quiz 4 Flashcards
Covalent bonding of Ethers
C-O-C
straight chained or branched nonaromatic hydrocarbon?
Aliphatic hydrocarbons
Why is molecular length important?
anesthetic effect of immobility is decreased or lost if carbon atom chain length exceeds a distance of four or five carbon atoms 5 angstroms

Halothane
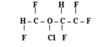
Isoflurane

desflurane

Sevoflurane
The addition of fluorine [F], chlorine [Cl], bromine [Br], or iodine [I] (Halogens) influences what anesthetic’s characteristics?
Potency - increases with heavier halogens AMU (Bromine)
Arrhythmogenic properties - more halogens, more arrythmias
Chemical stability - Enhance
Flammability - Reduced
What halogens are Disinfectants?
Bromine
Iodine
Chlorine
Typically , increasing the number of _______ atoms on an anesthetic molecule slows biodegradation.
fluorine
Currently used Volatile gas with most percentage liver metabolism?
Sevoflurane (5%)
(Halothane was 45%)
Absorption phase term?
Uptake
Metabolic phase term?
Biotransformation
Excretion phase term?
Elimination
Myer Overton Rule?
Lipid solubility is directly proportional to potency
A reduction in body temperature ______ anesthetic requirement
lowers
mediate ________ via glycine, sodium and NMDA receptors
Supraspinal Effects, causes amnesia
weak inward-rectifying K+ Channels, and inhibiting glycine and GABA receptors
Spinal Effects causing immobility
MAC % of Halothane
0.75%
Inhaled anesthetics “PROBABLY” produce anesthesia by ?
enhancing the function of inhibitory ion channels and by blocking the function of excitatory ion channels
Inhibitory channels?
Glycine
GABA
Effects of hypnosis are from what receptor?
GABA
Hyperpolarization of GABA when?
Influx of Cl- ions
Hyperpolarization of Glycine when?
Efflux of K+ ions
primary excitatory neurotransmitter
Glutamate
Ligand gated receptors? (3)
NMDA
AMPA
Kainate
How is immobility achieved via volatile gases?
Activation of descending noradrenergic pathways which originate in periaqueductal gray matter of the brainstem. Activation of these pathways inhibit nociceptive input in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord
What are highly probable targets for the amnesic effects of anesthetics?
amygdala
hippocampus
cortex
Limbic system
(supraspinal structures)
the relationship of concentration of a gas in solution to the partial pressure of the gas with which the solution is in equilibrium:
Henry’s Law
_____ potency correlates with ______ onset
High
Slow
Gases with a _____ oil:gas solubility have a _____ blood:gas solubility
High
High
The concentration of each gas in a mixture of gases in solution depends on two factors:
Its partial pressure in the gas phase in equilibrium with the solution.
Its solubility within that solution
Inhaled anesthetics equilibrate based on their _________ in each tissue, not based on their __________.
partial pressures
concentration
The concentration of anesthetic in a tissue depends on its _______ and ________.
partial pressure
tissue solubility
Best gas anesthetic for obese pt?
Desflurane
How to get fractional concentration?
Fractional Volume = P.anesthetic/P.barometric
Rank Gases from least to most Blood:gas soluble and Oil:gas soluble
NDSEIHM
MAC % of NO
104
MAC % of Desflurane
6
MAC % of Sevoflurane
2
MAC % of Enflurane
1.7
MAC % of Isoflurane
1.4


