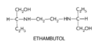CIS: Pharmacotherapy of Respiratory Infections Flashcards
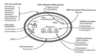
Site of Antimicrobial Action
Translation
Translation

Aminoglycosides (30S) & linezolid (50S)
Tetracyclines (30S)
Macrolides (50S) & clindamycin (50S)
Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Most likely infecting pathogen?
A. Haemophilus influenzae
B. Klebsiella pneumoniae
C. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
D. Staphylococcus aureus
E. Streptococcus pneumoniae
Case 1
Most likely infecting pathogen?
A. Haemophilus influenzae
B. Klebsiella pneumoniae
C. Mycoplasma pneumoniae
D. Staphylococcus aureus
E. Streptococcus pneumoniae
CAP – Common Infecting Organisms

Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Almost all of the major decisions regarding management of CAP resolve around….
Case 1
Almost all of the major decisions regarding management of CAP resolve around….
Initial assessment of severity
Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Vital signs: Temp 100 ˚F, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 100 bpm, RR 28 rpm
CURB-65?
Case 1

Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Vital signs: Temp 100 ˚F, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 100 bpm, RR 28 rpm
Which of the following drugs is most appropriate in the treatment of this patient?
A.Azithromycin
B.Ceftazidime
C.Clindamycin
D.Penicillin G
E.Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Case 1
Which of the following drugs is most appropriate in the treatment of this patient?
A.Azithromycin
B.Ceftazidime
C.Clindamycin
D.Penicillin G
E.Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
CAP – Empiric Antimicrobial Guidelines
Outpatient Recommendations
CAP – Empiric Antimicrobial Guidelines
Outpatient Recommendations
◦Previously healthy
Macrolide PO (azithromycin, clarithromycin)
-OR-
Doxycycline PO
◦DRSP risk (comorbidities, age > 65 years, use of antimicrobials within 3 months)
Respiratory fluoroquinolone PO (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)
-OR-
B-lactam PO [high dose amoxicillin or amoxicillin-clavulanate preferred (alternates: ceftriaxone, cefuroxime)] PLUS a macrolide PO
Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Vital signs: Temp 100 ˚F, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 100 bpm, RR 28 rpm
What is the mechanism of action of the drug most appropriate for treatment of this patient?
A.Binds DNA gyrase preventing relaxation of DNA supercoils
B.Blocks protein synthesis by inhibiting translocation
C.Disrupts cell membrane structure
D.Prevents initiation of protein synthesis
E.Prevents the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA to acceptor site
Case 1
What is the mechanism of action of the drug most appropriate for treatment of this patient?
A.Binds DNA gyrase preventing relaxation of DNA supercoils
B.Blocks protein synthesis by inhibiting translocation
C.Disrupts cell membrane structure
D.Prevents initiation of protein synthesis
E.Prevents the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA to acceptor site
Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Vital signs: Temp 100 ˚F, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 100 bpm, RR 28 rpm
Sputum gram stain: abundant neutrophils and gram-positive diplococci
Would this information change your treatment of choice?
A.Azithromycin
B.Ceftazidime
C.Clindamycin
D.Penicillin G
E.Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Case 1
Would this information change your treatment of choice?
A.Azithromycin
B.Ceftazidime
C.Clindamycin
D.Penicillin G
E.Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Vital signs: Temp 100 ˚F, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 100 bpm, RR 28 rpm
Sputum culture: S. pneumoniae with high-level penicillin resistance
Now which antibiotic would be most appropriate?
A.Azithromycin
B.Cefazolin
C.Doxycycline
D.Levofloxacin
E.Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Case 1
Now which antibiotic would be most appropriate?
A.Azithromycin
B.Cefazolin
C.Doxycycline
D.Levofloxacin
E.Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Vital signs: Temp 100 ˚F, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 100 bpm, RR 28 rpm
Sputum culture: S. pneumoniae with high-level penicillin resistance
What is the mechanism for penicillin resistance?
A.Alteration of the penicillin-binding protein
B.Beta-lactamase production
C.Efflux pumps
D.Poor penetration
E.Alternation of porin channels
What is the mechanism for penicillin resistance?
Case 1
What is the mechanism for penicillin resistance?
A.Alteration of the penicillin-binding protein
B.Beta-lactamase production
C.Efflux pumps
D.Poor penetration
E.Alternation of porin channels
Case 1
A 56 y/o male presents to his primary-care provider’s office because of fever, chills, productive cough and confusion for the past 4 days.
Chest X-ray: dense, right lower lobe infiltrate
Vital signs: Temp 100 ˚F, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 100 bpm, RR 28 rpm
Sputum culture: S. pneumoniae with high-level penicillin resistance
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae?
A.Age > 65 years
B.Alcoholism
C.Antibiotics within the past 3 months
D.Cruise within previous two weeks
E.Multiple medical comorbidities
Case 1
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae?
A.Age > 65 years
B.Alcoholism
C.Antibiotics within the past 3 months
D.Cruise within previous two weeks
E.Multiple medical comorbidities
CAP – Resistant Organisms
CAP – Resistant Organisms
- Drug-resistant S. pneumoniae (DRSP)
◦Age < 2 years or > 65 years
◦B-lactam use within previous 3 months
◦Alcoholism
◦Immunosuppressive illness or therapy
◦Exposure to child at day care
Case 2

