prolonged labour Flashcards
Define a prolongiued pregnancy
beyond the EDD by 2 weeks
incidence of prolonged pregnancy
10%
causes of prolonged pregnancy
- wrong EDD
- Meridatary
- Maternal factors
- primiparous
- previous prolonged
- over 40 y/o
- Fetal factors
- congenital abnormalities
- macrosomia
- Placental factors
- any abnormalities
dg of prolonged pregnancy
- Ask about Menstrual history for EDD
- check weight: 11-12kg normal
- Girth of the abdomen should be over (95cm)
- US
- observe placenta wuality and uteroplacental blood flow
- amniocentesis
- observe amount of amniotic fluid
what are the potential complication of prolonged pregnancy
MATERNAL
FETAL
shoulder dystocia
post maturity syndrome
meconium aspiration syndrome,
fetal malnutrition
stillbirths
.
management of prolonged pregnancy
induction of labour at 41 weeks
OR
fetal surveillance till 42 weeks
why IOL at 41 weeks
reduces the risk of still birth
when is the potential for still birth highest
around 1 week post term
what does the initiation of IOL in post term preg depend on
if it’s a complicated or uncomplicated case
criteria for complicated prolonged pregnancy
fetal post maturity syndrome plus high RF e.g.
- elderly primiparous
- preeclampsia
- RH incompatibility
- oligohydramnious
management of complicated prolonged pregnancy
elective C/S
how is IOL performed in uncomplicated prolonged pregnacy at 41 weeks if the cervix is unfavourable
Vaginal prostaglandins
- prepare the cervix for labour by ripening it,
- aid contraction of the smooth muscle of the uterus.
- DOSE
- tablet/gel regimen: 1 cycle = 1st dose, plus a 2nd dose if labour has not started 6 hours later.
Pessary regimen: 1 cycle = 1 dose over 24 hours.
tablet vaginal prostaglandin dose
1 cycle = 1st dose, plus a 2nd dose if labour has not started 6 hours later.
Pessary regimen:
1 cycle = 1 dose over 24 hours.
what is the max reccomended dose of vaginal prostaglandins
maximum of one cycle in 24 hours (IOL can sometimes take multiple days).
how prolonged pregnancy labour different than normal labour
- longer than normal d/2 larger baby
- requires more analgesia
- potential for shoulder dystocia
what if IOL is declined or fetal monitoring is decided
2x/ weekly CTG monitoring and USS with amniotic fluid measurement to I/D fetal distress.
fetal distress requires emergency C/S
what kind of monitoring is required before induction of labour
- Cervical ripeness
- CTG
how is cervical ripeness measured
BISHOP SCORE
what is the Bishop score

an assessment of ‘cervical ripeness‘ based on measurements taken during vaginal examination.
It is checked b4 and during induction to assess progress of prostaglandins
when is cervical ripeness measured
- 6 hours post-_tablet/gel_,
- 24 hours post-pessary):
meaning of Bishop Score ≥ 7
suggests the cervix is ripe or ‘favourable’
high chance of a response to interventions made to induce labour (i.e. induction of labour is possible).
meaning of Bishop Score of <4
suggests that labour is unlikely to progress naturally and prostaglandin tablet/gel/pessary will be required
management if Failure of a cervix to ripen despite use of prostaglandins
caesarean section.
list the methods of IOL
VAMoose
Vaginal Prostaglandins
Amniotomy
Membrane Sweep
what is an amniotomy
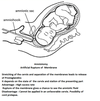
where the membranes are ruptured artificially using an instrument called an amnihook.
- releases prostaglandins in an attempt to expedite labour
- only performed when the cervix has been deemed as ‘ripe’
- infusion of artificial oxytocin (Syntocinon), to increase the strength and frequency of contractions

when is amniotomy used
if the use of prostaglandins are contraindicated e.g. high risk of uterine hyperstimulation.
what is a MEMBRANE SWEEP?

inserting a gloved finger through cervix and rotating it against the fetal membranes, aiming to separate the chorionic membrane from the decidua.
The separation helps to release natural prostaglandins in an attempt to kick-start labour.
when is membrane sweep is offered
nulliparous women 40 and 41 weeks
multiparous women : 41 weeks
what is IOL
Induction of labour (IOL) is the process of starting labour artificially.
indications of IOL
- Prolonged Gestation
- Premature Rupture of Membranes
- Maternal Health Problems
- hypertension, pre-eclampsia, diabetes and obstetric cholestasis.
- Fetal Growth Restriction
- Intrauterine Fetal Death
C.I of IOL

what is POST MATURITY SYNDROME
complication of prolonged pregnancy characterized by
- wrinkled, patchy scaly skin on palms & soles
- overgrown nails
- long thinning of the body
- severe growth resitriction
- advanced maturity w/ an alert baby
what is teh pathophys behind post maturity syndrom
- release of proapoptotic genes e.g. KISSEPTIN up regulated in post-term placenta =>
- placental apoptosis occurs at 41-42 wks =>
- reduction of fetal oxygenation & blood supply =>
-
↓ amniotic fluid vol
- => meconium release
- =>Meconium aspiration syndrome
- cord compression
- => meconium release
- both lead to FETAL DISTRESS
what is meconium aspiration syndrome
how does the baby appear after felivery of prolonged labour
- Static growth or potentially macrosomia
- Oligohydramnios
- Reduced fetal movements
- Presence of meconium
- Signs of meconium staining e.g. on nails
- Dry / flaky skin with reduced vernix
- ( white substance found coating the skin of newborn babies.)


