Renal all Flashcards
tf kidney is located back of abd cavity
t
kidney regulates blood —
composition
kidneys To balance body water and inorganic ions maintaining stable concentrations in the —– medium
To balance body water and inorganic ions maintaining stable concentrations in the extracellular medium
hematocrit is
rbc / blood vol
tf wbc carry substantial vol
F minimal vol
TF ureter comes from kidney and goes to urethra
F goes to bladder
What are the arows and what do they do
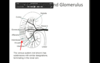
afferent arterioles(perpendicular to interlobular artery)
constrict and dilate
regulate flow of blood
tf aff artioles are innerve by PS innervat
F
Symp innerv.
glomerular filtration happens at
glom. capillaries
tf peritub cap come after the aff arterioles
F
comes after efferent arteriol
which comes in between the 2 arteriole
thick asc. limb
bowmans capsule
thick descendning limb
thick asc limb
number of distal tubules that drain into 1 collecting duct
10
rank the right order
calyx pelvis ureter
pelvis calyx ureter
ureter calyx pelvis
calyx pelvis ureter
TF for filtration to occur u need active transport to occur
F
u dont need anything to facilitate filtration
TF in juxtaglomerular nephron the glomeruli are bigger and loop of henle are longer than cortical nephron
T
granular and lot of dots
cortex with loop of henle
medulla
loop of henle
cortex with glomerular cap
cortex with glomerular cap

afferent arterioles
Vasa recta
exist in cortical nephron
are peritub cap of juxtagom nephron
are convoluted
are peritub cap of juxtagom nephron
arent convoluted
convoluted peritub cap
cotrical nephron
tf macula densa are apart of aff. arteriole
F
part of distal tubule
granular cells are derive from — — cells of the — —
smooth muscle , aff arteriole
in between eff. arteriole aff arterioles and distal tubule
mesangial cells
which of the following is nt a responce to stimulate renin production in the granular cells
composition of fluid going thru distal tubule
pressure in aff arteriole
sympathetic output of kidney
pressur of eff arteriole
pressur of eff arteriole
Na balance and Bp
Renin
sensor of fluid inside distal tubule
Macula densa
70 nm fenestration
endothelium covering BV
basement membrane
3rd layer outside glom cap
+ charge
glycoproteins
allows albumin which is negative charged
glycoproteins
correct the statement
podocytes make up parietal ep layer outside the glomerular cap. with interdigitating pedicels and form 40nm pores . they make up the 1st layer outside the BV.
podocytes make up visceral ep layer outside the glomerular cap.with interdigitating pedicels and form 4 nm pores . they make up the last layer outside the BV.
contraction of — and — regulate filtration permeability
mesangial cells and podocytes
mesangial cells and macula densa
macula densa and podocytes
mesangial cells and podocytes
layer preventing filtering of RBC
fenestartion
basement membrane
poocytes
fenestrations(endothelium)
which of the follwing wil not have a big drop in pressure
renal art
aff arteriole
eff arteriol
renal art
tf glom. cap pressure is function of pressure in aff and eff arterioles
T
tf filtration is an active process
F active
which of the following has a low reabsorption rate?
glucose
h20
Na
urea
urea
reabsorption changes in — with—
parrallel ; filtration
describe the process of urea reabs
h2o reabs
conc of urea inc in tubules
then moves down conc gradient to cap
H20 impremeable in
thick descending limb
prox tubule
ascending limb
ascending limb
which 2 structures are needed to absorb salt in prx tubule
microvilli and mitochondria
required to absorb Na in tubules
Na/ k atpase
thick descending limb
has lot of microvilli
dissolves salt
h20 imperm.
dissolves h20 but no NA
dissolves h20 but no NA
doesnt have much microvili or mit.
tf na/ k atpase are on the luminal side of tubes
F on basolat. membrane
tf Na exchange with H exists in the prox tubule (to get NA into the cell)
T

