Quiz 3 Flashcards
(188 cards)
True/False: This Patients does NOT have Urolith Calculi

False
*Cannot say for certain there are no Calculi since some Calculi are Non-Radiopaque. If you have clinical Signs that are suggestive of Calculi, you have to do further tests to Determine if there are Uroliths
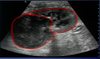
What can be diagnosed on this Ultrasound of the Spleen

Splenic Torsion
*LACY PATTERN- KNOW

Condition characterized by a Reduction in Liver Size where the Gastric Axis is moved Cranially
Microhepatia
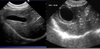
Diagnosis from this Ultrasound of the Kidney

Polycystic Kidney Disease

What Pathology can be seen in this Radiograph of the Abdomen

Pronounced Peritoneal Effusion
*Pendulous Abdomen tells us that it is a very full Abodmen
Diagnosis based on this Positive Contrast Study of the Stomach

Gastric Ulceration
*You can see Filling Defects

If a _____ study is Necessary, Survey Radiographs of the Abdomen should always be obtained prior
Contrast
Best Radiographic View to Diagnose Gastric Dilation Volvulus
Right Lateral
Four Differential Diagnoses for Microhepatia
Liver Shunting- Young Animal
Chronic Hepatitis- Older Animal
Cirrhosis- Older Animal
Diaphragmatic Hernia- Soft Tissue Opacity within the Thoracic Cavity and history of Trauma
What can be Diagnosed in this Portogram Radiograph?

Single, Extra Hepatic Portocaval Shunt
*Immediate Opacification of the Caudal Vena Cava- Not Normal. Should not see Opacification in the Heart Prior to Opacification of the Liver
*No Tree Pattern- Limited Arborizing Pattern
*Reference Point- Cranial to T13. If the Shunting vessel enters the Caudal Vena Cava Cranial to T13 we consider it to be Intrahepatic. In this case it is more likely to be Extrahepatic because the shunting occurs caudal to T13
Review of Large Colon Anatomy in a Dog


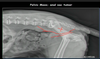
______ of L5-L7 Vertebral Bodies or the Bony Pelvis is Classic for Metastasis of Prostatic Neoplasia
Spondylitis
In a _____ View Radiograph of the Stomach, the Fundus will be Filled with Fluid and the Pylorus will be Filled with Gas
Left Lateral
*Left side of the Patient is on the Table
What is the Gas Filled Structure in this Ventral Dorsal View of the Abdomen

Pylorus
*Gas is mainly accentuated in the Pylorus but is spreading into other parts of the stomach

Pylorus is Normally Located on the ___ SIde of the Animal
Fundus is Normally Located on the ____Side of the Animal
Right
Left

Review of Ruptures with Excretory Urography
*Left Renal Ureter is Dilated with Leakage out of the Left Ureter- Tear or Rupture of the Ureter
*Bladder Rupture- Contrast Medium Leaking out of the Urinary Bladder. Urine has also probably Lead out leading to Loss of Serosal Detail

Diagnosis based on this Radiograph of the Small Intestine

Mechanical Ileus
*Foreign Material in the Small Intestine
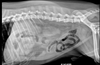
What is occuring in this Radiograph of the Abdomen?

Dystocia (Obstructed Labor)
*May be Related to Fetal Size
In a Patient in Right Lateral, where would we expect Contrast Medium (Barium) to Travel in the Stomach

Pylorus
*Pylorus is located on the Right Side of the Patient. In Right Lateral, Contrast will travel to the Right side of the Stomach
Diagnosis based on this Radiograph of the Stomach

Gastric Dilation Volvulus
*Pylorus and Fundus are in the Wrong Position

Diagnosis based on this Radiograph

Paralytic Ileus
*Sentinel Loop Sign!- Outlined in Purple (Duodenum)
*Gas in the Duodenum is commonly associated with Pancreatitis

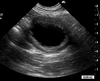
What Pathology can be diagnosed on this Ultrasoud?

Adrenomegaly

What can be Diagnosed based on this Positive Contrast Cystography of the Urinary Bladder

Wall Irregularity
Calculi

Small Area where the Ureters and Urethra Open into the Urinary Bladder
Trigone