Acute Medicine Flashcards
What is the APLS algorithm including;
- 4H’s + 4T’s
- Post resuscitation care

How long should you continue resuscitation for with good quality CPR?
30 minutes
What are the shockable rhythms?
What shock do you deliver?
VF + pulseless VT
4J/kg
What are the 4 types of shock?
- Cardiogenic
- Hypotensive
- Septic
- Anaphylactic
Describe the difference between a vasopressor + inotrope:
- Vasopressor: vasoconstriction and increases MAP
- Inotrope: cardiac + vascular effects: increases contractility + chronotropy
Effect, receptor + use of;
- Noradrenaline
- Adrenaline
- Dopamine
- Dobutamine
- Milrinone

Where does the spinal cord lie in this picture?
What is line A + B + C
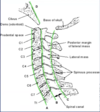
- Spinal cord lies between B + C
- A = anterior vertebral line
- B = posterior vertebral line
- C = spinolaminar line
What are the normal soft tissue dimensions in the cervical spine?
Above the larynx C2 : < 1/3 of the vertebral body width
Below the larynx C3-7: <1 vertebral body wifth
What does the median nerve supply?

What does the ulna nerve supply?

What sort of fracture is this?
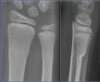
Buckle fracture: no breach of cortex
Only requires a splint
What type of # is this + what nerve is commonly injured?

Monteggia fracture-dislocation refers to dislocation of the radial head (proximal radioulnar joint) with fracture of the ulna.
- Anterior dislocation of the radial head is most common
- Radial nerve is most commonly injured
- Also look out for plastic deformation of the ulna

What type of # is this?

Galeazzi fracture-dislocation
- Fracture of the distal third of the shaft of the radius with a disruption to the distal radiual ulna joint (DRUJ)
What is the radiocapitellar line?

What overdose is MOST likely for a patient with the following ECG:

Tricyclic antidepressant overdose
- Right axis deviation
- Tall R wave in aVR
- QTc prolongation (predisposing to VT + VF) due to K blockade
- QRS prolongation
- >100ms seizures
- >160 VT/VF
What is the pathophysiology of tricyclic antidepressant overdose?
- Central + peripheral ACh receptor blockade (anticholinergic)
- Dilated pupils
- Tachycardia
- Vomiting
- Delirium, confusion, myoclonic jerks, seizures, ataxia, blurred vision
- Urinary reterntion, ileus
- Fast Na channel blockade
- Increases duration of repolarisation + refractory period
- Noradrenaline + serotonin reuptake blockade
- CNS depression / coma
- Seizures
- Alpha adrenergic receptor blockade
- Hypotension
Treatment of sodium bicarbonate
- ABCDE’s
- IV access: 1-2mmol/kg sodium bicarbonate
- Intubate + hyperventilate (aim pH 7.5-7.55)
- NGT + charcoal (generally contraindicated but can consider within 2 hrs)
- IV midazolam for seizures (PHENYTOIN CONTRAINDICATED)
- Fluid bolus for hypotension +/- noradrenaline
- If further arrhythmias repeat NaHCO3 then lignocaine
Pathophysiology of carbon monoxide poisoning
- Impaired oxygen offloading + impaired peripheral oxygen utilisation
- Binds to iron moiety of haem with x240 affinity of O2
- Allosteric change in haem protein = reduced ability of other three O2 binding sites to offload in the peripheral tissues = LEFT shift of O2 curve
What are the 3 snake antivenoms we have in Aus?
- Give if any evidence of neurotoxic paralysis: ptosis, opthalmoplegia, limb weakness, respiratory effects, significant coagulopathy INR >1.3 of prolonged bleeding, history of unconsciousness, collapse, seizure, arrest
- Black snake
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Anosmia long term sequelae
- Local signs at bite site ++
- Brown snake
- Most common cause of fatal snake bite
- Defibrinating coagulopathy
- Neurotoxicity rare
- Rhabdomyolysis does NOT occur
- Collapse 1/3 + arrest 5%
- Tiger snake
- Paralysis + rhabdomyolysis over hours
Anticholinergic vs sympathomimetic
Picking = anticholinergic

