Pregnancy, Childbirth and Puerperium II Flashcards
Postpartum urinary retention is typically related to bladder […].
Postpartum urinary retention is typically related to bladder atony.
temporary and reversible; confirmed by > 150 mL of urine upon urethral catheterization

Preeclampsia is defined as hypertension with […] or […] after the 20th week of gestation.
Preeclampsia is defined as hypertension with proteinuria or end-organ dysfunction after the 20th week of gestation.
patients with evidence of end-organ damage have preeclampsia with severe features

Preeclampsia is defined as hypertension with proteinuria or end-organ dysfunction after the […] week of gestation.
Preeclampsia is defined as hypertension with proteinuria or end-organ dysfunction after the 20th week of gestation.
patients with evidence of end-organ damage have preeclampsia with severe features

Preterm labor refers to regular contractions causing cervical dilation and/or effacement at
Preterm labor refers to regular contractions causing cervical dilation and/or effacement at < 37 weeks gestation.

Risk factors for placenta accreta include history of […] or […] and advanced maternal age.
Risk factors for placenta accreta include history of cesarean delivery or dilation & curettage and advanced maternal age.
Second stage arrest of labor is defined as no fetal descent after pushing for > […] hours (nulliparous) or > […] hours (multiparous).
Second stage arrest of labor is defined as no fetal descent after pushing for > 3 hours (nulliparous) or > 2 hours (multiparous).

Spontaneous abortion is unprovoked pregnancy loss at
Spontaneous abortion is unprovoked pregnancy loss at < 20 weeks gestation and is a common cause of first trimester bleeding.

Spontaneous abortions are most commonly the result of […] abnormalities.
Spontaneous abortions are most commonly the result of fetal chromosomal abnormalities
also associated with congenital abnormalities.
(e.g. teratogens) and mullerian anomalies (e.g. uterine septum)
Symptomatic maternal luteoma puts a female fetus at a high risk of […].
Symptomatic maternal luteoma puts a female fetus at a high risk of virilization.

Symptoms of magnesium toxicity include somnolence, respiratory […], and […]-reflexia.
Symptoms of magnesium toxicity include somnolence, respiratory depression, and hypo-reflexia
more mild symptoms include nausea, flushing, and headache

Symptoms of magnesium toxicity include […]-calcemia and cardiac arrest.
Symptoms of magnesium toxicity include hypo-calcemia and cardiac arrest.
more mild symptoms include nausea, flushing, and headache; hypocalcemia due to temporary suppression of PTH

Systemic lupus erythematosus flare during pregnancy is distinguished from preeclampsia by the presence of […] on urinalysis and classic symptoms of SLE (e.g. joint pain, malar rash).
Systemic lupus erythematosus flare during pregnancy is distinguished from preeclampsia by the presence of RBC casts on urinalysis and classic symptoms of SLE (e.g. joint pain, malar rash).
other findings consistent with SLE flare include decreased complement levels and increased ANA titers

The diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is made by a pregnancy test combined with […].
The diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is made by a pregnancy test combined with transvaginal ultrasound.
typically presents with a triad of vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and adnexal tenderness

The first-trimester combined test analyzes the risk for fetal trisomy 18 & 21 by measuring maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein and […], as well as […] translucency on ultrasound.
The first-trimester combined test analyzes the risk for fetal trisomy 18 & 21 by measuring maternal serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein and beta-hCG, as well as nuchal translucency on ultrasound.
performed between 9 - 13 weeks of gestation; not diagnostic

The major risk factor for shoulder dystocia is fetal […].
The major risk factor for shoulder dystocia is fetal macrosomia.
i.e. fetal weight > 4.5 kg (9.9 lb); conditions that predispose to macrosomia include post-term pregnancy, maternal obesity, gestational diabetes, and excessive weight gain during pregnancy

The optimal fetal positioning is occiput […].
The optimal fetal positioning is occiput anterior.
deviations from this position may cause arrest of the second stage of labor

The presence of amniotic fluid may be detected with the […] and/or […] test.
The presence of amniotic fluid may be detected with the nitrazine and/or fern test
a positive nitrazine test turns the test strip blue.

