Infectious Diseases Flashcards
How do vaccines work?
Induction of antibodies - Neutralizing capacity - Promoting opsonophagocytosis - Clearance of extracellular pathogens Induction of T cells - Support antibody induction - Produce cytokine / cytolytic activities - Clearance of intracellular pathogens
Location of antigen migration in non live vs live vaccines
Non live vaccines - Ag uptake + transport by APC and/ or free fluid diffusion of soluble Ag - Deltoid –> axillary lymph node - Thigh –> inguinal lymph node *Mostly LOCAL + UNILATERAL lymph node activation* Live vaccines - Minimal local retention / reaction - Replication - dissemination - pathogen specific pattern *MULTIFOCAL lymph node activation - stronger responses*
What are the different types of vaccines?
Live attenuated Inactivated - Polysaccaride - Protein - Conjugate - Toxoid
Live vaccines
BCG Oral poliovirus MMR Varicella Oral typhoid Rotavirus Smallpox Yellow fever Zoster Japanese encephalitis
Advantages + disadvantages of LIVE vaccines
Advantages - Organism multiplies (amplification) - Mimics natural infection - Generally induced T + B lymphocyte response - Provides long-lasting protection Disadvantages - Required a good cold chain - May retain some pathogenicity - May not be safe enough to vaccinate immunocompromised
Trajectory + type of Ig transport maternal - fetal unit
Placental transfer is highly selective for monomeric IgG + occurs by receptor mediated active transport NO transfer of IgM, IgA or IgE IgG transfer begins at 17 weeks By 33 weeks maternal = fetal IgG levels 40 weeks fetal > maternal IgG levels
What vaccines are contraindicated for a child with an egg allergy?
Yellow fever Rabies Q fever *MMR cultured on chicken cells but contains no egg allergen therefore safe to give*
Common adverse effects with vaccination: - MMR - HPV - VZV - Rotavirus - DTPa
MMR: high fever + rash for 5-12 days post vaccination HPV: headache, nausea VZV: maculopapular or papulovesicular rash Rotavirus: diarrhoea DTPa: extensive limb swelling reaction (not a contraindication for further)
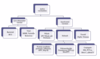
Vaccine classification
What is the MOST important factor for beta lactam effect?
What antibiotic has concentration dependent killing
Aminoglycosides - also has signigicant post antibiotic effect
What antibiotic do you use for the treatment of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia?
Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim + sulfamethoxazole)
What chemotherapy agent is associated with strep mitis?
What CT signs are associated with fungal infections?
What is the most appropriate 1st treatment for aspergillus?
Voriconazole
What antifungal agent do you avoid when using vincristine?
- Voriconazole due to hepatic toxicity
Which of the following is NOT an effect of CMV infection in a stem cell transplant recipient?
How do you treat PTLD?
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Rituximab
- Low dose chemotherapy
What is the varicella post exposure prophylaxis recommendations?
- Immune compromised
- Immune competent

What is the mechanism of action of eculizumab + what is an important consideration if you need to start it immediately?
- Mechanism of action: terminal complement inhibitor. Binds to complement protein C5
- Reduces complement activity
- Increases susceptibility to meningococcal infections therefore should be given a meningococcal vaccine before starting treatment
- Takes 2 weeks for the vaccine to amount a suitable response therefore if therapy can’t be delayed until then need to vaccinate + cover with amoxicillin OR ciprofloxacin
- What is the clinical diagnosis?
- What is the treatment?
- You are the registrar who has been looking after this baby for the last 4 days prior to the diagnosis is there anything you need to do?

Congenital syphillis
- Syphilis is caused by the bacterial spirochete Treponema pallidum
- During pregnancy there is a high risk of vertical transmission in early syphilis (~50% of infants are infected) and a lower risk in late syphilis (~40% in early latency and 10% in late latency)
Management of infants with congenital syphilis
- Infants should be treated with Intravenous benzyl penicillin 50mg/kg bd for 10 days.
- Follow up at 1,2,4, 6,12 months and until RPR negative.
- Infants with evidence of neurosyphilis should have repeat CSF at 6-monthly intervals to ensure changes have resolved.
- Infants with persistently reactive RPR should be re-evaluated (including CSF) and treated for 10 days with IV benzyl penicillin
Post exposure prophylaxis
- Asymptomatic persons exposed or possibly exposed should have Benzathine penicillin G x 1 IM dose of doxycycline BD for 2 weeks
What are diagnostic modalities for syphilis?
Non-treponemal tests are serological tests that detect lipoidal substances released from cells during syphilis infection.
- Tests include the RPR (Rapid Plasma Reagin) and VDRL (Venereal Diseases Research Laboratory).