Serotonin syndrome features

Serotonin syndrome vs. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
What does the handlebar sign indicate?
- Duodenal perforation
- Liver bleed
- Spleen bleed
Need to be admitted for serial examination despite normal CT scan as high risk for duodenal perforation
Younger children are more likely to have c-spine injuries where?
C1-3 whereas older children C3 onwards more likely
Location of needle decompression for pneumothorax
Location of chest drain insertion
Needle decompression: mid clavicular line 2nd intercostal space
Chest drain: 4-5th intercostal space mid axillary line
What is the treatment for raised ICP in trauma?
- Positioning
- Sedation + analgesia
- Controlled hyperventilation
- Hyperosmolar therapy
- 3% saline 3mL/kg
What are toxicology causes of hypoglycaemia?
- Beta blockers
- Insulin
- Oral hypogllycaemia agents
- Quinine
- Valproic acid
- Saliculate
What drug is contraindicated in toxicology seizures?
Phenytoin: acts on sodium channel (many of the toxicology agents act on the Na channel)
What are toxicology causes of seizures?
- Venlafazine
- Bupropion
- Tramadol
- Amphetamine
In toxicology what is the indication for neuromuscular paralysis?
Temp > 39.5
Need neuromuscular paralysis to prevent multi-organ failure
Specific antidotes:
- Tricyclic antidepressant
- Cholinergic syndrome (Organophosphate poisoning)
- Anticholinergic syndrome
- Digoxin
- Paracetamol
- Opiates
- Tricyclic antidepressant
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Organophosphate poisoning
- Atropine
- Anticholinergic syndrome
- IV fluids
- Diazepamfor agitation
- Physostigmine
- Digoxin
- Digibind
- Paracetamol
- NAC
- Opiates
- Naloxone
Toxicology: how does fast sodium channel blockade overdose manifest on an ECG?
- Widening of QRS in lead II
- Right axis deviation
- Bradycardia
- VT + VF
Toxicology: how does blockade of K+ efflux overdose manifest on an ECG?
QT prolongation –> Torsades —> VF
Decontamination in paediatrics
- Induced emesis + gastric lavage: NOT used
- Single dose of activated charcoal: USED in paeds
- Super heated distilled wood pulp
- Aspiration is a risk
- Does NOT work very well for: hydrocarbons/alcohol, metals, corrosives (acids/alkalis)
- Whole bowel washout: USED in paeds
- Polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution used + continue until faeces is clear
- Useful in iron overdose (>60mg/kg), SR K+, diltiazem, verapamil, arsenic, lead ingestion, “body packers”
Techniques for enhancing elimination in toxic ingestions
- Multiple dose activated charcoal
- Urinary alkalinisation
- Haemodyalysis + haemofiltration
- Charcoal haemoperfusion
- Multiple dose activated charcoal
- Carbamazepine
- Urinary alkalinisation
- Salicylates
- Phenobarbitone
- Haemodyalysis + haemofiltration
- Lithium
- Metformin lactic acidosis
- Salicylates
- K+
- Charcoal haemoperfusion
- Theophylline
Serotonin syndrome features + management
- Mental state changes
- Agitation, confusion, anxiety
- Autonomic stimulation
- Diarrhoea, flushing, hypertension, fever, sweating, mydriasis, tachycardia
- Neuromuscular excitation
- Clonus, hyperreflexia, increased tone, rigidity, tremor
Management
- Diazepam for seizures
- Cyproheptadine
Drugs of abuse that can cause serotonin syndrome
- Amphetamines
- MDMA; ecstasy
Signs + symptoms of cholinergic syndrome
Diarrhoea
Urination
Miosis
Bronchosplasm
Emesis
Lacrimation
Salivation
Most common cause of cholinergic syndrome
Organophosphate poisoning