Theca lutein cysts arise due to ovarian hyperstimulation secondary to markedly elevated […] levels.
Theca lutein cysts arise due to ovarian hyperstimulation secondary to markedly elevated beta-hCG levels.
e.g. complete hydatidiform mole, multifetal gestation

Treatment for eclampsia includes blood pressure control, […] for seizure prevention, and expedient delivery.
Treatment for eclampsia includes blood pressure control, magnesium sulfate for seizure prevention, and expedient delivery.
if magnesium sulfate does not control seizures, diazepam or phenytoin are second-line options

Universal screening for group B Streptococcus colonization is typically done by vaginal and rectal culture at […] - […] weeks gestation.
Universal screening for group B Streptococcus colonization is typically done by vaginal and rectal culture at 35 - 37 weeks gestation
the result is most accurate within 5 weeks of the anticipated delivery.

Uterine rupture classically occurs in a woman with prior […].
Uterine rupture classically occurs in a woman with prior uterine surgery.
e.g. prior cesarean delivery or myomectomy; inelastic scar may not be able to withstand labor contractions
What acid-base disturbance is physiological during normal pregnancy?
Chronic respiratory alkalosis
due to increased minute ventilation

What are the current recommendations for influenza vaccination during pregnancy?
All pregnant women should receive the inactivated (injectable) influenza vaccine
the intranasal (live) influenza vaccine is contraindicated

What are the first-line agents (3) for maternal hypertensive crisis?
nifedipine, hydralazine, or labetalol

What are the most common causes (2) of hyperandrogenism in pregnancy?
luteomas and theca luteum cysts
may manifest as new-onset hirsutism and/or acne

What are the most common causes of acute cervicitis?
Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection

What are the target 1-hour and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose levels in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus?

What changes detected by maternal quadruple screen are indicative of trisomy 18 (Edward syndrome)?
AFP: […]
Estriol: […]
beta-hCG: […]
Inhibin A: […]
AFP: decreased
Estriol: decreased
beta-hCG: decreased
Inhibin A: normal
decreased hCG and normal inhibin A help differentiate trisomy 18 from trisomy 21 (increased hCG and inhibin A)

What changes detected by maternal quadruple screen are indicative of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)?
AFP: […]
Estriol: […]
beta-hCG: […]
Inhibin A: […]
AFP: decreased
Estriol: decreased
beta-hCG: increased
Inhibin A: increased
elevated hCG and inhibin A help differentiate trisomy 21 from trisomy 18 (decreased hCG, normal inhibin A)

What complication of shoulder dystocia manifests as a “claw hand”, an impaired grasp reflex, and Horner syndrome in a newborn?
Klumpke palsy (due to lower trunk injury involving C8 and T1)

What complication of shoulder dystocia manifests as a “Waiter’s tip” with an impaired biceps/moro reflex in a newborn?
Erb-Duchenne palsy (due to upper trunk injury involving C5 and C6)
most common type of brachial plexus injury

What exercise regimen is recommended for healthy women with uncomplicated pregnancies?
20 - 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise on most or all days of the week
contact sports and activities with high fall risk should be avoided; women with risk for preterm delivery, preeclampsia, or severe cardiopulmonary disease should also avoid exercise

What is the best screening test for gestational diabetes mellitus?
50g 1-hour glucose challenge
more sensitive than a fasting glucose

What is the first step in evaluating risk of preterm delivery in a patient with a history of cervical surgery (e.g. cold knife conization)?
transvaginal ultrasound measurement of cervical length in the 2nd trimester
short cervical length is a strong predictor of preterm labor

What is the first-line intervention for a woman in the first stage of labor with recurrent variable decelerations and moderate variability on fetal heart tracing?
Maternal repositioning (e.g. left lateral decubitus)
amnioinfusion is a possible second-line intervention; assisted vaginal delivery could be indicated if the patient was fully dilated

What is the first-line treatment for magnesium toxicity?
Calcium gluconate
magnesium becomes toxic at concentrations > 8 mg/dL

