Eczema + Topical steroids Flashcards
dermatitis vs. eczema
eczema is defined by:
spongiotic dermatitis
red scaling patches
itch
define spongiosis
intercellular edmea
peri-vascularlymphocytic inflammation in dermis
reaction pattern of:
- lymphocytes following vascular pattern
- stretching of intracellular bridges
- collection of fluid from intraepidermal edema
clinical pattern of acute eczematous reactions
morphology: papules, vesicles, plaques, bulla
secondary morphology: excoriations, erosions, crusts
clinical features: vesiculation visible clinically
clinical features of sub-acute eczematous reactions
morpholoy: plaques
secondary morphology: crusts, erosions, excoriations
clinical features: inflammation less than acute, intercellular edema results in weeping erythematous plaque
clinical features of chronic eczema
morhology: plaques
secondary morphology: lichenification, scaling, erosions, fissues
clinical: dry red scaling plaques, lichenified (prominent skin folds, thickening of epidermis), chronic irritation from rubbing
dermatitis in a linear pattern often means an _____ etiology
exogenous/external
most common hapten to cause ACD
nickel
what is this a presentation of?
seborrheic dermatits
describe the presentation of seborrheic dermatitis
morphology: patch
secondary morphology: scale
clinical features: erythema and scaling in sebum rich areas of face
greasy, bran-like scaling
seborrheic dermatitis has a link to commensal yeast called
malassezia
epi of seborrheic dermatitis
M > F
most common form of eczema
adults and infantile form
adult peak 4-6th decade
cradle cap is a form of ______
seborrheic dermatitis
what is this a presentation of?

nummular dermatitis
morphology: plaque
secondary morphology: erosions, crusts, excoriations
clinical features: sub-acute eczema, coin shaped eczematous lesions which may be widespread
what is this a presentation of?

stasis dermatitis
morphology: sub-acute or chronic eczema
clinical fearures: eczematous eruption seen in association with lower leg edema, control underlying edema with compression garments
topical steroids
describe asteatotic dermatitis/xerosis
morphology: patch
secondary morphology: scale
result of external and internal causes, aging is most common cause, dry climate with low himidity, exposure to water and soap
desiccation of stratum corneum results in small cracks, stinging and itching sensation
atopic dermatitis typically begins in _____ and has Fx of ______
infancy/early childhood
hay fever
morphology of atopic dermatitis lesions
acute, sub-acute, or chronic pattern of eczema may be seen
infantile: face and extensor extremities
older children: felxures, antecubital and popliteal fossae
what is this a presentation of?
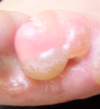
pomphylx
pattern of hand dermatitis where small vesicles are seen on fingers/palms
what is the therapeutic ladder for AD
avoidance of triggers
basic care for dry skin
topical anti-inflammatory agents
phototherapy
systemic therapy with immuno-suppressive, biologic, and anti-inflammatory therapy
most children outgrow food triggers for AD T/F
T
What is the risk from overuse of topical steroids?
atrophy
what is an advantage/disadvantage of calcineurin inhibitors?
indicated for skin at high risk of atrophy such as face, body folds
risk of malignancy from chronic use, side effect of skin irritation
what are two sedating antihistamines used to reduce pruritus?
diphenhydramine, hydroxyzine
ointments use _____ vehicles and are ______ potent
petroleum jelly, more potent
best at delivering drug
least irritating
indications for lotion as a vehicle
easy to apply
poured or pumped out of bottle
very irritating
less potent than oiuntment
describe gels as a vehicle
easiest to use for hairy skin
irritating to broken skin, can have drying effect
side effect of steroids
atrophy
opthamologic complications
striae distensae
exacerbation of periorificial dermatitis
steroid acne
dosage for steroid cream (grams, how much to prescribe)
3g each for head/face and arm
6g for a leg
9-12g for the trunk
30g for whole body once
when do you use weak steroids (hydrocortisone cream)
face
body folds
when do you use mid-potency (betamethasone 0.1%)?
torso, arms, legs
when do you use high-potency (clobetasol 0.05%)?
pams and soles
when should you stop using steroid creams?
48 hours after itching stops
psoriasis –> chronic use


