Probability Theory Flashcards
What is the Markov assumption?
That Pr(Y_i = y_i | y_i-1, y_i-2, … ) = Pr(y_i | y_i-1)
Define marginal distribution
Joint distribution when other variable is ‘integrated out’
Define conditional distribution
Joint distribution where other variable takes a specific value
What is the definition of a moment
Expectation of a function of a random variable E[g(x)]
Define kurtosis
E [( (X - mean)/stdev )^4] = E [(X - mean)^4] / (E [(X-mean)^2] )^2
Define covariance
E [ (X - E(X)) (Y - E(Y) )
Cov(a + Bx)
B cov(X) B’
What is the martingale property?
E (Y_i | Y_i-1, Y_i-2, … ) = Y_i-1,
Define convergence in distribution
If there exists a CDF F where Fn(y) -> F(y) for all y, where F is continuous, then F is the limiting CDF of {Yn} and Yn converges in distribution to Y
Define convergence in probability

What is the Slutsky theorem?

What is the weak law of large numbers?

What is the Lindenberg-Levy Central Limit Theorem?
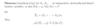
What is the likelihood function
Start with the density function. Hold the observation fixed while let the parameters be variable. Take the product across all observations
What is the score in ML estimation?
The derivative of the log-likelihood w.r.t. parameters
What is the Central Limit Theorem of MLEs?

What is the information equality?

What are the conditions for an estimator to be consistent?
Bias must go towards zero
Variance around true value must be going towards zero
What does the Probability transform property say
That applying the true CDF to a continuously distributed variable will give a variable that is uniformly distributed on 0 to 1
What is the density of an exponential distribution?
lambda * e^(-lambda * x)


