Nervous system: The Spinal Cord Flashcards
(27 cards)
What is main function of the spinal cord?
It allows information to be transferred from the brain to the periphery and vice versa
Where does the spinal cord start?
At the base of the brain
Between each vertebrate, what is at each level?
A spinal segmental level
Label the diagram
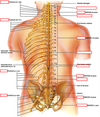

What is the range of the cervical enlargement?
C4 - C8
What makes the spinal cord enlarged at the cervical enlargement?
This is where the nerves of the ARM join up with all the other nerves so there need to be more space for connections therefore enlarged here
Where does the spinal cord terminate? What is this point called?
At L1
at the Conus medullar
What makes the spinal cord enlarged at the lumbar enlargement?
This is where the nerves of the LEG join up with all the other nerves so there need to be more space for connections therefore enlarged here
How many paired nerves are there in the body?
31 pairs
What does the homunculus structure of the brain indicate interns of neuron quantity and sensation?
Where the corresponding parts of the brain are large, there are more nerves going there which means there is more discriminative sensation
What is discriminative sensation?
Sensation that is sent to the spinal cord and allow the ability to be able to detect differences
What does discriminative sensation on the lips vs the back tell us about the nerves going to these places?
In the lips you can detect two points that are only millimetres apart, on your back can only detect two points within 10cm
This indicates that there is a far higher density of nerves in the lips than in the back
Where do the peripheral nerves come INTO the spinal cord?
Though the dorsal root (i.e. a ganglia)
What is the white matter made of?
Lots of nerve fibres
What is grey matter made of?
Lots of cell bodies
What is a ganglia?
A clump of nerve cell bodies
What are the two types of capsulated nerves? What do they detect?
Meisner’s corpuscles: touch
Pacinian corpuscle: pressure
What is surrounding the corpuscle nerve endings? What does this allow? What does this show about its function?
Myelin, allows rapid info transfer (50ms-1)
Shows that it is used very often
What do parisian corpuscles detect? How does their behaviour describe this?
Changes in pressure
They will quickly activate sensing pressure change but then quickly deactivate
What do free nerve endings detect?
Pain and temperature
What is on the end of a free nerve ending?
Nothing, it is connected directly into the skin
Is there myelin along a free nerve? What does this mean for its ability to transmit information and show about its function?
No
It means it transmits information very slowly (~1ms-1)
This indicates that it is not used very often
What is the first cervical nerve? Where does it come from?
Atlas, comes from between the first vertebrate and the skull
What is the name of this diagram? What does it describe?

Dermatome, it describes the location where the nerves from the spinal cord connect to the skin




