Radiology Flashcards
Identify the numbered landmarks

- Iliac crest
- Tuberosity of the ilium
- Ant. Sup. iliac spine
- Median sacral crest
- Pelvic sacral foramina
- Sacroiliac jt.
- Coccygeal segments
- Ischial spine
- Ischial spine/tuberosity
- Obturator foramen
- Pubic symphysis
- Pubic tubercle
- Body of pubis
- Inf. Pubic ramus
- Sup. pubic ramus

What imaging position is used to display the femoral head in acetabulum?
What is this position used to diagnose?
Frog leg Lateral
Used to diagnose FAIS (Femoroacetabular Impingement Syndrome)

If you see a line between greater and lesser trochanters, what is it?
Intertrochanteric Crest, may be viewed from anterior through the femur due to aditional density of bone
In the plain film frog leg lateral shot, what three lines are we able to scrutinize?

Base of cup
Anterior Rim of cup
Posterior rim of cup
What does the groin lateral view - plain film visualize?

Used for visualizing ant. & post. head of femur and for analyzing angle between shaft and neck/head of femur

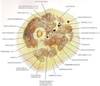
What stands out here? What kind of image? What are the things that light up?

Gluteus maximus - longitudinal vs. the others
CT W/Contrast through upper thigh, apex of femoral triangle
Lighted up stuff = arteries (except the femur of course)
What does the white circle represent?

Adductor Canal
What structure is represented by the red star?

Articularis Genu
What does the orange line point to?

Tibial and common fibular nn
Identify the numbered structures
What shot is this?

A-P Standing Plain Film
- Patella
- Adductor tubercle
- Medial femoral epicondyle
- Lateral femoral epicondyle
- Medial femoral condyle
- Lateral femoral condyle
- Lat. & med. Intercondylar eminences
- Lateral tibial condyle
- Medial tibial condyle
- Tibial tuberosity
- Fibular head
- Joint space
- Groove for tendon of popliteus
Identify the numbered structures. What angle is this shot?

Medial knee plain film

- Patella
- Adductor tubercle
- Medial femoral condyle
- Lateral femoral condyle
- Intercondylar notch of femur
- Intercondylar eminences
- Fibular head
- Tibial tuberosity
What is the arrow pointing to?

Fabella: Sesamoid bone(s) within the lateral head of the gastrocnemius
What is this view called? What is it used for?

“Sun Rise” View Plain Film
Used for visualizing patellofemoral joint space; Looking for patellofemoral syndrome

What is this image type? What is it visualizing? What is it used to assess?

Coronal MRI Knee
Cruciate ligaments and menisci
Used to assess laxity or rupture of ligaments

What image type? What are we visualizing here?

Sagittal MRI
Anterior and Posterior cruciate ligaments
What structures are indicated by the arrows?

Top: anterior and posterior medial meniscus
Bottom: ant. and post. lateral meniscus
Which two of these Salter-Harris classes of femoral epiphyseal fractures have the worst prognosis?

III and IV
Identify the structures

Fibula
- Head
- Neck
- Shaft
- Tibial tuberosity
Interosseous membrane separates the anterior and posterior compartments. Where are the vessels relative to this membrane?
Anterior tibial vessels are anterior to the interosseous membrane, posterior tibial and fibular vessels are posterior to the interosseous membrane and tibialis posterior muscle
Image type? Position? Three bright dots?

Axial CT with contrast
mid-leg
Arteries
Why doesn’t a-p ankle plain film give a very good view?
Too many bones piled up. Obscure view
What view is best for the tibiofibular articulation?
Lateral Oblique Ankle, plain film

What view is best for assessment of transverse tarsal joint?
Medial ankle, plain film

What does the lateral oblique foot plain film let you view well?
View affords assessment of the 5th metatarsal















