Radiology Exam #3 Flashcards
Fracture of this anatomical structure is called?

Femoral Neck Fracture
(Broken Hip)

Identify the fracture in the Image

Displaced femoral neck fracture
(More Severe than standard femoral neck fracture)
Identify the Image
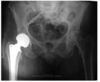
Hip Replacement
What type of fracture is depicted in the
image on the right? What is depicted on the
left image?

Comminuted Fracture
Intact Femoral Neck

What is a Communited Fracture?
A fracture where at least three separate pieces of bone are present
What is myositis osificans?
A process by which ossification of soft tissue
(usually muscle or tendon) abnormally occurs due to some cause.
What is being depicted in the Image?
What disease is it associated with?

Calcification (which is a part of ossification)
Mytosis Ossificans
Identify K.
What disease is being depicted in the image?
What is its cause?

K = Kidney
Bilateral Aseptic Necrosis of the Hips
Steroid Use or Trauma
Identify the disease associated with the Image

Aseptic Necrosis of the Left Femoral Head
Identify the disease depicted in the Image.

Bone Infarcts aka Avascular Necrosis
How do Bone Infarcts or Avascular Necrosis
Occur?
Sickle Cell disease or as a result of decompression
sickness after prolonged scuba diving.
What are bone Infarcts (aka Avascular Necrosis)?
Diffuse and amorphous calcification within the medullary space is seen here in the distal femur
Identify the disease associated with the image
below.
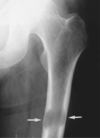
Lytic Bone Metastases
Identify the finding depicted in the image.

Pathological Fracture of the Femur
(Likely due to Lytic Bone Metastases)
Identify the finding indicated in the Image.

Knee Effusion
Identify the Finding Depicted in the Image

Patellar Fracture
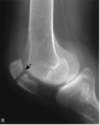
Identify the finding depicted in the image.

Patellar Fracture
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Total Knee Replacement
(Semi-Constrained Prosthesis)
Identify the finding associated with the image
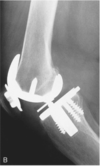
Total Knee Replacement
(Prosthetic Tricompartemnt)
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Tibial Fracture
Identify the finding assoicated with the Image.

Spiral Fracture of the Distal Tibia
(With override)
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Fracture of the proximal fibula (with override)
Identify the finding associated with the image.
(Which view)

Intermedullary fixation of a tibial fracture
(Lateral)
Identify the finding associated with the image.
(Which view)

Intermedullary fixation of a tibial fracture
(AP view)
Identify the structures associated with the image.
(What view)

(AP view of the Ankle)

Identify the structures associated with the image.
(What view)

(Lateral Projection)

Identify the indicated structures/finding associated
with the image.
(What view is the image?)

Fibular Fracture
(Mortise View)

Identify the finding associated with the image.

Ankle Effusion
Identify the findings associated with the image.
(What is the likely cause of this injury?)

Fracture of the medial malleolous and distal fibula
(Dislocation of the talus)
(Eversion injury)
Identify the view associated with each image.

A.) Lateral Projection
B.) Anteroposterior Projection
C.) Oblique Projection
Indentify the findings associated with the image.

Acromioclavicular Joint
Coracoid Process

Indentify the findings/structures associated with the image.


Identify the finding associated with the image.

Acromioclavicular Separation
Identify the view and structures associated with the image.

Normal Oblique or Y view of the shoulder
Scapula and Humeral Head
Identify the finding associated with image A
and Image B

A.) Anterior Dislocation of the Shoulder
B.) Oblique/Y View after Relocation of the Shoulder
Identify the sturctures associate with the image.


What view and imaging modality is associated with the image?

MRI Coronal view of the shoulder with a T1 Weighted Resonance Scan
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Midclavicular Fracture
Identify the finding associated with the image.

Degenerative Arthritis of the Shoulder
Identify the structure covered by the blue box and describe it’s abnormality.

Anterior fat pad it should normally be right up agains the bone
Indentify the structures associated with the image.

Humeral Condyles
Olecranon Process
Ulna
Radius
Indentify the clinically relavent finding associated with the image.

Olecranon Fracture
Identify the indicated structures in the image

Right: Anterior Fat Pad
Left: Posterior Fat Pad
Identify the structures associated with the image from upper left clockwise.

No Visible Posterior Fat Pad
Normal Anterior Fat Pad
Radius
Ulna
Identify the finding and structure associated with the image.
What is the imaging modality?

Finding: Fracture line in radial head
Structure: Ulna
Axial CT scan
Identify the finding associated with the image

Isolated Ulnar Shaft Fracture
(aka Nightstick Fracture)
Identify the structures indicated by a red line and red astrisk.

Red Line: 2nd Metacarpo-phalangeal joint
Astrisk: 4th Middle Phalanx
What is occuring as we move from the left image to the right image?

Increasing Fracture visibility with time
Identify the finding associated with the image

Scaphoid or Navicular Fracture
Identify the finding associated with the image.
This normal variant is associated with what diseases?

Short 4th Metacarpal
Turner’s syndrome
Sickle Cell Disease
Infections
Metabolic Bone Diseases
Identify the findings associated with the images.
Which views are displayed?

Complete dislocation of the proximal interphalangeal joint
A.) Posteroanterior View
B.) Lateral View
Identify the finding associated with the image

Glass within the soft tissue of the hand
Identify the finding associated with the image

Boxer’s Fracture
(Usually seen at the head of 5th metacarpal)
Identify the finding associated with the image.
Also identify the structures indicated by the black
arrows and the white arrow

Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist and Hands
Dark Arrow: Subchondral Cyst Formation
White Arrows: Periarticular Erosions
Indicate the pathology associated with the image
also indentify the condition that occurs at a late stage in the pathology

Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Wrist and Hands
Ulnar deviation at the metacarpophalangeal joint
Indicate the pathology associated with the image
also identify the structures indicated by the white
arrows

Rheumatoid Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist
Silicone Joint Replacement


