
Rules for acid base disturbances
Check pH for alkalosis or acidosis
- Is it metabolic or respiratory?
- Calculate anion gap
- Is compensation appropriate? (Calculations listed on the next slide) If not it is a mixed disorder.
5. What clinical condition is present that will explain the blood gas changes?
6. A sole primary disorder with normal compensation will never correct back to normal pH of 7.40.
Compensation Equations
Metabolic Acidosis
Compensation Equations
Metabolic Acidosis → (delta)pCO2 = 1.2 X DHCO3
Compensation Equations
Metabolic Alkalosis
Compensation Equations
Metabolic Alkalosis → (delta)pCO2 = 0.7 X DHCO3
Compensation Equations
Acute Respiratory Acidosis
Compensation Equations
Acute Respiratory Acidosis →
(delta)HCO3 = 0.1 X (delta)pCO2
Compensation Equations
Chronic Respiratory Acidosis
Compensation Equations
Chronic Respiratory Acidosis →
(delta)HCO3 = 0.4 X (delta)pCO2
Compensation Equations
Acute Respiratory Alkalosis
Compensation Equations
Acute Respiratory Alkalosis →
(delta)HCO3 = 0.2 X (delta)pCO2
Compensation Equations
Chronic Respiratory Alkalosis
Compensation Equations
Chronic Respiratory Alkalosis →
(delta)HCO3 = 0.5 X (delta)pCO2
A 48 y/o male with cirrhosis of the liver is brought to the ER after ingesting 30 ASA tablets in a suicide attempt. Temperature is 38.8 C (102 F) with pulse of 100. Respirations are 28 breaths/min. He has ascites, peripheral edema, and carpopedal spasms. Sodium is 120 meq/L, BUN is 60 mg/dL with creatinine is 2 mg/dL. Glucose is 60 mg/dL. A blood gas is drawn and shows:
pH = 7.60 – acidosis or alkalosis?
HCO3 = 21 meq/L
pCO2 = 20 mmHg
What is this acid base problem called?
(on top of the fact that this dude puts the DUH in “Big Huge Attention Grabbing Dumb Butt”)

pH = 7.60 – acidosis or alkalosis?
ALKALOSIS
What is this acid base problem called?
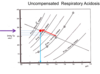
Uncompensated Acute Respiratory Alkalosis

Uncompensated Acute Respiratory Alkalosis
or as represented by a chart

A 48 y/o male with cirrhosis of the liver is brought to the ER after ingesting 30 ASA tablets in a suicide attempt. Temperature is 38.8 C (102 F) with pulse of 100. Respirations are 28 breaths/min. He has ascites, peripheral edema, and carpopedal spasms. Sodium is 120 meq/L, BUN is 60 mg/dL with creatinine is 2 mg/dL. Glucose is 60 mg/dL. A blood gas is drawn and shows:
pH = 7.60
HCO3 = 21 meq/L
pCO2 = 20 mmHg
If the respiratory alkalosis were to continue for 2-3 days?
If the respiratory alkalosis were to continue for 2-3 days, the kidneys will compensate by Excreting HCO3:
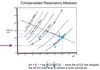
If the respiratory alkalosis were to continue for 2-3 days?
Useless Stupid @$$ chart format

Causes of Respiratory Alkalosis
Causes of Respiratory Alkalosis
- SIRS
- Hypoxia
- Cirrhosis
- Pregnancy
- ASA poisoning
- Anxiety-Hyperventilation
- Cerebral hemorrhage or thrombosis