Reproduction Flashcards
1
Q
Diploid (2n)
A
Two copies of each chromosome. One set from mom and one set from dad. i.e. autosomal cells
2
Q
Haploid (n)
A
Contains only one copy of each chromosome. One copy from mom OR one copy from dad. i.e. sex cells
3
Q
Cell Cycle
A
Consists of 4 stages: G1, S, G2, and M.

4
Q
Interphase
A
- G1, S, G2
- longest part of the cell cycle.
- chromosomes aren’t visible
- In form of chromatin
5
Q
G0 Stage
A
The cell is simply living and serving its function with no preparation for division.
6
Q
G1 Stage
A
- Cells create organelles for enery and protein production, while increasing their size
7
Q
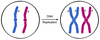
S Stage
A
- The cell replicates its genetic material (DNA synthesis)
8
Q
G2 Stage
A
- The cell passes through another quality control checkpoint.
- Cell checks to ensure there are enough organelles and cytoplasm for division
9
Q
Mitosis
A
- PMAT Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
- Results in 2 identical daughter cells

10
Q
Prophase
A
- Chromatin to Chromosomes
- centrosomes move to poles & spindles form
- nuclear membrane dissolves

11
Q
Metaphase
A
- Centrioles are at opposite ends of cell
- Chromosomes align at metaphase plate

12
Q
Anaphase
A
- Centromeres split, so each chromatid has its own centromere
- Sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards poles

13
Q
Telophase
A
- Spindles disappear
- nuclear membrane reforms
- chromosomes uncoil
- cytokinesis: separation of cytoplasm and organelles

14
Q
Meiosis
A
- Occurs in gametocytes
- results in up to 4 non-identical sex cells
- 1 round of replication, 2 rounds of division

15
Q
Meiosis 1
A
- Homologous chromosomes being separated; reductional division
16
Q
Meiosis 2
A
- Separation of sister chromatids; equatorial division
17
Q
Prophase 1
A
- Same as mitotic prophase, except chromosomes intertwine through synapsis and crossing over occurs

18
Q
Metaphase 1
A
- homologous pairs (tetrads) align at the metaphase plate and each pair attaches to a separate spindle fiber

19
Q
Anaphase 1
A
- homologous pairs separate and are pulled to opposite poles (disjunction)

20
Q
Telophase 1
A
- nuclear membrane forms around each new nucleus
- Each chromosome still consistes of two joined sister chromatids
- Cells are now haploid
- cytokinesis

21
Q
Prophase 2
A
- Nuclear envelope dissolves, nucleoli disappear, centrioles migrate to poles, spindles form

22
Q
Metaphase 2
A
- Chromosomes line up on the metaphase plate

23
Q
Anaphase 2
A
- centromeres divide, seprating the chromosomes into sister chromatids.
- Chromatids pulled to opposite poles

24
Q
telophase 2
A
- nuclear membrane forms around each new nucleus
- Up to 4 haploid daughter cells are produced

25
Pathway of sperm
**SEVE(N) UP**
* **S**eminiferous tubules
* **E**pididymis
* **V**as deferens
* **E**jaculatory duct
* (**n**othing)
* **U**rethra
* **P**enis
26
Oogenesis

27
Testosterone
* Produced by testes
* increases dramatically during puberty
* Production stimulated by LH
* Develops/maintains male repro system and secondary sexual characteristics
28
Estrogens
* Secreted in response to FSH
* development/maintenance of female repro system and secondary sexual characteristics
* lead to thickening of uterus (endometrium) each month
29
Progesterone
* Secreted by corpus luteum
* development and maintenance of endometrium
* supplied by placent after first trimester
30
Menstrual Cycle
* Follicles mature during the follicular phase (FSH, LH)
* LH surge at midcycle triggers ovulation
* Ruptured follicle becomes CL, whihc secretes estrogen/progesterone
* If fertilization does not occur, CL atrophies, progesterone/estrogen levels fall, menses occur, LH and FSH levels rise

31
Spermatogenesis