early prox tubule
NA contransport with solutes
Na contransport withK and Cl
has a Na channel to get Na into the tubule cell
NA contransport with solutes
contains cotransport of Na and Cl to get Na into tubules cell
Prox tubule
Distal tubule
TAL
Distal tubule
which part of the renal tubule reab 67% of NA
prox tubule
tf all glucose get reab at prox tubule
T
Glucose tranport
SGLT1/2 on basolat. membrane
Na glucose cotransport on lumenal membrane
Na Glucose exchanger on luminal membane
invole GLUT 1 and 2 to get glucose into cap side
more than 1
more than 1
invole GLUT 1 and 2 to get glucose into cap side
Na glucose cotransport on lumenal membrane
filtered glucose is a function of
plasma glucose*GFR
Tm limited
Na
Glucose
h20
glucos
transporter get saturated and cause excretion of Glucose because glucose cant get into cap (reabs)
2/3 get reabs in prox tubule
h20
na
glucoese
h2o and Na
h20 reabs is — in the prox tubule
isosmotic(follows salt)
high osmolarity in medulla causes H2O reabs in
descending limb
diabetes mellitus
nill reabs of glucose
no gradient for h2o
h20 in tube and get excreted
aqp1
exists in?
prox tubule and thick descending limb
(on luminal membrane and basolateral mem)
ADH triggers — from vesicles to fuse on luminal membrane
AQP1
AQP2
AQP3
AQP4
AQP2
contain proteins
Glom cap
peritub cap
larger oncotic pressure than hydrostatic pressure of tubes
tub. secretion important for
H and K
H and K
secreted in tubules
na and h2o
not secreted
vol of ecf reg by
amt of salt in body
most of Na available in
ECF
pressure or vol inc from Na are detected by
baroreceptors
responce of baroreceptors to inc(pressure or vol)
tell kidney to excrete salt
load dependent
more Na filtered more resorbed Proxt tubule and Thick ascending limb
maintain intak=excretion
distal tube and CD
limited capacity for resorption of NA
distal tube and CD
tf when u gain or lose NA the first site to be affected is distal segment
T
tf when there is loss of salt then more na is resorbed in the prox tubule
T
NO acts in NA constraction stimulates na resorption at prox tubulte inh na resorbtion at prox tubule
inh na resorbtion at prox tubule happens when NA inc(ecf expansion)
tf symp and ang1 stimulate na resorption at prox tubule when there is loss of NA
F symp and ang2
tf NA amt reabsorbed in distal tubule is low
F small percent but large amt
which of the following doesnt inh. resorption of NA at distal tubule? no PG ANP ALdosterone
aldosterone inc NA absorption when Na is intaken(ecf expansion)
which of the function is function of aldoesteron Na resorption by kidney inc adh sec and leads to water retention more thirst arteriolar vasoconstrictor(restore BP)
Na resorption by kidney other by Ang 2
which of following reg how much aldosterone secreted in plasma renin ang1 ang 2 angiotensinogen
renin
renin released
from granular cells
ANP
inc in high ecf cases(NA intake)
TF RAA system inc na excretion
f dec it
h20 reabs in prox tubule is
isoosmotic follows NA
tf most of water is reabsorbed at prox tubule anddistal tubule
F distal tubule is imperm to water
tf passive transport maintain 200 mOsm gradient in the medulle between tubules cells and int fluid
f active transport
equilibrates with interstitial fluid
descending limb
oblig water loss
.5l / day
diuresis
low adh
in diuresis osmomolarity is more in cd osmolarity in less in cs salt cant be reabrorb in CD
osmolarity in less in cs because salt is reabsorbed in CD
active transport out of ascending limb
concentrate the interstitium
action of ADH to reabsorb water at CD needs
loop of henle needed to set up stage of concentrating interstitium
wat helps maintain int. molarity
vasa recta
adh constrict —-,; results in—- solute in medulla
vasa recta; less
adh sec by
post pit
tf to restore osmolarity osmorecptors alone are adequate to inc adh
f need to drink h2o
tf baroreceptor only inh ADH receptors when you have inc vol
f they are constantly inhibiting ADH receptors
tf osmorecptor and baroreceptor both both have adh as effectors
t
vol receptor
baroreceptor
sense plasma osmolality
osmoreceptor
ecf expansion and anp
inh thirst and adh release
tf body temp is highest from 3-6 pm
T lowest from 3-6 am
tf ovulation has .5 degree celcus dec in temp
f inc
homeotherms
maintain body temp in narrow range
major way to get heat from core to skin
convection
which of the following isnt a way to eliminate heat convection conduction radiation
radiation
convection
fluid movement
conduction
diffusion and collision of particles
bigger velocity
–> bigger gradient in temp (convection)
True false being in cold water increases the amount of heat that is lost from you
T water has higher heat capacity than air
wate vapour pressure on skin — with sweat and carries — because of the —-
inc;heat; gradient(water more pressure than air)
where do temp sensors exist
pre optic area and ant hyp, entire skin surface
tf temp sensory have merkel corpsucle
F have free nerve ending
example of acral skin
face lip finger
tf trunk and limbs have low conc of temp receptor
T
tf acral skin have higher onc of temp receptor
T(fine temp discrimination
tf when warm receptor stim there is depol and action potential
T ion channel open depol inc in AP
capsaicin
stim warm receptor
menthol and oil or wintergreen
stim cool sensation
tf in body core thermoreceptor there are only cold thermoceptors
F only warm
which is false about core thermceptors in brain in SC responds to 10 degree diff between mean can exist in muscles
responds to 10 degree diff between mean –> 2-4 degree
skin therm receptors tell u to turn on heat loss mech more agresive in hot env to turn on heat loss mech more agresive in cold env to turn on heat loss mech less agresive in hot env
to turn on heat loss mech more agresive in hot env
tf core body thermoceptors inc met rate same amt for diff skin thermoceptors.
F for higher skin thermoceptor the temp is less skin thermoceptors alter sensitivity to body core thermceptor
Brown adipose tissue
inc rate of metab
cutaenous ciruclation
inc blood to skin
vasocontrict to skin
less heat loss
TF ANS control cut circulation
T
shivering
invol clonic rhythmic contractions and relaxation
which of the following has noradrenagenic stim for cut circ of skin vasoconstrition vasodil of acral skin vasodil of non acral skin
vasoconstriction
tf vasodil of acral skin involves bypassing cap
t
tf vasodil of acral skin use symp ns
F doesnt
kallikrein is released in vasoconstrition vasodil of acral skin vasodil of non acral skin
vasodil of non acral skin
kallikrein; bradykin 1st second second 1st vasodil; comes from activated sweat gland involved in vasodil of acral skin
1st second
tf brown adipose tissue only found in infants
F
Infants
thin shell of fat and skin and more susceptible to heat loss
which 2 inc UCP T3 and FA FA and T2 protein kinase and T3 5 deiodinase and alpha 1 receptor
T3 and FA
in brown adipose tissue B3 stim by NE ultimately make Lipase (convert TG to FA) B3 stim by NE make 5’ deiodinase T3 converts to T2 via 5’ deiodinase
B3 stim by NE ultimately make Lipase (convert TG to FA)
TF in brown adipose tissue UCP reverse gradient of H + into inner mit membrane. ATP synthase does the opposite
T
Non shiver thermogenesis happens in
brown addpose cells
hyperthermia
core temp above limits
hyperthermia
hot humid env with phys activity
tf in hyperthermia inc in core temp by less radiative heat loss less conductive heat loss more evap heat loss 1 and 2
1 and 2
inc radiation and metabolism
cause hyperthemia
tf in hypothermia shivering and cutaneous constriction is sufficient
F not sufficienct have to get out of water
fever in hot env
heat loss mech off
fever in cold env
heat loss mech on
fever in—