- These tests are more sensitive but less specific than treponemal tests.
- False positives are common (EBV,hepatitis, varicella, measles, lymphoma, TB, malaria, pregnancy, cord blood).
- These tests usually correlate with disease activity and become negative after adequate treatment. Successful therapy is generally regarded as a 4-fold fall in RPR titre (e.g. from 1:32 to 1:8).
Treponemal tests are serological tests that detect syphilis antigens.
- These assays include TPPA (Treponema Pallidum Particle Agglutination), TPHA (Treponema Pallidum Haemagglutination), FTA (Fluorescent Treponemal Antibody absorption) and syphilis EIA (enzyme immunoassay).
- These tests are generally more specific and less sensitive than non-treponemal tests.
- These tests do not correlate with disease activity and usually remain positive for life.
Darkfield microscopy can be used to visualise treponemes from a primary chancre or nasal secretions. Failure to identify treponemes does not exclude a syphilis diagnosis. Note – it is not possible to culture T Pallidum using standard media
Syphilis PCR can be performed on swabs from a primary chancre, nasal secretions or CSF. It is not adequately sensitive for screening (e.g. on blood).
CSF should be collected for VDRL, FTA-Abs or PCR testing where neurosyphilis is suspected.
In Australia, pregnant women are screened for syphilis (preferably in the first trimester) using a treponemal test. Women will then be offered treatment with penicillin (usually benzathine penicillin, according to the Australian Therapeutic Guidelines[9]) and their RPR titre will be monitored to ensure that is has fallen 4-fold prior to delivery.
A 3 yr old girl has fever. Urine is collected by catheterization for culture. What is the minimum concentration of bacterial growth in the culture that would generally be considered diagnostic of a urinary tract infection in this young girl?
1 bacterium/mL
10 bacteria/mL
103 bacteria/mL
105 bacteria/mL
103 bacteria/mL
Urine obtained by suprapubic puncture is normally sterile. Urine collected by catheterization is likely to reflect infection if there are ≥ 103 organisms/mL. Clean-voided urine is considered abnormal if ≥ 105 organisms/mL are present and possibly abnormal if 104-105 organisms/mL are present.
What is MAB used to prevent severe RSV?
Palivizumab – humanized monoclonal antibody (IgG) directed against an epitope in the A antigenic site of the F protein of RSV. It is used in the prevention of Respiratory syncytial virus
Palivizumab Adverse reactions:
Common (>1%)
Fever, rash, rhinitis, wheeze, cough, diarrhoea, injection site reaction
Infrequent (.01-1%)
Anaemia, elevated liver enzymes
Rare (<0.1%)
Hypersensitivity (including anaphylaxis)
What is the meaning of antibiotic susceptibility:
- Sensitive
- Intermediate
- Resistant
-
Sensitive (S): organism is inhibited by the serum concentration of the drug that is achieved using the usual dosage
- MIC < 2 mcg/mL
-
Intermediate (I): organisms are inhibited only by the maximum recommended dosage
- MIC 4-8 mcg/mL
-
Resistant (R): organisms are resistant to the usually achievable serum drug levels.
- MIC >8 mcg/mL (>4 for amoxicillin)
**However in serious conditions e.g. meningitis have a WAY lower MIC*
Why is salmonella rarely associated with outbreaks of diarrhoea in child care setting?
Person to person spread with salmonella is uncommon
What diseases are causes by;
- Night biting mosquitos
- Day biting mosquitos
- Night biting mosquitos
- Malaria
- Yellow fever
- Japanese encephalitis
- Filariasis
- Day biting mosquitos
- Dengue
Where is body temperature regulated?
Thermosensitive neurons located in the preoptic or anterior hypothalamus
What 3 mechanisms can produce fever?
Endogenous pyrogens
- IL1 + IL6
- TNF
- INF beta + gamma
- Prostagalndin E
Exogenous pyrogens
- Microbes, toxins etc which stimulate macrophages to produce endogenous pyrogens
Endotoxins
- Drugs: vancomycin, amphotericin B, allopurinol
What causes a tertian fever?
Fever on 1st and 3rd days
Malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax
What causes a quartan fever?
Fever on 1st + 4th day
Malaria caused by Plasmodium malariae
What are the periodic fever syndromes?
Familial Mediterranean fever
Cyclic neutropenia
Periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, and adenopathy (PFAPA)
Hyper–immunoglobulin D syndrome
Hibernian fever (tumor necrosis factor superfamily immunoglobulin A–associated syndrome [TRAPS])
Muckle-Wells syndrome
A 4 yr old girl has a temperature of 41.8°C. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
Cerebellar disorders
Hypothalamic disorders
Excessive sweating
Ventricular shunt malfunction
Most bacterial infections
Hypothalamic disorders
Similarly, temperatures in excess of 41°C are most often associated with a noninfectious cause. Causes for very high temperatures (>41°C) include central fever (resulting from central nervous system (CNS) dysfunction involving the hypothalamus), malignant hyperthermia, malignant neuroleptic syndrome, drug fever, or heatstroke.