What is the initial management for a hemodynamically unstable pregnant patient that presents with abruptio placentae following a motor vehicle accident?
IV fluid resuscitation and left lateral decubitus positioning
left lateral decubitus position displaces the uterus off the aortocaval vessels and maximizes cardiac output
What is the initial screening test of choice for fetal aneuploidy in pregnant women with high-risk factors (e.g. age > 35)?
Cell-free fetal DNA testing
higher sensitivity and specificity for detecting aneuploidies than both the first-trimester combined test and second-trimester quadruple screen; not diagnostic (must confirm with CVS or amniocentesis)

What is the likely diagnosis in a hemodynamically unstable patient with a gestational sac in the uterine cornu and free fluid in the posterior cul-de-sac on transvaginal ultrasound?
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
i.e. a cornual or interstitial ectopic pregnancy; often presents as abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding

What is the likely diagnosis in a laboring patient with > 6 cm dilation that experiences abnormally slow cervical dilation?
Protraction of active labor
the active stage of labor typically begins at > 6 cm dilation

What is the likely diagnosis in a laboring patient with > 6 cm dilation that experiences no further dilation for 4 hours despite adequate contractions?
Arrest of active labor
arrest of active labor is also diagnosed if there is no cervical change for > 6 hours with inadequate contractions (< 200 MVUs in a 10-minute period)

What is the likely diagnosis in a newborn with thin, loose skin, a thin umbilical cord, and a wide anterior fontanel?
Fetal growth restriction
risk factors include maternal hypertension, gestational diabetes, genetic abnormalities, and congenital infection

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that is 6 hours postpartum that presents with inability to void, diffuse lower abdominal tenderness, and persistent urinary dribbling?
Postpartum urinary retention
risk factors include primiparity, regional anesthesia, operative vaginal or cesarean delivery, and perineal injury

What is the likely diagnosis in a patient that presents one week after an elective abortion with fever, vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, and purulent vaginal discharge? Pelvic ultrasound reveals a thickened endometrial stripe.
Septic abortion
pelvic examination typically reveals an enlarged, boggy, tender uterus

What is the likely diagnosis in a postpartum patient on post-operative day 2 that presents with fever, uterine tenderness, and purulent lochia?
Postpartum endometritis
most common cause of postpartum fever

What is the likely diagnosis in a postpartum patient on post-operative day 5 with a fever that is unreponsive to broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy with a negative infectious workup?
Septic pelvic thrombophlebitis
diagnosis of exclusion; due to an infected thrombosis of the deep pelvic or ovarian veins

What is the likely diagnosis in a postpartum woman that presents with lactation failure, amenorrhea, fatigue, and hypotension for months after a spontaneous vaginal delivery complicated by uterine atony?
Sheehan syndrome
symptoms are due to hypopituitarism secondary to ischemic infarction and necrosis of the pituitary gland following massive obstetric hemorrhage

What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant patient that develops encephalopathy, nystagmus, and gait ataxia after several days of hyperemesis gravidum?
Wernicke encephalopathy
secondary to thiamine deficiency

What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant patient that presents with painless third-trimester bleeding with a normal fetal heart tracing?
Placenta previa
painless bleeding helps rule out placental abruption; normal FHR helps distinguish placenta previa from vasa previa

What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant patient that presents with painless third-trimester bleeding with bradycardia on fetal heart tracing?
Vasa previa
fetal bradycardia is an important distinguishing feature from placenta previa; occurs because the hemorrhage is of fetal origin (versus maternal origin in placenta previa)

What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant woman at 10 weeks gestation that presents with hyperemesis gravidarum? Pelvic ultrasound reveals an intrauterine gestation enlarged for gestational age and bilateral 10-cm, multilocular ovarian masses.
Theca lutein cysts (secondary to a complete hydatidiform mole)
occurs due to ovarian hyperstimulation from markedly elevated beta-hCG levels

What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant woman at 35 weeks gestation that experiences irregular uterine contractions (~3-5 per hour) with a closed cervix on pelvic examination?
False labor
characterized by mild, irregular contractions (Braxton Hicks contractions) that cause no cervical change

What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant woman at 35 weeks gestation that has experienced leakage of fluid over the past two days? The fluid is nitrazine-positive.
Preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM)
defined as rupture of membranes at < 37 weeks gestation (preterm) and before labor has begun (premature)
What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant woman at 35 weeks gestation that presents with abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding and a firm, tender uterus?
Abruptio placentae (placental abruption)
also may have high-frequency, low-intensity uterine contractions; bleeding may be concealed

