Neurological Pharmacology Flashcards
What are some of the key clinical features of Parkinsonism
- Tremor
- Rigifity
- Bradykinesia
- Postural instability

What are some of the non motor manifestations of Parkinsonism?
- Mood changes
- Pain
- Cognitive change
- Urinary symptoms
- Sleep disorders
- Sweating
- Swallowing problems
What is the underlying pathological basis of Parkinson’s Disease?
Low Dopamine due to loss of neurones in the substantia nigra

How is idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease diagnosed?
Based on:
- Clinical features
- Exclude other causes e.g. drug induced, vascular, progressive supranuclear palsy etc
- Responding to treatment
- Normal structural neuro imaging
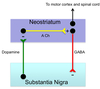
Explain how a decrease in dopamine leads to the motor symptoms seen in Parkinsons
- A decrease in Dopamine leads to less inhibition on the neurostriatum
- Less inhibition = increased acetyl choline production
- Signals ot the motor cortex are altered; indirect pathway (inhibitory) is overstimulated and direct pathways (excitatory) is understimulated → reduced movement
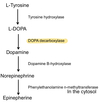
Describe the synthesis of Dopamine
- L- Tyrosine precursor converted to L-DOPA
- L-DOPA converted to Dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase
- Further conversion turn dopamine into norepinephrine/ epinephrine
How is dopamine degraded?
Dopamine converted to Homovanillic acid via enzymes monoamine oxidase and catechol-O-methyl transferases (COMT)

What is measured on a DAT scan?
A type of PET scan measuring the re-uptake of neurotransmitters
In Parkinson’s re-uptake is reduced as there are less neurones to release neurotransmitter in the first place

Why can Parkinson’s disease not be treated by simply giving dopamine directly? What is given instead?
Dopamine cannot cross the blood brain barrier
L-DOPA is a dopamine pre-cursor that can cross the blood brain barrier (by active transport)

Why does L-DOPA start as a good treatment for Parkinson’s but then become less reliable over time?
- Levodopa needs to be taken up by dopamingergic cells in the substantia nigra to be converted to dopamine
- Over time, the number of neurones becomes less and less so the effect is not as great
Describe the pharmacokinetics if L-DOPA
- Orally administered
- 90% in inactivated in the intestinal wall due to MOA and DOPA decarboxylase
- T 1/2 of 2 hours → need frequent dosing 3-5x day
- 9% broken down peripherally by DOPA decarboxylase
- <1% enters the CNS
What should patients taking L-DOPA be mindful of when taking their medication and why?
Need to avoid meals with large protein content at the same time as taking drug
Why?: L-DOPA is taken up by active transport , amino acids from protein compete with L-DOPA and less L-DOPA can be absorbed

Why is L-DOPA used in combination with a peripheral DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor?
The DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor will reduce the amount of L-DOPA broken down in the periphery before reaching the brain
Allows for:
- Reduced doses required
- Reduced side effects
- Increased amount of L-DOPA reaching the brain

Give the name of 2 L-DOPA and DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor combinations
- Sinemet (Co-careldopa)
- Madopar (Co-beneldopa)
What are the advantages of L-DOPA to treat Parkinsonism?
- Highly efficacious
- Low side effects, the ones that do exist:
- Nausea and anorexia
- Hypotension central and peripheral
- Psychosis (hallucinations, delusion, paranoia)
- Tachycardia
What are some of the disadvantages of L-DOPA?
- Only a pre-cursor; needs converting by enzyme
- Loss of efficacy long term (only effective in presence of dopaminergic neurones)
- Motor complications
- on/ off
- wearing off
- dyskinesias
- dystonia
- freezing
Which vitamin can cause a increase in peripheral breakdown of L-DOPA?
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Important to consider if patient is taking multivitamins
What is one of the main risks of giving MAO inhibitors?
Risk of hypertensive crisis
Mainly at high doses
Name some dopamine receptor agonists used in Parkinson’s treatment
- Amantadine
- Apomorphine (subcutaneous)
- Ropinirole
- Rotigotine (patch)
How are dopamine receptor agonists used in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease?
Either as de novo or add on therapy
Apomorphine only to be used in patients with severe motor fluctuations
What are the advantages and disadvantages of dopamine receptor agonists?
Advantages:
- Directly acting
- Less dyskinesi/ motor complications
- Possible neuroprotection
Disadvantages:
- Less efficacious than L-DOPA
- Impulse control disorders
- More psychiatric side effects
- Expensive
What are some of the side effects of dopamine receptor agonists?
- Sedation
- Hallucination
- Confusion
- Nausea
- Hypotension
What behaviours are seen in dopamine dysregulation syndrome? (something to be mindful of when Rx dopamine agonists- always ask for history of these)
- Pathological Gambline
- Hypersexuality
- Compulsive shopping
- Desire to increase dosage (due to reward effect)
- Punding (collecting and arranging pointless things)
How do monoamine oxidase B inhibitors help treat Parkinsonism?
Block the breakdown of dopamine so that effects of dopamine are enhanced