Quantum Experiments to know for exam1 Flashcards
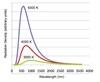
Blackbody radiation
- one of the first experiments that lead to quantum mechaincs
- started with observation that when you heat a metal it becomes red, then yellow and lastly white as temp. increases
- Kirchhoff’s law states that a body that radiates strongly at some wavelength absorbs radation strongly at the same wavelength
- black body radiator is a perfect absobrer/emitter of radiation
- graph shows that radiation of the body only depends on the temperature of the body
- hotter the temperature, greater radiation and lwower teh wavelength
What is interference?
Superposition of two or more waves resulting in an increase (constructive) or decrease (destructive) in amplitude
What happens when waves are “in phase”?
Constructive interferece, they have overlapping crests so wave with twice the amplitude results
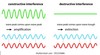
What happens when waves are out of phase?
Destructive interference, crests from one overlap with the trough of another, the waves cancle out eachother

What is diffraction?
When a wave encounters an obstacle or slit that is comparable in size to wavelength it bends around it

Describe the double slit experiment
- Combines concepts of diffraction and interference
- each slit acts as a new wave source and the 2 new waves interfere with eachother
- Result: series of bright and dark lines that can be viewed on a screen that was placed a short distance from the slits
- at the center of the screen, the waves interfere constructively to produce a bright line
- small distance away from center, 2 waves travel at slightly different distances which makes them out of phase (destrcutive interferece), which creates a dark line

Describe the photoelectric effect
- Observation that many metals emit electrons when light shines upon them
- classical theory predicted that the rate at which electrons would leave metal would increase as the intensity of the light increases
- other predictions of classical theory: when dim light was whone on metal there was expected to be a lag time, representing the minimum amount of time required for the dim light to transfer Energy to electron to dislodge it
- Actual results: observed threshold frequency which is the minimum amount of frequency of light to dislodge electron from the surface
–below threshold frequency, no electrons are emitted, no matter how long the light shines on surface
–intensity doesn’t effect release of electronm the frequency does (high freq. ejects electrons no matter the intensity, low frequency below threshold doesn’t eject electron)
What equations explain the photoelectric effect?
E=hv, v is frequency or E=hc/lambda
KE =hv-binding energy of electron
What is the emission spectrum?
The range of wavelengths emitted by a particular element that can be used to identify it
White light spectrum vs emission spectra of elements?
- White light specturm is continous
- emission spectra of elements are not continous, there are bright lines a specific wavelengths with complete darkness in between

What did Rydberg analyze?
Atomic spectra and developed equation that predicts wavelengths of hydrogen emission spectrum
-but his equation doesn’t explain why emission spectra of elements are discrete
*look at Rydberg equation
Bohr Model
Explains atomic spectrum for hydrogen
- e travels around nucleus in circular orbit
- e orbiting nucleus in stationary state emits no electron, it must transfer it lower or higher energy level
What is atomic spectroscopy overall?
Study of EM radation absorbed and emitted by electrons
-wave nature of particles


