Reproductive and Post Reproductive Pharmacology Flashcards
What molecule are sex hormones synthesised from?
Cholesterol
(large aromatic ring makes them hydrophobic)
What are the 2 forms of oesterogen that are predominant in reproductive life and menopause respectively?
Reproductive life: Estradiol
Post Menopause: Estrone
What kind of receptors are steroid hormone receptors? How do they exert their effects
Nuclear receptors
Exert their effects by altering gene transcription
(there is also a membrane receptor for oestrogen)
What are the 3 broad classes of sex hormone drug groups?
Sex steroid hormones
- Oestrogens
- Progestegens
- Androgens
Inhibitors & antagonists
- RU486
- Finasteride
Mixed agonists/ antagonists
- SERMs and SPRMs
What are the major effects of Oestradiol?
- Stimulates growth of the endometrium & breast
- Stimulates production of progesterone receptor
What are the major effects of progesterone?
- Stimulates growth of the endometrium & breast
- Maintains pregnancy
- Inhibits production of oestrogen receptors
What are the major effects of testosterone?
- Stimulates male characteristics
- Hairy body
- Deep voice
- Anabolism
- Aggression
What are the main pharmacological actions of oestrogen?
- Mildly anabolic
- Sodium and water retention
- Raises HDL and lowers LDL
-
Decreases bone resorption
- good during reproductive life but no post menopause as lack of oestrogen increases bone resorption
- Impairs glucose tolerance
- Increased blood coagulability
What are some of the side effects of oestrogen on the body?
- Breast tenderness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Water retention
- Increased blood coagulability
- Thromboembolism
- Impaired glucose tolerance
- Endometrial hyperplasia (may cause cancer)
- Ovarian metaplasia (may cause cancer)
- Breast hyperplasia (may cause cancer)
What are the main effects of progesterone on the body?
- Secretory endometrium
- Anabolic
- Increases bone mineral density
- Fluid retention
- Mood Changes
- Maintains pregnancy
What are some of the side effects of progesterone?
- Weight gain
- Fluid retention
- Anabolic
- Acne
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Irritabilty, Depression, PMS
- Lack of concentration
Surge of what hormone causes ovulation?
LH
What is the combined effect of oestrogen and progesterone on the HPA?
inhibits the HPO axis to stop release of GnRH
What are the different routes that hormonal contraception can be given by?
- Oral
- Nasal
- Transdermal
- Implants
Describe the pharmacokinetics of oestrogen
- Natural and synthetic oestrogens are well absorbed in the GI tract
- Also, readily absorbed from skin and mucus membranes
- Metabolised in the liver
- Excreted in urine as glucoronides and sulfates
Describe the pharmacokinetics of progesterone
- Injected progesterone binds to albumin and some is stored in adipose tissue
- Metabolised in the liver
- Excreted in urine as conjugated glucoronic acid
What is the main adverse effect of the combined pill and what factors increase this risk?
Thromboembolism (Overall effect is however, small)
Increased risk by:
- smoking
- long term use in women >35
- obesity
- hypertension
What drugs can reduce the efficacy of COCP and POP and why?
Both COCP and POP are metabolised by CYP450s
Efficacy of drug is reduced by anything that induces the activity of CYPS including..
- anti-epileptics e.g. carbamezepine / phenytoin
- some antibiotics e.g. rifampicin and rifabutin
- some over the counter e.g. St John’s Wort
All increase production of CYP450s
What is the effect of soya protein products on oestrogen absorption?
Soya protein products enhance the absorption of eostrogen and reduces storage in adipose and muscle
Net effect: reduces t1/2 from 15 to ~7 hours
What hormonal changes happen in the menopause?
- Ovarian follicle supply is depleted
- Consquently, ovarian sex steroid production stops
- Loss of oestrogen and progesterone end reproductive capacity and have a range of systemic effects
Why prescribe HRT? And for what reason should you not prescibe HRT
- Prescribe to:* help with symptoms (hot flushes, swears and dyspareunia- painful sex) and to help prevent osteoporosis
- Do not prescribe to*: prevent heart disease (used to be the case but no longer supported)
What oestrogen steroids can be prescribed in HRT?
- Synethtic derivatives e.g. ethinylestradiol
- Premarin
What progesterone steroids can prescribed as HRT?
- Medroxyprogesterone acetate
- Norethisterone
- Levonorgestrel
What is the main risk of unopposed oestrogen (ERT)?
Increases risk of developing endometrial & breast cancers
(in women who have uterus- better for those with TOTAL hysterectomy)
What is the main risk of opposed oestrogen HRT?
(opposed= with progresterone)
Increases risk of developing breast cancer
Explain the mechanism by which HRT can increase risk of venous theomboembolism?
- Increased activity of activated protein C resistance (natural anticoagulant resistance)
- Increased thrombin activation
- Decreased activity of antithrombin III
- Decreased levels of protein S
- Decreased Factor VII
- Decreased tissue factor pathway inhibitor (tissue factor activates the extrinsic pathway of clotting)
What effect does HRT on lipid profiles?
Beneficial effect:
- Increased HDL
- Decreased oxo LDL
- Decreased TAG
- Decreased lipoprotein effect
Will not have an effect if patient already overweight
What is the association between HRT and stroke?
Use of oral (not transdermal) oestrogen has a small increase in risk of stroke in women >60
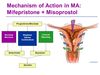
What is Mifepristone (RU486) used for? Explain its MoA
Used for the termination of pregnancy
- Normal effect of progesterone makes myometrium quiescent
- Mifepristone is a progesterone receptor antagonist
- Acts as an anti-progesterone by sensitising the myometrium to prostaglandin induced contractions
What is a SERM? Give 2 main examples
Selective Oestreogen Receptor Modulator
Have varying effects in differing tissues
e.g. tamoxifen, raloxifene
What is clomiphene used to treat? Explain its MoA
Clompihene used to treat anovulation
MoA: Competes with oestrogen for the oestrogen receptor, once bound acts as a partial agonist
Pituitary thinks there is no oestrogen, increases oestrogen production for follicle stimulation
What is tamoxifen used to treat? Explain how it works?
Used to treat breast cancer
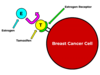
A pro-drug, metabolised into active derivative in the liver
Competes with oestrogen binding to oestrogen receptor in breast
What are the different effects of tamoxifen in different tissues?
- Breast acts as an ER antagonist → cell cycle arrest
- Endometrium acts as an ER agonist → promotes proliferation
What are the 2 types of emergency contraception? How long can each be used for?
- Progestogen: Levonorgestral
- Progesterone Receptor Modulator: Ulipristal Acetate
Explain how Ulipristal Acetate works (ellaOne)
- Selective preogesterone receptor modulator
- Primary mode of action as emergency contraception is to delay/ prevent ovulation
- Also effective in treatment of uterine fibroids