All of the following organisms are recognized as an important cause of occult bacteremia of infants and children EXCEPT:
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
Moraxella catarrhalis
Neisseria meningitidis
Salmonella
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Moraxella catarrhalis
Approximately 30% of febrile children in the 3-36 mo age group have no localizing signs of infection. Viral infections are the cause of the vast majority of fevers in this population, but serious bacterial infections do occur and are caused by the same pathogens listed for patients 1-3 mo of age, except for the perinatally acquired infections. S. pneumoniae, N. meningitidis, and Salmonella account for most cases of occult bacteremia. Hib was an important cause of occult bacteremia in young children before universal immunization with conjugate Hib vaccines and remains common in underdeveloped countries that have not implemented these vaccines.
What are the mechanisms of resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics?
- ALTER the target site (PBP)
- Destroy the beta-lactam antibiotic
- Decrease the concentration of beta-lactam antibiotics inse the cell
What are poor prognostic factors for meningococcal disease?
Poor prognostic factors on presentation include
- hypothermia or extreme hyperpyrexia
- hypotension or shock
- purpura fulminans
- seizures
- leukopenia
- thrombocytopenia (including DIC)
- acidosis
- high circulating levels of endotoxin and TNF-α.
The presence of petechiae for < 12 hr before admission absence of meningitis, low or normal ESR indicate rapid, fulminant progression and poorer prognosis.
Which of the following is associated with a poorer prognosis for persons presenting with meningococcal disease?
Presence of petechiae for < 12 hr
Meningitis
Thrombocytosis
Leukocytosis
High ESR
Presence of petechiae for < 12 hr
Which of the following contacts should receive rifampin chemoprophylaxis after diagnosis of invasive Neisseria meningitidis in a child?
All children and adults in the same household if there is an unimmunized or partially immunized child younger than 48 mo
All children and adults in the same household or daycare facility regardless of immunization history
All healthcare workers involved in care of the child, as well as household and daycare contacts
Unimmunized or partially immunized children in the same household and in the same daycare facility
All unimmunized or partially immunized healthcare workers involved in care of the child, as well as unimmunized or partially immunized household contacts
All children and adults in the same household or daycare facility regardless of immunization history
Close contacts of patients with meningococcal disease are at increased risk for infection. Antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated for household, daycare, and nursery school contacts and for anyone who has had contact with the patient’s oral secretions during the 7 days before onset of illness. Prophylaxis of contacts should be offered as soon as possible, ideally within 24 hr of diagnosis of the patient. Because prophylaxis is not 100% effective, close contacts should be carefully monitored and brought to medical attention if they experience fever. Prophylaxis is not routinely recommended for medical personnel except those with intimate exposure, such as through mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, intubation, or suctioning before antibiotic therapy was begun.
A 13 yr old boy develops fever with petechiae and a few purpura. Mild hypotension responds to intravenous fluids without the need for pressor support. A blood culture yields Neisseria meningitidis. The patient improves greatly after 7 days of antibiotic therapy and is ready for discharge. Which of the following is most likely to reveal an abnormality that may have predisposed him to develop meningococcal disease?
- Quantitative immunoglobulins (IgM, IgG, and IgA)
- Serial complete blood counts to assess for cyclic neutropenia
- Genotype analysis of the TNF-α promoter region
- Screening assay for deficiencies of complement factors (CH50)
- Total lymphocyte subsets (B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells)
Screening assay for deficiencies of complement factors (CH50)
Persons with inherited deficiencies of properdin, factor D, or terminal complement components have up to a 1000-fold higher risk for development of meningococcal disease than complement-sufficient persons. Among persons with complement deficiencies, meningococcal disease is more prevalent during late childhood and adolescence, when carriage rates are higher than in children < 10 yr; meningococcal infections may be recurrent. Although meningococcal disease can occasionally be overwhelming in patients with late complement component deficiency, cases are more typically described as being less severe than in complement-sufficient persons, perhaps reflecting the fact that these cases are often caused by unusual capsular groups such as W-135 and X. Although protective against early infection, extensive complement activation and bacteriolysis may contribute to the pathogenesis of severe disease once bacterial invasion has occurred.
What is the treatment for pertussis?
- Neonate: azithromycin for 5 days
- Children: azithromycin or clarithromycin for 5 days
- IF macrolide contraindicated: bactrim for 7 days


