Presentation and Complications of T2DM Flashcards
What is the role of glucose?
- Fuel required to sustain life - it is the key source of energy in aerobic respiration.
- Critical in the production of protein and fat.
- Energy generated by the production of ATP through the oxidisation of glucose to produce CO2 and water.
What is the normal range for glucose?
At what level does blood glucose define diabetes?
- Blood glucose is maintained in a narrow range.
- Normal fasting glucose is between 3.0-5.5 mmol/L.
- Fasting glucose above 7.0 mmol / L defines diabetes.
- 5.6-6.9 is called impaired fasting glycaemia
What is the role of the pancreas in glucose homeostasis?
- Endocrine and exocrine function.
- Exocrine function:
- Releases digestive enzymes that break down foodstuffs e.g. amylase, triptase, lipase.
- Endocrine function:
- Pancreatic islets are responsible for the endocrine function producing insulin and glucagon.
- Insulin to lower glucose from β cells.
- Glucagon to increase glucose α cells.
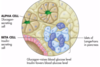
What do the alpha cells of the pancreatic islets secrete?
Glucagon
Raises blood glucose level
What do the beta cells of the pancreatic islets secrete?
Insulin
Lowers blood glucose level
What is the role of the liver in glucose homeostasis?
- The liver has an important role in maintaining glucose in the fasting state.
- In the fasting state, glucose release is driven by glucagon - glycogenolysis.
What is the role of muscle in glucose homeostasis?
- Muscle has a small store of glycogen.
- Insulin promotes glucose uptake into the muscle.

Describe the role of insulin.
Removes glucose from the circulation post-prandially into tissues for energy use or into body stores.
Describe the role of glucagon.
Facilitates the release of glucose from stores (liver, muscle, fat) and into the circulation during the fasting state.
Describe how the brain uses glucose.
The brain needs a constant supply of glucose to maintain function but has no glucose stores and no insulin receptors, so will take up whatever glucose is available.
What is diabetes?
Persistent hyperglycaemia related to insulin deficiency or insulin resistance or a combination of both.
What is the criteria for diagnosis of DM?
- Diabetes is diagnosed when:
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 7 mmol/L
- OR
- Random plasma glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L (or ≥ 11.1 mmol/L after oral glucose load)
- OR
- HbA1c ≥ 48 mmol/mol
- HbA1c should not be used to diagnose T1DM or gestational diabetes
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 7 mmol/L
Why is the incidence of diabetes increasing?
- Ageing population
- Changes in diagnostic tests
- Better survival
- Changes in lifestyle and diet
- Why is obesity on the rise?
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Increased calorie consumption along with a change in the types of foods we consume - high fat, high sugar foods are readily available to everyone
What are the symptoms of hyperglycaemia?
- Polyuria
- Blurred vision
- Tiredness
- Extreme thirst
- Weight loss
- Itchy or sore genitals
Describe the clinical manifestations of T1DM.
- Acute symptoms
- 3 Ps
- Polyphagia
- Polydipsia
- Polyuria
- Weight loss
- Ketonaemia / ketonuria
- Fatigue
- Visual changes
- Dehydration / electrolyte disturbance
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
Describe the clinical manifestations of T2DM.
- Symptoms usually more insidious.
- Often incidental detection during routine checks.
- Recurrent infections / delayed wound healing / recurrent candidiasis.
- Tiredeness / lethargy.
- Visual disturbance.
What are the risk factors for T2DM.
- Age
- Over 40s are more likely to develop T2DM - risk increases with age, although incidence in younger people is rising.
- Ethnicity
- Afro-Caribbean or South Asian are more likely to develop T2DM and they are likely to develop it younger and at a lower BMI (‘at risk’ group classed as >25 years).
- Genetic factors
- 50% may have FHx, however polygenetic inheritance.
- Steroid therapy / antipsychotic medications
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
What are the microvascular complications of diabetes?
- Retinopathy - background retinopathy or proliferative retinopathy.
- Can cause damage to the tiny blood vessels which supply the retina.
- Early treatment with laser can prevent damage to sight.
- Protective - good glycaemic control, annual eye screening, good BP control.
- Nephropathy
- Damage to the tiny blood vessels which supply the kidneys.
- Hyperglycaemia and hypertension damages glomerular basement membrane and causes microaneurysm formation.
- Leading cause of renal failure.
- 20-25% of patients may develop nephropathy.
- Protective - good glycaemic control, annual urine screen and BP control (<130/80). ACE-I can prevent progression.
- Neuropathy
- Chronic hyperglycaemia damages blood vessels supplying nerves.
- Typical = glove and stocking distribution. Symptoms are tingling, numbness and pain.
- Peripheral neuropathy can affect sensation and motor function (e.g. to feet).
- Autonomic neuropathy can affect digestion (gastroparesis), cardiac function, BP.
- Prevention - glycaemic control, BP control, smoking cessation, control of cholesterol levels. Foot screening.
What are the macrovascular complications of diabetes?
- Increased risk of:
- Acute coronary artery syndrome / MI
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Peripheral arterial disease
- Focus should be on managing risk factors associated with atherosclerosis.
Describe how diabetes increases the risk of CV disease, MI and cerebrovascular ischaemia.
- Atherosclerosis in blood vessels can damage heart and circulation.
- Cholesterol target usually <4.0 mmol.
- Balance between HDL and LDL cholesterol is important.
- BP target <130/80.
- Smoking causes:
- Increased risk of angina
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Poor circulation
- Diabetes + smoking leads to even higher risk.
What are the causes of foot problems in diabetes?
- Foot problems can be due to neuropathy and / or ischaemia (peripheral arterial disease).
- Risk of ulceration, infection and necrosis (requiring amputation).
-
Foot screening:
- Foot examination
- Sensation tests - monofilament
- Palpation of pulses
- Temperature
Describe the correlation between diabetes and mental health.
- People with diabetes are more likely to have anxiety and depression as a consequence of living with a chronic illness.
- Eating disorders are more common.
- There is a role for screening for psychological symptoms.
- HADS - Hospital Anxiety and Depression Score.
- EAT and BITE questionnaires used for disordered eating.
What is involved in diabetes annual review?
- Every patient with diabetes should be offeren an annual review within their GP practice in addition to annual retinal screening.
- Annual review determines risk / presence of complications through assessment of HbA1c, weight, BP, smoking status, urinary ACR, creatinine, total cholesteroland a foot screen.
- Review of wellbeing.
What is the role of HbA1c in assessing diabetes control?
- HbA1c gives an average of what blood glucose has been over an8-12 week period.
- The target is less than 58 (which means that daily blood glucose is <4-7mmols.
- An HbA1c of <58 means risk of DM complications decreases.

How can the risks of diabetes be reduced?
- Blod glucose control
- BP control
- Lipid lowering
- Diet and lifestyle factors
- Smoking cessation
- Regular review
What is the glycaemic index?
- Refers to how quickly carbohydrate is digested and absorbed as glucose into the bloodstream.
- Low ranked foods are slowly absorbed.
- High ranked foods are quickly absorbed.


