Radiography pictures - Musculoskeletal Flashcards

Black triangle. Possible ACL tear.

T2 MRI showing edem at femoral head. Often won’t show on xray “plain film”.

Lateral femoral condyle slamming into tibial groove causing a bone bruise. heals faster than fracture but doesnt show up on xray

Fx of posterior element of back. Sensitive (shows a fracture) but not specific (not what kind or why). Doesn’t tell what it is but can tell it’s a break.

Bone Scan. 88 y/o male with metastatic prostatic adenocarcinoma.

Ultrasound showing Achilles’ tendon rupture, Quad tendon rupture

Ultrasound. Used to locate foreign body in soft tissue. Left is AP, right is Lateral.

4th metacarpal looks narrower than others

Xray on left (fine), MRI on right showing bone bruise
Which under, which normal, which over penetrated?

Under, normal, over



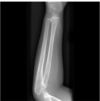
Lucent fracture lines. Most fractures appear as a radiolucent line.

Not a lucent line. Not a fracture. Flare of tibia.

Yes, fracture lucent line.

Compression fractures may appear as a sclerotic line. Most common in distal radius and vetebral bodies.

Important to know. Lucent line goes into joint.

Displacement fx. NOT angulated! If both ends are touching then nondisplaced, if not touching then displaced.
Displaced or angulated?

Displaced.

Nondisplaced Fracture. still lines up.

Nondisplaced Fracture. still lines up. can see a lucent line.

Angulated. Described in terms of position of the distal fragment with respect to the proximal.

Rotation Fx.

Distraction. Some fractures separated by a gap with no overlap: described as distracted. Due to tug of different muscles.

Anterior dislocation of 5th metacarpal base. No fx.