Renal 3/4: Micturition and The kidney’s in homeostasis Flashcards
Urine composition is very different to filtrate. What are the 3 differences?
- Important molecules are reabsorbed (eg. Glucose, amino acids)
- Waste products are concentrated (eg. Urea, drugs)
- Ions & water vary depending on blood concentration
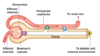
How is filtrate different to plasma?
filtrate is like plasma but without proteins
What is the function of ureters?
Transports urine to bladder
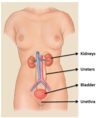
What are the 2 functions of the bladder?
- Storage of urine
- Stretches to accommodate urine, contracts during voiding

What are the 2 functions of the urethra?
- Transports urine to exterior
- Transit of urine is controlled by sphincters

Micturition involves the relaxation of two _____.
sphincters
What are the 2 sphincters in charge of micturition?
- Internal urethral
- External urethral

What are the 3 characteristics of the internal urethral sphincter?
- Smooth muscle
- Involuntary
- Part of the bladder wall

The internal urethral sphincter is made of _____ muscle
Smooth muscle
The internal urethral sphincter is ____ (voluntary/involuntary).
involuntary
What are the 2 characteristics of the external urethral sphincter?
- Skeletal muscle
- Voluntary

The external urethral sphincter is made of _____ muscle
skeletal

The external urethral sphincter is ____ voluntary/involuntary.
voluntary

The micturition reflex is _____ (voluntary/involuntary) and controlled at the _____.
involuntary; spinal cord

Filling of the bladder stimulates ____ receptors
stretch

Stretch receptors trigger ____ stimulation of the bladder muscle (contraction), which results in the opening of the ____ urethral sphincter.
parasympathetic; internal

What is the process of the micturition reflex?

Micturition reflex inhibits motor neurons innervating the ____ urethral sphincter
external

Micturition is is involuntary- but have voluntary control over it (by controlling ___ sphincter)
external
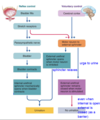
Micturition occurs when there is _____ (opening/closing) of both urethral sphincters?
opening
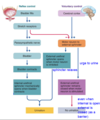
Voluntary signals from cerebral cortex over-rides inhibition of motor neurons. What does that mean for the external sphincter?
can override opening of external sphincter (relax) = exhibition = contract = closed (done by sending AP)

The kidneys help to maintain _________ in the body by controlling the composition of the ECF
homeostasis
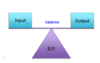
What are 5 inputs into the kidney? How is it produced?
- Ingestion
- Inhalation
- Absorption through body surfaces
- Injection
- Produced through metabolism
What are 4 outputs into the kidney? How are they consumed?
- Kidneys
- Lungs
- Digestive tract
- Body surface (sweat, tears)
- Consumed through metabolism
The body is in balance when _____ and _____ are equal
input; output

What is the acid-base balance?
regulation of unbound H+in body fluids
What is an acid?
Substances that separate in solution to release H+(and an anion)
What is a base?
Remove H+from solution (bicarbonate- H+ ion can bind to this)
The H+concentration in solution is measured by pH.
An increase H+= _____ (increase/decrease) pH (acidic).
A decrease H+= ______ (increase/decrease) pH (basic/alkaline)
decrease; increase
Blood pH is maintained within a ____ (wide/narrow) physiological range (7.35-7.45)
narrow

Disturbances in pH can result in ______ (below 7.35) or ______ (above 7.45)
acidosis; alkalosis

Why is blood pH regulation important? What are 3 factors?
Changes in H+concentration affect
- Enzymatic activity (they are a certain shape -> to become activated; H+ changes shape)
- Excitability of nerve & muscle cells
- K+concentration in the body
Where do H+come from? List 3.
- Cellular respiration (CO2)
- CO2 + H2O ⇔H2CO3 ⇔ H+ + HCO3-
- Breakdown of nutrients
- Eg. Sulfuricacid & phosphoric acid
- Metabolic intermediates
- Eg. Fatty acids & lactic acid

What are 3 mechanisms for acid-base balance?
- Buffer systems
- Respiratory response
- Renal response
What are buffer system? ECF; ICF; urine.
Substances that resist (buffer) pH changes by releasing or binding H+ (in all part of body- copes with small changes
Can withstand/resist changes in pH= balance (by binding or releasing H+ ions)
- ECF: Carbonic acid –bicarbonate system
- ICF: Protein buffers, phosphate buffer
- Urine: Phosphate buffer, ammonia

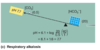
What is respiratory response? List 2 effects.
- Ventilation can be regulated to increase or decrease CO2release from the body
- Quick response (minutes)

