Reactive skin lesions Flashcards
what is this a presentation of?

Exanthematous or morbilliform eruptions
cell-mediated hypersensitivity
7-14 days after start of new medication
trunk and upper extremities
progressively confluent
pruitis
describe the lesions on exanthematous or morbilliform eruptions
erythematous macules
summetric distribution
slightly palpable
what drugs induce exanthematous eription
aminopenicillins
sulfoamides
cephalosporins
anticonvulsants
what do severe forms of exanthematous eruption present with?
DRESS (drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms)
eripheral eosinophilia, renal and or hepatic dysfunction and fever
what is this a presentation of?

Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) and Steven Johnsons Syndrome (SJS)
morphology: macules, bullae and/or patches
clinical feature: erythematous macules in symmetric distribution (can be slightly palpable)
characterized by mucocutaneous tenderness, erythema and extensive exfoliation
what is the threshold of SA involvement to distinguish bw SJS and TEN
<10% body surface area (epidermal detachment) for SJS
>30% body surface area for TEN
what drugs commonly trigger SJS/TEN
allopurinol, NSAIDs, antibiotics, anticonvulsants
occur 7-12 days after initiation
stop offending medication, rapid supportive care and therapy
what is this a presentation of?

erythema nodosum
morphology: tender, erythematous subcutaenous nodules
clinical: distributed symmetrically over pretibial areas
later stages acquire a bruise-like appearance
accompanied by fever, arthralgias and malaise
what is erythema nodosum associated with
oral contraceptives, estrogen, suphonamides, penicillins, TNF inhibitors
sarcoidosis, post strepococcal illness
what are the three classification of vasculitis?
small, medium, large vessel
what small vessel vasculitis is usually as a result secondary to medications
leukocytoclastic vasculitis (LCV)
abundance of neutrophils on pathology
what is this a presentation of?

leukocytoclastic vasculitis
morphology: purpuric papules
50% idiopathic
15-20% drug induced
allopurinol, sulfa-drugs, penicillin related medications, antibonvulsants
what is the most common cause of vasculitis in children?
Henoch Schonlein Vasculitis (sub category of LCV)
palpable purpura
coalescing lesions will show skin necrosis with central pustulation
management of LCV
history and PE
skin biopsy
blood work (internal organ involvement)
what lab evaluations are required for patients with confirmed cutaneous vasculitis?
hematologic: CBC, differential, plt, EST, C-reactive protein, serum and urin protein electorphoresis,
GI: LFT, Stool
renal: BUN, creat, urinalysis, lytes
infectious: hep C, B, HIV
immunologic: rheumatoid factor, C3, C4, ANA, anti-dsDNA, ENA
neoplasms: CT, bone marrow biospy,
how to treat cutaneous and extracutaneous involvement?
cutaneous: conservative
extracutaneous: oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agent (steroid sparing)
what is this a presentation of?

urticaria
plaques
also known as wheals
transient skin or mucosal swellings due to plasma leakage
superficial: wheals
deep: angioedema
can range from small papules to large palm sized plaques
what is this a presentation of?
angioedema
tumid plaque
differ in depth of inflammatory process from wheals
what is the most common of acute urticaria
idiopathic
mostly exogenous causes
less than 6 weeks
what causes chronic urticaria
endogenous causes
genetic factors
more than 6 weeks
2 most common idiopathic chronic urticaria
dermatographism
cholinergic urticaria
what is this a presentation of?

dermatographism
what is this a presentation of?
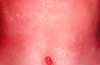
colinergic urticaria
multiple transient papular lesions
approx. 2-3mm in diameter
within 15 min of sweat inducing stimuli
stress, baths


