Respiratory Flashcards
(78 cards)
Bronchiectasis CXR findings
Peribronchial thickening Retained secretions Compensatory emphysema Tubular / cystic
Bronchiectasis causes
Childhood infections - Measles, pertussis Bronchial obstruction Chronic aspiration Kartagener’s syndrome - Bronchiectasis, dextrocardia, absent frontal sinuses Immune deficiency
Causes of pulmonary oedema
Cardiac failure Fluid overload Cerebral CVA, head injury, raised ICP Drowning Aspiration Radiation Thoracocentesis Drugs Inhaled toxins (smoke, hydrocarbons_ Shock lung
What is asthma?
- Heterogenous disease usually characterised by
- Chronic airway inflammation
- Wheeze, SOB, chest tightness. cough
- Variable expiratory airflow limitation
- No SINGLE gold standard diagnostic test
What are the factors that increase the risk of asthma?
Exposure to paracetamol + antibiotics in 1st year of life

What is the pathophysiology of asthma?
- Smooth muscle hyperplasia
- Thick tenacious mucus plugs
- Thickened basement membrane
- Muscus oedema –> abnormal mucociliary clearance
- Eosinophili of the submucosa + secretions
- Increased mast cells in smooth muscle


Raised exhaled nitric oxide
- Elevated in ANYONE with atopy + eczema
- Therefore need a even high level if patient you are testing also has eczema

B
Asthma spirometry

Other than spirometry can you use in asthma?
- Direct challenges are more likely to provoke a response

At what age do we diagnose asthma?
Does inhaled corticosteroids affect growth?
YES
Frequent use can reduce height by 1.5-2cm
What questions do you ask for asthma control?
- Daytime asthma symptoms > 2 /week
- Any night waking?
- Reliever needed for symptoms >2/weel
- Any activity limitation due to asthma
Spacer vs mask use in asthma
- When to use + effect on lung deposition


Check inhaler technique + adherence
Montelukast side effect: ADHD like behaviour, suicidal ideation, sleep difficulties
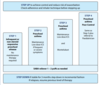
What is the treatment algorithm for preschool wheeze with frequent symptoms?
If this does not work requires further investigation for CF/ bronchiectasis / immune deficiency
Why don’t we give LABA’s without ICS?
LABA increase the risk of sudden death + severe exacerbations therefore ALWAYS need to give them with ICS
What is the treatment algorithm for asthma?


D: ultrafine doubles the potency
Fluticasone 1/2 as potent as beclomethasone
What are the concerns about SABA only treatment in asthma?
- SABA only treatment is associated with increased risk of exacerbations + lower lung function
- Regular use increases allergic responses + airway inflammation
- Beta receptor down regulation, decreased bronchoprotection, rebound hyperresponsiveness, decreased bronchodilatory response
- Over use of SABA (e.g. > 3 canisters / year) is associated with increased risk of severe exacerbations
- >12 canisters / year is associated with increased risk of asthma related death

A wrong- would make it worse
B wrong- binds to IgE in the blood but doesn’t work if IgE levels are > 1500
- Would give this if IgE wasn’t so high
C Mepolizumab
What is the mechanism of action of omalizumab (anti IgE)
10 % risk of anaphylaxis
1st time the dose is given need to be in hospital for 4hrs post
Subseqent doses requires to wait 25min post administration

What is the mechanism of action of mepolizumab, reslizumab + benralizumab (anti IL5)?