What is renal response? List 2 effects.
- Regulate H+and HCO3-secretion & reabsorption (unlike respiratory response)
- Slower response (hours to days)

What are the 4 response to acidosis?
Inside the tubule cell:
- CO2and H2O → H+& HCO3-
- HCO3-is transported into the blood
- H+is actively secreted
- H+is excreted in the urine

What are the 2 response to alkalosis?
- Less common than acidosis
- Specialised cells in the distal tubule (Type B intercalated cells) secrete HCO3-and reabsorb H+

What are 2 things that acid-base imbalance?
- Can arise from either respiratory dysfunction or metabolic disturbances
- Deviations divided into four general categories
- Respiratory acidosis
- Respiratory alkalosis
- Metabolic acidosis
- Metabolic alkalosis

What is respiratory acidosis? What is it too much of? What is it caused by? Does renal compensation occur?
Too much CO2 ( Increase PCO2)
Cause: Hypoventilation
Renal compensation: Kidneys conserve HCO3-(& excrete H+)

What respiratory alkalosis? What is it too little of? What is it caused by? Does renal compensation occur?
Reduced CO2(Increase PCO2)
Cause: Hyperventilation
Renal compensation: Kidneys excrete HCO3-(& conserve H+)
Water is the most abundant molecule in the body. Females: _____% of body weight Males: ____% of body weight
50; 60
What are the two fluid compartments in the body?
- Extracellular fluid (ECF) –plasma & interstitial fluid
- Intracellular fluid (ICF)
How much fluid is in each compartment?
ECF = 33% (1/3) ICF = 66% has more water (2/3)
How is fluid balance regulated?
- ECF fluid consists of solutes (eg. Na+& Cl-ions) and water
- The kidneys control (blood volume) - salt (Na+) reabsorption to maintain ECF volume (&blood pressure)
- (If put salt in blood –> will retain more water = increase volume) –water reabsorption to maintain ECF osmolarity (dilute= absorb water (can unpair))
_______ of water in the nephrons helps to control ECF osmolarity
Selective reabsorption
What is osmosis?
The movement of water from an area of low osmolarityto an area of high osmolarity…..= diluting salt out of blood
(from high [water] –> low [water])
can’t move water against gradient (no active transport)
What are 3 things that happens to water molecules if the ECF becomes too concentrated? (>300mOsm) (eg. diarrhea)
- ECF becomes hypertonic
- Water moves into the ECF until equilibrium (to dilute)
- Cells shrink

What are 3 things that happens to water molecules if the ECF becomes too diluted?
- ECF becomes hypotonic
- Water moves out of the ECF until equilibrium (into cell)
- Cells swell

To maintain a constant water volume, water intake must _____ water output.
equal
Water reabsorption is an ______ (active/passive) process.
Passive
Water reabsorption is osmotically linked to ______ reabsorption. Water reabsorption is hormonally controlled in _____ tubule & ______.
Na+ ; distal; collecting duct
Most water is reabsorbed thorugh ______.
aquaporins

What are aquaporins?
Type of channels (for water molecules)

What happens to water reabsorption in the proximal tubule?
water reabsorption paired with Na reabsorption

________(moves Na out of cell) provides _______ gradient- to draw water from ______ of cell into _____ into the _______ and then finally into the _____ capillary. interstitial fluid, capillary (through osmosis)
Na/K pump; osmotic; lumen; proximal tubular cell; interstitial fluid; peritubular capillary
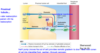
In the proximal tubule _______ are permanently inserted in the _______membrane. As Na+is reabsorbed, ____follows
aquaporins; tubular cell; water

The water permeability of the distal tubule and collecting duct is controlled by _______-dependent insertion of aquaporins in the ________ membrane
vasopressin; luminal

What is vasopressin?
a hormone that is also called anti-diuretic hormone
What is vasopressin/antidiuretic hormone produced by?
by hypothalamic neurons

Where is vasopressin/anti-diuretic hormone stored and secreted?
from the posterior pituitary
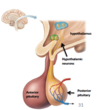
When is vasopressin/anti-diuretic hormone released?
when ECF osmolarityis too high (dominant factor) or blood pressure is very low
reduces amount of urine = help to reabsorb water

Is vasopressin’s action directly proportional or inversely proportional to the number of aquaporins.
directly proportional
What is vasopressin’s action?

How is high osmolarity, low ECF volume and low arterial blood pressure relived?

