Cardiovascular system: Blood circuits 2/2 Flashcards
What is the base of the heart?
The point where all the blood vessels connect into the heart (i.e. the top of the heart)
Where is the apex of the heart?
It is at the point of the left ventricle
What direction is the apex of the heart pointed?
Inferiorly (i.e. downwards), anteriorly (to the front) and to the left
What is the distribution of the mass of the heart inside the chest cavity relative to the midline of the body?
About one third of the mass lies to the right, two thirds to the left
What is the pericardium?
A double layer of mesothelial cells that contain the heart
What is the structure of pericardium?
A layer of mesothelia cells (simple squamous cells similar to endothelium but not exposed to the enviro FYI) that is folded over itself forming an outer layer (parietal pericardium) and an inner layer connected to the heat (visceral pericardium) and the gap in between (pericardial space) is filled with serous membrane

What is the purpose of the serous fluid?
It allows the parietal and viscera surfaces to slide without friction as the heart beats
Is the heart inside the pericardial space? Explain
No it is not, it is enclosed in the double layer of mesothelial cells that overlap (i.e. imagine your fist in a balloon, your fist is not in the balloon it is surrounded by the balloon and the air is inside the balloon)
What is the name of the mesothelial layer when it is considered connected to the heart vs when it is apart of the pericardium?
When it is apart of the pericardium it is called visceral pericardium (how it is more commonly referenced) and when considered connected to the heart it is called epicardium
If the wall of the left ventricle is punctured, where will blood from the ventricle collect? What is this called?
When it is punctured, blood from the ventricle drains into the pericardial space, this is called cardiac tamponade
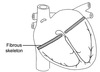
What part of the heart cannot contract as acts as an electric insulator?
The fibrous skeleton of the heart
What is the purpose of the fibrous skeleton?
Allt he vales are on a similar plane which makes it a weak plane for the heart so a fibrous skeleton is used to reinforce these points
Label the diagram

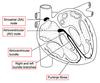
What are the two types of nerves in this diagram? What are the differences?

Myocyte muscle nerve top, Purkinje cells on the bottom
The myocytes nerve is not found in the heart, purkinje cells only found in the heart, Myocytes are more contractile but not as good at conduction compared to purkinje cells
What is the pathway of electrical conduction in the heart?
1 - The SA Node depolarises and creates an action potential, propagating through the atriums which cause it to contract
2 - The fibrous skeleton is an electrical insulator so the action potential is re-propogated using the AV Node
3 - The AV node then depolarises the purkinje cells in the ventricles causing them to contract

What is the relative speed of action potential propagation in the atrium?
Medium speed
What is the relative depolarisation speed of the AV node? What does this allow?
Very slow (100ms contraction delay)
Delay allows the atrium to contract before the ventricles so that there is time for the atrium to fill the ventricle
What would happen if there was no delay between atrial and ventricular contraction?
The contractile force of the ventricle would overwhelm the atrial contractile force meaning the atrium would not be very effective at fill the ventricles up
What is the relative speed of electrical conduction in the ventricles? Why this speed?
Very fast
This is so that there is even ventricular contraction
What side of the heart is this for? What process is happening at each step?

This is for the left side
1 - Ventricular filling
2 - Atrial contraction
3 - Isovolumetric ventricular contraction
4 - Ventricular ejection
5 - Isovolumentric ventricular relaxation

What is happening during ventricular filling?
This is when the left atrium and ventricle are filling up PASSIVELY as the heart relaxes after contraction
How much of the hearts blood goes into the heart during ventricular filling?
80%
What happens during atrial contraction?
This is when the left atrium contracts to further fill the left ventricle with blood
Does much more blood comes into the left ventricle during atrial contraction? Why this amount?
It fills the ventricle by about 20%, this is because there are no valves on the atrium so when it contracts it is leaking blood backward and also it is not very strong so it can’t push much more blood into the heart
What blood vessel goes into the left atrium?
The pulmonary vein
What happens in isovolumetric ventricular contraction?
The left ventricle begins to contract increasing the blood pressure in the ventricle but it is unable to push blood out
What makes isovolumetric ventricular contraction isovolumetric (i.e. no change in volume)?
Because the valves into the atrium are closed and the pressure in the aorta is still too high as the ventricle, having only just contracted, has not developed enough pressure to push blood through outlet/semi-lunar valve
What happens during ventricular ejection?
The pressure in the ventricle is now large enough to overcome the pressure in the aorta so blood is pumped through the aorta
What happens during isovolumetric ventricular relaxation?
The ventricle relaxes after contraction and the pressure is greater is the aorta so outlet valve closes and the pressure in the atrium is lower so the inlet valve is closed therefore pressure inside ventricle drops with no change in volume
What processes during the cardiac cycle are the atriums systolic?
Systolic during atrial contraction
What processes during the cardiac cycle are the ventricles systolic?
Systolic during isovolumetric ventricular contraction and ventricular ejection
What processes are diastolic for both the atrium and ventricle?
Ventricular filling (passive) and isovolumetric ventricular relaxation
What is the diastolic and systolic pressure?
Diastolic pressure is the lowest pressure for which the blood can be pumped in the aorta
Systolic is the peak pressure the ventricle produces during contraction
What is the normal time of a cardiac cycle?
0.8 - 1 second
During exercise, what happens to the phases of the cardiac cycle?
They get shorter
What part of the cardiac cycle gets particularly shorter? Why this phase?
Ventricular ejection
The amount of blood pumped out is an inverse relationship (i.e. blood flow rate out of heart decreases over time) so by the end of ventricular ejection not much blood is being pumped out so by shortening it, you are not losing much blood and can get back to the peak pressure again quicker