A 68 y/o female presents to the ED with a two day history of productive cough and fever.
She complains of shortness of breath and sharp pains in her chest when she breathes deeply.
Three weeks ago she was treated with ciprofloxacin for a urinary tract infection.
Demographics: 68 y/o female, 2 day history productive cough/fever.
Ciprofloxacin three weeks ago for a urinary tract infection.
Temp: 101 ˚F, BP 125/75 mmHg, HR 90 bpm, RR 32 rpm,
O2 saturation (RA) 88%
WBC 15,000 cells/mm3, band neutrophils 9%
Chest X-ray: left lower lobe infiltrate
68 y/o female, admit to hospital with community-acquired pneumonia
Ciprofloxacin three weeks ago for a urinary tract infection.
Which of the following regimens is most appropriate?
A.Ceftriaxone
B.Ceftriaxone plus azithromycin
C.Doxycycline
D.Levofloxacin
E.Levofloxacin plus azithromycin
Case 2
Which of the following regimens is most appropriate?
A.Ceftriaxone
B.Ceftriaxone plus azithromycin
C.Doxycycline
D.Levofloxacin
E.Levofloxacin plus azithromycin
CAP – Empiric Antimicrobial Guidelines
Inpatient, Non-Intensive Care Unit Recommendations
CAP – Empiric Antimicrobial Guidelines
- Inpatient, Non-Intensive Care Unit Recommendations
- Respiratory FQ IV or PO (levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)
- OR-
- B-lactam IV (ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, or ampicillin preferred) PLUS macrolide IV (azithromycin)
Case 2
68 y/o female, admit to hospital with community-acquired pneumonia. Ciprofloxacin three weeks ago for a urinary tract infection.
Which of the following parameters is not routinely monitored during antibiotic therapy to determine response?
A.Adverse effects
B.Chest X-ray
C.Fever
D.Respiratory rate
E.WBC count
Case 2
Which of the following parameters is not routinely monitored during antibiotic therapy to determine response?
A.Adverse effects
B.Chest X-ray
C.Fever
D.Respiratory rate
E.WBC count
CAP
Signs of clinical improvement:
CAP
Signs of clinical improvement:
- Temperature ≤ 37.8 ˚C
- HR ≤ 100 bpm
- RR ≤ 24 breaths/min
- SBP ≥ 90 mmHg
- Arterial 02 saturation ≥ 90%
- Ability to maintain oral intake
- Normal mental status
Case 2
68 y/o female, admit to hospital with community-acquired pneumonia Ciprofloxacin three weeks ago for a urinary tract infection.
Which of the following antimicrobial regimens does not cover atypical pathogens?
A.Azithromycin
B.Ceftriaxone
C.Doxycycline
D.Levofloxacin plus ceftriaxone
E.Moxifloxacin
Case 2
Which of the following antimicrobial regimens does not cover atypical pathogens?
A.Azithromycin
B.Ceftriaxone
C.Doxycycline
D.Levofloxacin plus ceftriaxone
E.Moxifloxacin
Case 2
68 y/o female, admit to hospital with community-acquired pneumonia
Height 5’6”, Weight 135 lbs
SCr 2 mg/dL
Which of the following does NOT need to be dose adjusted if prescribed to our patient?
A.Amoxicillin
B.Ampicillin/sulbactam
C.Ceftriaxone
D.Levofloxacin
E.Ertapenem
Case 2
Which of the following does NOT need to be dose adjusted if prescribed to our patient?
A.Amoxicillin
B.Ampicillin/sulbactam
C.Ceftriaxone
D.Levofloxacin
E.Ertapenem
[140 – age (years)] x mass (kg) x (0.85 if female)/ 72 x SCr (mg/dL) = ~26 mL/min
Case 3
A 76 y/o male was admitted to the hospital 13 days ago for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
Post-CABG, patient was recovering slowly and was unable to be extubated.
He developed a fever and became agitated with increasing oxygen demands.
76 y/o male, CABG13 days ago, unable to be extubated
Temp 102.8 ˚F, WBC 23,500 cells/mm3, band neutrophils 20%
SCr 1.2 mg/dL
Two blood cultures: pending
Sputum culture: 4+ WBC and gram-negative bacilli
Diagnosis?
Case 3
Diagnosis?
Ventilator-associated pneumonia
Case 3
76 y/o male, CABG13 days ago, unable to be extubated
Temp 102.8 ˚F, WBC 23,500 cells/mm3, band neutrophils 20%
SCr 1.2 mg/dL
Two blood cultures: pending
Sputum culture: 4+ WBC and gram-negative bacilli
What is the most likely infecting pathogen?
A.Bacteroides fragilis
B.Candida albicans
C.Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D.Staphylococcus aureus
E.Streptococcus pneumoniae
Case 3
What is the most likely infecting pathogen?
A.Bacteroides fragilis
B.Candida albicans
C.Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D.Staphylococcus aureus
E.Streptococcus pneumoniae
HCAP, HAP & VAP
HCAP, HAP & VAP
Early onset (< 4 days) vs. late onset (5+ days)