While, the concentration of urine can be varied to meet the body’s needs, water movement is always ________ (ie. Down the concentration gradient).
passive
How can we make urine that is a DIFFERENT concentration to the normal ECF (300mOsm/L)?
Medullary osmotic gradient- inside the kidney- vary how much is absorbed
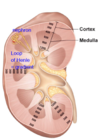
What is the medullary osmotic gradient?
Interstitial fluid in medulla becomes more concentrated towards the renal pelvis

What is the purpose of the medullary osmotic gradient?
Gradient allows selective reabsorption of water in the distal tubule & collecting duct as the filtrate moves towards the renal pelvis
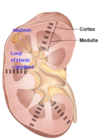
The medullary osmotic gradient is established by the _______. How?
Loop of Henle process is too complicated- don’t need to know how
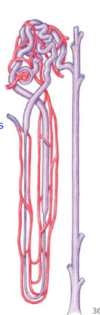
The medullary osmotic gradient is maintained by the _______.
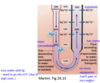
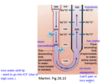
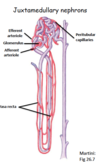
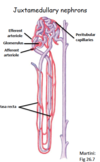
vasa recta
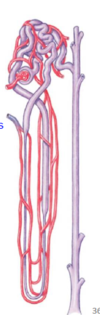
What is vasa recta?
capillary that goes around specific nephrons (juxta-medullary nephrons)
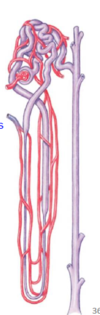
The medullary osmotic gradient is used by the _______.
collecting duct

What do the features in the medullary look like?

The loop of Henle plays an important role in _____the osmotic gradient in the renal medulla
establishing
Specifically, the _______ nephrons span the depth of the medulla and control the osmotic gradient –Humans = 20% of nephron
juxtamedullary

What are the 2 limbs of the Loop of Henle?
- Descending limb
- Ascending limb

What are 2 characteristics of the descending limb of the Loop of Henle?
- Highly permeable to water (lots of aquaporins)
- Does not reabsorb Na+

Th descending limb of the Loop of Henle is ______(highly/lowly) permeable to water. This means that it has (many/very little) aquaporins.
highly; many

Th descending limb of the Loop of Henle ____ (does/doesn’t) absorb Na+.
doesn’t

What are 2 characteristics of the ascending limb of the Loop of Henle?
- Actively reabsorbs NaCl
- Impermeable to water (no aquaporins)

The ascending limb of the Loop of Henle actively reabsorbs _____.
NaCl

The ascending limb of the Loop of Henle is ______ permeable/impermeable to water. This means that it has (many/very little/no) aquaporins.
impermeable; no

______ (different/similar) reabsorption capabilities of the descending and ascending limbs allow the gradient to be formed
Different

The filtrate equilibrates with the medullary interstitial fluid in the_____ (descending/ascending) loop of Henle as water leaves the tubule through aquaporins (permeable to water)
descending
The filtrate concentration decreases in the ___ (descending/ascending) limb of the loop of Henle as _____ and _____ are pumped out of the filtrate
ascending; Na+; Cl-

Filtrate leaving the loop of Henle has a ___ (higher/lower) concentration than interstitial fluid.
lower (100 mOsm/L)
The ________ maintains the medullary osmotic gradient
vasa recta
What is countercurrent exchange?
The hair-pin loop of the vasa recta allows the blood vessels to supply nutrients & oxygen withoutinterrupting the medullary gradient
The hair-pin loop of the vasa recta allows the blood vessels to supply nutrients & oxygen _____ (while/without) interrupting the medullary gradient
without

What would happen if the vasa recta was straight and exited the kidneys through the medulla?
NaCl in the medulla would gradually be “washed away” in the blood= no longer have gradient

The shape of the vasa recta retains the ______ (hyper/iso/hypo)tonicity of the medulla and the ______ (hyper/iso/hypo)tonicity of the blood
hyper; iso
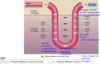
The _________ uses the osmotic gradient to control the osmolarity of urine.
collecting duct
Vasopressin- how much water is reabsorbed- unpaired to Na reabsorption

Filtrate leaving the loop of Henle is (hyper/iso/hypo)tonic at ____mOsm/L.
hypo; 100
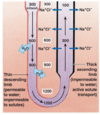
The presence/absence of ______determines whether the filtrate stays hypotonic or becomes hypertonic
aquaporins

What happens to vasopressin during over hydration? What does that cause?
No further reabsorption of water occurs in the distal tubule or collecting duct if vasopressin is absent

What happens to vasopressin during dehydration? What does that cause?
Release of vasopressin (ADH) causes the insertion of aquaporins and reabsorption of water in the distal tubule and collecting duct.
out of tubule –> interstitial fluid because interstitial fluid is so concentrated