fever in cold env
inc of temp in fever
improve t lymph proliferation
tf t lymphocyte proliferate greater in vitro when at 39 then 37 degrees Celsius
T
heat loss neurons on
fever i cold
shift balance point of temp of 37 dgress celcius
Fever or excersize
at the thick ascending limb
K is transferred to caps at basolateral membrane by
cotransport wih Cl
pump
channel
1 and 3
1 and 3

tf
at prox tubule k is reabs intracellularly and secondary to water and diffusion
F
reabs paracellularly
how does K get into tubular cell at luminal membrane
cotransport wih 2 cl and na
TF collecting duct and distal convoluted tubule
can reabsorb and sec K
T
hypokalemia (low plasma K) which cells in CD reab K
intercalated cells
tf principla cell secrete K into urine
T
Lot of K in diet
Principle cells work to take secrete K in CD andDCT
At basolateral membrane of Principle cells
K/Na atpase bring K into cell from cap
K/Na atpase bring K into cap from tubular cell
K channels bring K into tubular cell to be secreted
K/Na atpase bring K into cell from cap
What is on the lumanal membrane of principle cells to secrete K
K channel
K channels are on intercalated cells to
transfer K from lumen to Tubular cell
reabsorb K from tub. cell to cap
take ATP to reabs K
reabsorb K from tub. cell to cap
In urine
1-20% excreted of K
determine amt of K goes to urine
principle cells of CD
tf hyperkalemia stimulates NaK pump and inc. luminal permeability independent of Aldosterons sec.
T
inc plasma K levels will:
inc Na/K pump at prox tubule
inc. luminal permeability of CD
dec. aldosterone secretion
inc. luminal permeability of CD
inc. ald and inc. Na k pumps on basolater side of CD cells
aldosterone
insert transport proteins
and make transporter
acidosis
inc. k excretion
dec. K excretion
inc. K excretion
effect of inc. tubular flow
inc. k excretion
metabolism produces
h ions
gain H; lose H
kidney ;urine
buffer for H
bicarb
resp acidosis
accum of CO2 which makes H
any problem with ventilation
inc CO2
diabetics and hypoxia
produce acid
normal diet
make diet
net exogenous acid production
acid made from protein digestion and diabetes and hypoxia
tf amt of acid in body is less than ingest per day
true
tf most of bicarb reabsorption occurs in prox tubule an none goes into urine
t
tf bicarb is reabsorbed at all parts of renal tubule
t
at the prox tubule — bicarb is reabs and — h+ is secreter
1;1
prox tubule luminal mebrane how do you get H+ out into lumen
thru exchanger(with NA) and pumP