Common pathogens
◦Aerobic gram-negative
P. aeruginosa
E. coli
K. pneumoniae
Acinetobacter spp.
◦GPCs
MRSA (more common in diabetes, head trauma, those hospitalized in ICUs)
◦Oropharyngeal commensals
Viridans group streptococci
Coagulase-negative staphylococci
Neisseria spp.
Corynebacterium spp.
Case 3
76 y/o male, CABG13 days ago, unable to be extubated
Temp 102.8 ˚F, WBC 23,500 cells/mm3, band neutrophils 20%
SCr 1.2 mg/dL
Two blood cultures: pending
Sputum culture: 4+ WBC and gram-negative bacilli
What is the most likely infecting pathogen?
A.Bacteroides fragilis
B.Candida albicans
C.Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D.Staphylococcus aureus
E.Streptococcus pneumoniae
Case 3
What is the most likely infecting pathogen?
A.Bacteroides fragilis
B.Candida albicans
C.Pseudomonas aeruginosa
D.Staphylococcus aureus
E.Streptococcus pneumoniae
Case 3
76 y/o male, CABG13 days ago, unable to be extubated
Temp 102.8 ˚F, WBC 23,500 cells/mm3, band neutrophils 20%
SCr 1.2 mg/dL
Two blood cultures: pending
Sputum culture: 4+ WBC and gram-negative bacilli
Which of the following empiric treatment regimens is most appropriate for this patient?
A.Ceftazidime plus gentamicin plus vancomycin
B.Ceftriaxone
C.Levofloxacin plus metronidazole
D.Piperacillin/tazobactam plus gentamicin
E.Vancomycin
Case 3
Which of the following empiric treatment regimens is most appropriate for this patient?
A.Ceftazidime plus gentamicin plus vancomycin
B.Ceftriaxone
C.Levofloxacin plus metronidazole
D.Piperacillin/tazobactam plus gentamicin
E.Vancomycin
Empiric Therapy – Late Onset
Empiric Therapy – Late Onset
- Potential pathogens (MDR):
◦P. aeruginosa
◦K. pneumoniae (ESBL+)
◦Acinetobacter
◦MRSA
- Treatment:
◦Antipseudomonal cephalosporin (cefepime, ceftazidime) OR antipseudomonal carbapenem (imipenem, meropenem) OR B-lactam/B-lactamase inhibitor (piperacillin-tazobactam)
PLUS
◦Antipseudomonal FQ (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) OR aminoglycoside (gentamicin, tobramycin)
PLUS
◦Linezolid OR vancomycin
Case 3
76 y/o male, CABG13 days ago, unable to be extubated
Temp 102.8 ˚F, WBC 23,500 cells/mm3, band neutrophils 20%
SCr 1.2 mg/dL
Two blood cultures: pending
Sputum culture: 4+ WBC and gram-negative bacilli
Your attending would like to use meropenem. Which class of antimicrobials does meropenem belong to?
A.Carbapenems
B.Fluoroquinolones
C.Monobactams
D.Penicillins
E.Tetracyclines
Case 3
Your attending would like to use meropenem. Which class of antimicrobials does meropenem belong to?
A.Carbapenems
B.Fluoroquinolones
C.Monobactams
D.Penicillins
E.Tetracyclines
Case 4
A 55 y/o male presents to the ED with a 6-hour history of a bloody nose. He says he has been unable to stop the bleeding.
PE: multiple bruises on lower legs and forearms.
PMH: significant for atrial fibrillation
INR 5.8
You ask if he has taken any other medications and he says he was recently prescribed an antibiotic for pneumonia.
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of the antibiotic most likely prescribed?
A.Binds the 50S ribosomal subunit
B.Blocks attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site
C.Causes misreading of mRNA information
D.Inhibits folate synthesis
E.Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
Case 4
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of action of the antibiotic most likely prescribed?
A.Binds the 50S ribosomal subunit
B.Blocks attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA to the A site
C.Causes misreading of mRNA information
D.Inhibits folate synthesis
E.Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
Case 5
A 25 y/o female presents to the hospital for a CF “tune-up” as she has had increasing yellow-green sputum production, shortness of breath, and post-tussive emesis.
She complains of a decreased appetite and a 2.8 kg weight loss since her previous clinic visit.
Case 5
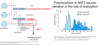
Cystic Fibrosis and Lung Health

Prevalence of Bacteria Identified in Respiratory Secretions from pts. w/Cystic FIbrosis

Case 5
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Case 5
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Aztreonam = S
- Cefepime = S
- Ceftazidime = S
- Ciprofloxacin = R
- Imipenem = S
- Levofloxacin = R
- Meropenem = S
- Piperacillin/tazobactam = S
- Tobramycin = S
- Amikacin = I
*