Reproduction system: basics Flashcards
(38 cards)
How much does infertility affect couples?
1 in 7 couples
What are the four main causes of infertility?
STI’s, cigarette smoking, obesity, increasing age of child bearing
What is the males ability to be reproductively available and how does this change?
Males are constantly fertile producing ~300million sperm a day, this declines with age
What is the females ability to be reproductively available and how does this change?
Cyclical fertility (3-5 days per month fertile) and women are born with ~7million follicles (egg cells) and ovulate ~400, once these are gone women is infertile
What is the difference in size and weight between the sperm and egg?
Sperm is the smallest and egg the largest cell in the body and egg weight ~175,000 times more
What are the endocrine glands that control the reproductive processes?
Hypothalamus, pituitary gland, adrenal gland and ovary/testes
What are the most important endocrine organs for the reproductive system?
Testes and ovaries
What is the function of the testes and ovaries?
Produces/store the sex cells and produce most of the reproductive hormones
What is the main type of hormone produced by the reproductive organs?
Paracrine steroid hormones (i.e. lipid soluble hormones that circulate the body)
What are the different types of peptide and protein hormones produced for reproduction? Where are they primarily produced?
Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) - Hypothalamus
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) - Anterior pituitary
Luteinising hormone (LH) - Anterior pituitary
Oxytocin - Posterior pituitary
What are the different types of steroid hormones produced for reproduction? Where are they primarily produced?
Androgens - Testes
Oestrogen - Ovary
Progestogens - Ovary
What does GnRH do?
It stimulates the production of FSH and LH
What are the different types of androgens?
Testosterone and 5α dihydrotestosterone
What are the different types of oestrogen?
Oestradiol (most important FYI), oestrone and oestriol
What is the principle type of progestogen produced? When is it produced and what is its function?
Progesterone, produced during the second half of the menstrual cycle for the preparation of pregnancy (only produced by females FYI)
What are all the steroid hormones made of?
Cholesterol
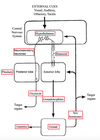
Label the diagram, what is it showing?

The hierarchy of endocrine organs and how they result in amplification of signals
How are neurosecretory neurones different from normal neurones?
Normal neurones can conduct a nerve impulses and release a neurotransmitter while neurosecretory neurones can do that and synthesise, carry and release hormones
What is the humoral system?
The system that relates to information transfer by hormones/blood
What are the two neurosecretory peptide hormones? What are they?
Oxytocin and Antidiuretic hormone (i.e. ADH/vasopressin)
These are hormones that are produced by cells that are stimulated by the nervous system
What is the function of oxytocin?
It stimulates the relaxation of smooth muscles and as a mood enhancer
What is the function of ADH?
Helps kidneys to retain water
How is the hypothalamus connected to the anterior pituitary gland? What is this structure?
Via the Hypophyseal portal system
This is a portal vein that connects two capillary beds without going through the heart
Why is a portal system used between the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary gland?
So that that minute amounts of chemical produced by the hypothalamus are directly delivered to the target organ (pituitary gland) and not diffused through the body




