Pro/Euk Cell structures and types Flashcards
(110 cards)
What organisms are represented as Prokaryotes?
Bacteria and Archaea
What organisms are represented as Eukaryotes?
Protists, Fungi, Animals, Plants
All Eukaryotes are multicellular except
protists and yeasts
What is the main component of the cell wall of prokaryotes?
peptidoglycan
What are the main components of the cell walls of eukaryotes?
Cellulose-Plants Chitin-Fungi and Arthropods No cell wall- animals
How do prokaryotic cells divide?
Binary fission
How do eukaryotic cells divide?
Mitosis & Meiosis
What are the 4 universal components of cells?
A cytoplasm, DNA, Plasma Layer, Ribosomes
Is a ribosome a organelle?
no
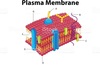
What is A

The prokaryotic Flagellum
What is B

The inclusion body/Food granule
What is C?

Ribosomes
What is D?

pilus
What is E?
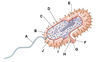
The nucleoid
What is F?

Capsile layer/Slime Layer
What is G?

The cell wall
What is H?

The plasma Layer
What is I?

The cytoplasm
What is J?
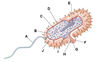
The plasmid (DNA extrachromosomal)
Describe the Chromosome of a Prokaryotic cell.
(Physical/Function)
Located in the Nucleoid of the cell
It is a bundle of DNA,RNA, and associated proteins.
Genetic blueprint of the cell
Not inclosed in a membrane (no nucleus)
Describe the Plasmid of a Prokaryotic cell.
(Physical/Function)
A circular extrachromosomal(outside of the chromosome) DNA in some Bacteria
Not vital
encodes genes necessary for survival
up to 12 plasmids
Allow antibiotic resistance
Describe the inclusion body of a Prokaryotic cell.
(Physical/Function)
Granules
SOME Used for the storage of glycogen
SOME used as gas vesicles for flotation
*bacteria fat*
Describe the endospore of a Prokaryotic cell.
(Physical/Function)
Only found in some Bacillis and Clostridium bacteria
The toughest of all micro structures
Composed of layers of Clacium and Dipicoinic acid
Survives adverse env. conditions
can live up to 100 years
A survival structure
What does the calcium component of the endospore provide in terms of protection?
Heat protection