Diuretics Flashcards
(51 cards)
What are the 4 main functions of the kidneys?
- Regulatory
- Excretory
- Endocrine
- Metabolism
What kind of things do the kidneys regulate?
- Fluid balance
- Acid-base balance
- Electrolyte balance
What endocrine substances do the kidneys produce?
- Renin
- Erythropoietin
- Prostaglandins
- 1-alpha calcidiol
What kind of things do the kidneys metabolise?
- Vitamin D
- Polypeptides e.g. insulin
- Drugs e.g. morphine, paracetamol
What is the effect of a diuretic?
Increased production of urine (doesn’t necessarily get rid of salt)’
What is the definition of a natriuretic?
A drug that induces loss of sodium in urine
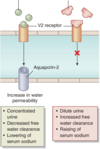
What is the definition of an aquaretic?
A drug that causes loss of water without loss of electrolytes
What is the primary site of action of osmotic diuretics?
Work throughout the tubule but primary action at the PCT
What is the primary site of action of Thiazides?
Primarily act at the DCT
What is the primary site of action of ADH blockers?
Primarily act at the collecting duct
What is the primary site of action for SGLT2 inhibitors?
Primarily act at the PCT
Where do loop diuretics act?
At the loop of Henle
What is the primary site of action for K+ sparing diuretics?
Act mainly at the DCT
Explain the mechanism of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
- Inhibit carbonic anhydrase therefore, stop breakdown of H2CO3 in the lumen
- More NaHCO3 is lost in urine
- As there is more Na is delivered to the collecting duct this activates ENaC channels which absorb Na+ in exchange for K+ therefore causing increased loss of K+ and hypokalaemia

In What circumstances are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors most commonly used? Why are they not commonly used as a diuretic?
Used in glaucoma and mountain sickness
Not frequently used as tolerance develops after 2-3 days
What is the mechanism of action of osmotic agents ?
Osmotic agents remain in the lumen of the kidney tubule, as they’re osmotically active they draw water into the tubule by osmosis
Net effect of loss of water

Name the most commonly used osmotic agent?
Mannitol
What are the risks of using osmotic agents as diuretics?
Risk of Hypernatriemia as no salt is lost, just water
Explain the mechanism of action of SGLT2 inhibitors as diuretics
Inhibit the SGLT2 ( sodium, glucose co transporter) at the proximal convoluted tubule. Therefore promotes Na+ excretion (natriuretic) and glucose excretion
Leads to decreased plasma glucose, decreased body weight, decreased blood pressure, decreased plasma uric acid, decreased glomerular hyperfiltration

What is a side effect of SGLT2 inhibitors?
Patients can become hypoureamic
Where in the loop of henle do diuretics normally act?
Act at the thick ascending limb
Explain the mechanism of action of loop diuretics
Loop diuretics block the NKCC2 transporter which normally reabsorbs 25% of sodium

What are the main effects of a loop diuretic?
- Loss of sodium and water
- Hypokalaemic metabolic alkalosis
- Increased calcium loss ( can be used to treat hyper calcaemia)
Why do you see hypokalaemic metabolic alkalosis when using loop diuretics?
- Blockage of NKCC2 means more Na is delivered to the collecting ducts, promoting expression of ENaC
- ENaC absorbs sodium in exchange for a K+, so more potassium lost in urine leading to hypokalaemia