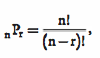Quant: Probability Concepts Flashcards
(19 cards)
Empirical, A Priori and Subjective Probabilities =
Empirical is based on analysis of past data
A Priori is based on reasoning/inspection
Subjective is based on personal judgment
Conditional Probability (Notation) =
probability of an event given another event’s occurence.
P(A|B), probability of A given B
Multiplication rule of probability =
To find joint probability
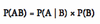
Addition rule of probability =
To find probability that at least one of two events will occur.
For mutually exclusive events P(AB) = 0, so P(A or B)=P(A) + P(B)
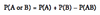
Total probability rule =
Used to determine the unconditional probability of an event, given conditional probabilities. The set of conditional events must be exhaustive and mutually exclusive.
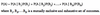
Rearranged multiplication rule, used for P(A|B) =
P(A|B) = P(AB) / P(B)
Independent events (notation) =
inependent if P(A|B) = P(A)
If not satisfied, events are dependent
Expected Value =
probability weighted average of the possible outcomes.
Use of conditional expectations in investment applications =
used to consider outcomes given other occurences (EBITDA for a firm if wider macro growth increases and improved consumer sentiment helps sales)
Covariance =
measures how two assets move together. Expected value of the product of the differences between the two random variables and their respective expected values.
- The covariance is a general representation of the same concept as the variance. That is, the variance measures how a random variable moves with itself, and the covariance measures how one random variable moves with another random variable.
- The covariance of RA with itself is equal to the variance of RA; that is, Cov(RA,RA = Var(RA) .
- The covariance may range from negative infinity to positive infinity.
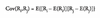
Covariance for a joint probability model =
probability weighted average of the products of the random variable’s deviations from their means for each outcome. The probability weighting just provides an expected value WEIGHTED BY PROBABILITY OF AN INITIAL OUTCOME.
p214 Schweser

Correlation Coefficient =
Correlation measures the strength of the linear relationship between two variables (-1 to 1)
Not that Corr(R1,R2) can be notated as p(R1,R2)

Expected Return (for a portfolio) =
sum of market weighted expected returns for each individual holding in the portfolio.

*Portfolio Variance (1) =

*Portfolio Variance (2) =
The formula is expanded and then simplified. Note that Cov(Ra, Ra) is reduced to σ2(Ra), as covariance of a variable with itself is its VARIANCE (standard deviation squared)

Bayes’ Formula (updated probability) =
Given P(B), P(A|B) and P(A|Bc) we can calculate P(B|A)
IE. we know the chances of a stock having a positive return given the fact that the market goes up. We can find out the updated probability that the market will go up.

Labelling =
Where n = number of items, n1 = number of items with label 1, and so on.
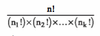
Combinations =
k (or n) = 2, as in there are two labels, chosen and not chosen. Formula is for calculating the number of ways to choose r items from n (binomial formula)
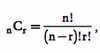
Permutations =
How many different groups of size r in a specific order can be chosen from n objects.