Quiz 2 Flashcards
(71 cards)
Who came up with the idea of natural selection besides Darwin?
Alfred Russel Wallace
Phenotypic environment = ____ + _____
genes + environment
Natural selection acts on _______.
individuals
Traits which give fitness advantage in a given environment are called ________.
adaptations
Evolution is a ______ in the allele _______ in a population over _____.
change frequency time
Natural selection results in an increase in adaptive traits and decrease in ________ traits
maladaptive
J. Losos performed an experiment on lizards that colonized islands. What genus? What did he find?
- Anolis - Larger diameter perch branches leads to longer hind limb -
What Augustinian monk discovered heritable discrete packets?
Gregor Mendel
What are some of the commonalities between Russel’s theory and Darwin’s theory?
- Organisms make like organisms - Variation btwn. individuals - Heritable traits - More offspring are produced
Natural selection acts on _______.
individuals
Gregor Mendel helped establish that there are alternate forms of genes: ______. And some prevent the __________ of others.
alleles expression
________ ________ among individuals in a population is a result of the combined effects of genes and environment.
Phenotypic variation
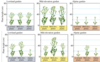
Adaptation by _________ to local environmental conditions in Potentilla glandulosa.
ecotypes
Bring plants from different places together, to grow them in the same environmental conditions.
Common Garden
Could a common garden experiment be done with animals?
It depends
Discuss the expected outcome of the P. glandulosa plant experiment and the actual outcome
- Plants will grow according to altitude
- But, all the plants grew different outside their home region
What was the deal with whitefish?
- It was discovered that there was Genetic Variation in Alpine fish.
- Whitefish move up into headwaters and became isolated
- Microsatellite DNA → populations are highly diverse and exhibit a high level of differentiation
What changes were discovered among Alpine (whitefish)?
Microsattelite DNA → diverse populations exhibit differentiation
What are the 5 factors to hold Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
- random mating
- no mutations
- large populations
- no immunology
- equitable fitness between all genotypes
Hardy-Weinberg states that allele frequencies will ______ ______ from generation to generation.
remain constant
What type of population distribution exists when the extreme phenotypes are selected against?
What does it prevent?
- Stabilizing selection
- Prevents changes in a population
What type of population distribution exists when 1 extreme is more represented?
Directional selection
What type of population distribution exists when 2 extremes are selected for?
What is the sciency word used to describe the distribution?
Disruptive Selection
Bimodal distribution
Can you have natural selection w/o heritability?
No


