PHARM Lecture Flashcards
How many NMJ per myofiber?
1
What are the steps involved in NMJ transmission?
1)Axonal conduction
●
2)Junctional transmission (cholinergic)
1)Synthesis of acetylcholine (ACh)
2)Storage of ACh
3)Release of ACh
4)Destruction of ACh
●
3)ACh signaling
●
4)Muscle contraction
Describe step 1

Choline transporter: membrane channel that transports choline into the cell
Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT): enzyme that combines acetyl coenzyme A (AcCoA) and choline to form ACh
Patients with Alzheimer Disease (AD) have reduced cerebral production of what?
ChAT
Describe step 2
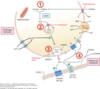
ACh vesicular transporter: ATP dependent transporter that immediately shuttles ACh into storage vesicles after ACh synthesis
Describe step 3

- Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels: open upon depolarization and allow Ca2+ to enter the cell
- Ca2+ promotes vesicle membrane fusion
- VAMP and SNAPs: vesicular and plasma membrane proteins that initiate vesicle-plasma membrane fusion and release of ACh
What are the two main classes of snares?
V snares and T snares
Botulinum toxin has what effect?
Cleave V or T snares, and prevents release of Ach
Describe VAMPs
•vesicle associated membrane protein (v-SNARE)
Describe SNAPs
•synaptosome-associated proteins (t-SNARE)
Describe step 4

•Acetylcholinesterase (AChE): enzyme that cleaves ACh into choline and acetate
•
•Choline is recycled back into the motor neuron via the choline transporter
•
•Endocytosis occurs at the nerve terminal to replenish the number of available vesicles
What are the two subsets of receptor that ACh signaling utilize?
Nicotinic and muscarinic
Describe the nicotinic subtype of receptor
- nAChRs
- Activated by ACh and nicotine
- Ligand-gated ion channel (Na+)
- Pre- and postjunctional
- NMJ: Na+ increase causes muscle action potential
What subtype of ACh receptor is at the NMJ?
Nicotinic Receptor
Nicotinic receptors are what kind of receptor?
Ionotropic
Describe muscarinic receptors
- mAChRs
- Activated by ACh and muscarine
- G-protein coupled receptor
- Pre- and postjunctional
- NOT located at skeletal NMJ
Both nicotinic and muscarinic receptors can be found…
either post or pre synaptically
What agonists work on nAChR?
Acetylcholine
Nicotine
Where are mAChR found?
Cardiac muscle
- SA Node
- AV Node•Atrium
- Ventricles
What kind of receptor is pictured?
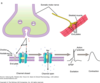
Nicotinic
What is important about nAChR subunit composition?
Diversity in subunit composition permits drug selectivity. Neuronal and muscle subunit configuration are different.
Describe post junctional nAChR activation
- ACh binds at two sites on the NM receptor
- A conformational change opens the channel pore
- Positively charged ions (mostly Na+, but also K+ and Ca2+) pass through the channel
- The muscle cell is depolarized and an action potential is initiated

describe pre-junctional nAChr activation
•Mobilization of additional ACh for subsequent release
•ACh vesicles move toward the synaptic membrane
•
•
•mAChR activation results in ACh-mediated inhibition of further ACh release
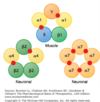
Key concept about these receptors…
Found on…
Actions dependent upon…
… before and after the synapse
… on the subunit conformation
Describe tetrodotoxin
•(puffer fish): similar mechanism as local anesthetics (different binding site on Na+ channels)
Paralysis, including the diaphragm, leading to suffocation
How do local anesthetics function?
•inhibition of voltage-gated Na+ channels prevents axonal conduction
Describe Botulinum Toxin (Botox):
•cleaves components of the SNARE complex (VAMP/SNAP proteins)

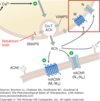
What are two agents that block muscle depolarization?
What are they used for?
Curare alkaloids
succinylcholine
•Used for causing muscle paralysis during anesthesia
What do curare alkaloids do?
nondepolarizing competitive nAChR antagonists
Succinylcholine does what?
•depolarizing neuromuscular blocker that binds to skeletal muscle nAChRs and initially causes depolarization (acts as an agonist); continued depolarization leads to receptor blockade and paralysis
(Can’t initiate a new depolarization or muscle contraction)
What drugs are represented by the green and red shapes?
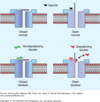
Green - Curare Alkaloids
Red - Succinylcholine
What are the clinical uses of Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
- Myasthenia gravis **** Highly useful
- Dementia associated with Alzheimer or Parkinson disease
- Reversal of neuromuscular blockade during anesthesia
- Nerve gas and organophosphate pesticide exposure
How do AChE inhibitors work?
- Bind to AChE and block its enzymatic activity
- Increase the concentration of ACh at the NMJ
What is Sarin gas an example of?
How can you prevent death due to this?
AChE inhibitor, extremely high concentration and long acting.
Atropene, or a short acting AChE inhibitor to bind the AChE first, preventing binding of the warfare agent.
Describe dantrolene’s action
•Inhibits ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplamic reticulum and blocks release of Ca2+

What clinical uses are there for Dantrolene?
•nical uses include malignant hyperthermia and spasticity associated with upper motor neuron disorders


