Cardiovascular L8/9: Venous system & blood pressure regulation Flashcards
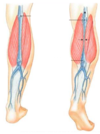
What are 4 characteristics of venules?
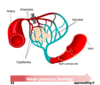
- In the microcirculation, blood flows from capillaries into venules
- These converge to form veins that exit the organ
- They have little tone or resistance
- Communicate with arterioles, chemically, to match inflow & outflow
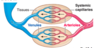
Capillaries –> ________ –> veins.
venules

Venules look a lot like _____ and they have a layer of _____ cells and ____ (for strength).
capillaries; endothelial; collagen

How does an increase in venule pressue cause damage?
Increase pressure in venules = increased intra capillary pressure = damage

Veins are _______ reservoirs.
volume

What do veins do?
Return blood toward the heart

What are 4 characteristics of veins?
- Large radius
- Low resistance
- Less smooth muscle with little myogenic (can’t contract/relax) tone (compared to arterioles and arteries)
- Less elastin so little recoil (compared to arterioles and arteries- whihc can hold pressure and excess blood- energy)

Why are veins called capacitance vessels?
Highly compliant -> huge storage capacity

What can’t veins do?
Recoil

Blood flow varies throughout the vascular tree. True or false.
False
it is the same

At rest, veins store ______ blood. Infact, it stores ___ of the total blood.
extra; 64%

At rest, _____ store blood but it is not stagnant. How?
veins; they are not storage tanks, because blood still moves through

If more blood enters the vein, when the capillary beds are closed, blood bypasses –> enters vein –> which ____ the vein –> _____ (increase/decrease) the total CSA. This means the blood moves _____ (more/less) slowly and this ______ (increases/decrease) velocity. However, when exercising, the blood flow will become______ (faster/slower)
stretches/distends; more; decreases; faster

When required (if need more blood), the capacity of the reservoir decreases to _________ venous return to the heart.
increase

What is stroke volume?
How much blood is pumped out with each beat.

What is end-diastole volume (EDV)?
How much blood is in the heart as it has filled, when it is just about to contract. Increased venous return

What are 2 reasons why increased venous return, causes an increase in EDV and in turn increases stroke volume?
- Increased volume that is going into the heart
- Stretch myocardium to optimal length of contraction

How does stroke volume increase with exercise?
Need more blood during exercise (in arterial system) –> decreased capacity to increase more blood to the heart –> increased stroke volume

What is increased effective circulating blood volume?
When venous capacity decreases, more blood is pumped by the heart

What is reduced effective circulating blood volume?
When venous capacity increases, less blood is pumped by the heart

_______ (A lot/not a lot) of pressure has been lost by the time blood reaches the venous system
A lot

But atrial pressure is near zero so there is sill a ______ pressure from heart contraction (it’s small, but enough). What does this mean?
driving pressure
is lower downstream = drive blood through

Which vessels is a site of pressure loss? Why?
Arterioles
high resistance and frictional loss

F ∝ ΔP / R. This means that flow is ____ (directly proportional/inversely proportional) to pressure gradient and ____ (directly proportional/inversely proportional)to resistance.
directly proportional; inversely proportional