how does HCO3 get to cap at basolat membrane of Prox tubule
cotransport with NA
exchange with Cl

at luminal side of the collecting duct
H get secreted by
pump with H+
and exchange with K(need ATP)

how does hco3 get to cap side in CD
exchange with CL

tf in prox tubule and collecting duct
h secreted and HCO3 reabsorbed
t
and both 1;1
intercalated alpha type cell occurs
at CD to resorb bicarb
in intercalated beta cells of the cd
hco3 secreted in eaxchanged for
- CL

principal cells have wat features
aqp2 and Na channel
located in CD
exhange of h with urinary buffer
h+ with atp pump
bicarb exchange for CL

interacalated cells
H pump
beta intercalated types cells are used to
transfer hco3 to tube in alkalosis(excess hco3 in blood)
purpose of interacalated alpha; vs beta cells
reabsorb bicarc; secrete bicarb
reabs H+ and secretion of Bicarb occurs in
interacalate alpha
intercalated beta
prox tubule
intercalated beta
tf ammonium production and bicarb reabsorption are 1;1 in the proximla tubule
(h excretion from urine)
T
NH4 reabsorbs —–
and get resecreted as —–
at thick ascending limb
nh3 in the collecting duct
contributes to 2/3 of acid excretion from urine
ammonium production
tf ammonium production to excrete acids in urine is ridge and take up 2/3 of total acid excretion in urine
f
flexible
2/3 correct
during ammonium formation to excrete acid in urine
glut braks down to bicarb and nh4(1;1)
nh4 dissolves away to tubular fluid alone
nh3 is exchanged for na on the tub. membrane
glut braks down to bicarb and nh4(1;1)
renal failure
patient cant get rid of acid
diabetic acidosis
inc nh4 and ta in cap
acidosis
inc in acid in tubular cells
what does acidosis trigger
transporter and enzyme secretion to transport acids(nh4 and TA) to urine
excersizing
met. acidosis
diahrreha
met. acidosis
vomit
met. alkalosis
trigger hypervent
met acid.
trigger hypovent
met. alk.
tf metabolic acidosis results in low ph and high pCO2
F
low both
tf most of k is in interceullular fluid
T
t/f 2/3 of fluid in body is ecf
f it is icf(28l to 14 l)
plasma k when lower than 3.5 meq/l
hypokalemia
normal plasma conc
3.5-5 meq/l
what is the effect on the right

low k outside
hyperpolarized and hard to get to threshold
symptoms of the curve on right

increased K on outside
very excitable
det resting potential
k out
after a meal plsma k increases stim k uptake thru
na/ k atpase
insuline and epeniephrine
inc k uptake by inc. na k atpase turnover rate
hyperkalemia
caused by insulin deficiency and beta antagonist
epinephrine bind to – to inc na/k atpase turnover rate and k is brought into the cell
beta receptor
treatment for hyperkalema
b agonist and insulin
2 factors inc na/k atpase pump
so that k can be absorbed in tissue cells
plasma k
insulin and epinephrine
tf after plasma K inc after a meal it immediately get translocated in a tissue cell and then immediately the plasma k level goes down to normal
F the plasma k level stays elvated to signal kidney to get rid of K by having more pumps activated
tf after k accumulates in tisses cells after intestinal absorption there is fast renal excretion
F
renal excretion is very slow (little by little goes ijnto urine)
plasma k
and aldosterone
signal excretion k in urine
tf after K is absorbed in the intestines it immediately stays in the ECF
F
ECF doesnt want to saturate and it get transferred to Tissues
inc volume
signal for kidney to excrete more salt
less o2 and insulin
cause Acid from fat and carb
carotid bodie and chemoreceptor
trigger hypervent when there is in H from food
tf int.alpha cells reabsorb most HCO3
F
proximal kidney cells do
tf K is more prevalent in ECF
F
alpha int and principle cells
K transport in CD
Alkalosis
stimulates potassium secretion
heat loss to water
ex of convection
inc. flow thru arteriovenus anastomoses
cut. circulation
symp. vasodil
non acral skin
kallikrein released in cut circ of
non acral skin
sweat gland act by
symp.
impaired ability to shiver and sweat
infants
tf warm core thermoreceptors are always on
t