What is the likely diagnosis in a pregnant woman with preeclampsia that develops sudden-onset dyspnea, hypoxia, and crackles?
Pulmonary edema
rare but life-threatening complication of severe preeclampsia

What is the likely diagnosis in a sexually active woman that presents with postcoital bleeding and mucopurulent discharge with a friable cervix on pelvic examination?
Acute cervicitis
less common symptoms include dysuria, dyspareunia, and vulvovaginal pruritus

What is the likely diagnosis in a stillborn fetus with multiple limb fractures and a hypoplastic thoracic cavity?
Type II osteogenesis imperfecta
due to mutations in type 1 collagen; type II OI is the most severe type and often manifests as fatal perinatal disease

What is the likely diagnosis in a woman that develops abdominal pain and hemorrhagic shock after failing to deliver the placenta? There is a smooth, round mass protruding through the vagina.
Uterine inversion
risk factors include nulliparity, fetal macrosomia, placenta accreta, and rapid labor & delivery

What is the likely diagnosis in a woman with a history of transient ischemic attacks and recurrent miscarriages?
Antiphospholipid syndrome
diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of at least one of the antiphospholipid antibodies; hypercoaguable state results in increased risk for placental thrombosis and miscarriage

What is the likely diagnosis in an adolescent girl at 15 weeks gestation that presents with symptoms of preeclampsia with severe features?
Hydatidiform molar pregnancy
the presence of preeclampsia with severe features at < 20 weeks gestation can be a complicati

What is the likely diagnosis in an afebrile patient that recently delivered a macrosomic baby and now presents with sharp lower midline abdominal pain that radiates to the legs and is exacerbated by ambulation?
Pubic symphysis diastasis
physiologic diastasis normally occurs during pregnancy but traumatic delivery (e.g. to a macrosomic baby) can result in symptomatic diastasis

What is the likely diagnosis in an afebrile postpartum woman that presents with bilateral, symmetric warmth and tenderness of the breasts 3 days after delivery?
Breast engorgement
common 3-5 days after delivery when colostrum is replaced by milk; improves with breastfeeding

What is the likely diagnosis in an afebrile postpartum woman that presents with unilateral firmness and tenderness of the breast?
Plugged duct
differentiated from mastitis by the lack of fever and systemic symptoms and from galactocele by the presence of pain

What is the likely diagnosis in an African-American woman at 20 weeks gestation that presents with new-onset hirsutism and acne? Pelvic ultrasound reveals an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates and bilateral 8-cm solid ovarian masses.
Luteoma
versus theca luteum cysts, which typically arise due to high hCG levels (e.g. molar pregnancy or multiple gestation)

What is the likely diagnosis in an intrapartum patient that presents after >18 hours of membrane rupture and prolonged labor with fever and tachycardia? Fetal heart tracing demonstrates fetal tachycardia.
Chorioamnionitis (intra-amniotic infection)
intra-amniotic infection caused by migration of vaginal or enteric flora through the cervix, typically in a patient with premature or prolonged rupture of membranes; intrapartum fever is a distinguishing feature

What is the likely diagnosis in an obese, multiparous pregnant woman at 34 weeks gestation that presents with intermittent leakage of clear fluid and a negative nitrazine/fern test?
Stress urinary incontinence
differentiated from rupture of membranes by negative nitrazine/fern tests and absence of vaginal pooling

What is the most common cause of a non-reactive non-stress test?
Fetal sleep cycle
vibroacoustic stimulation may be used to awaken the fetus; sleep cycles can last as long as 40 minutes therefore a non-reactive test should be extended to 40 - 120 minutes
What is the most common cause of primary postpartum hemorrhage?
Uterine atony
results from failure of the uterus to contract and compress the placental site blood vessels
What is the most common cause of second stage arrest of labor?
Fetal malposition (e.g. occiput transverse)
the optimal fetal position is occiput anterior

What is the most common risk factor for placental abruption?
Hypertension
other important risk factors include maternal trauma and cocaine use

What is the most common site of implantation for ectopic pregnancy?
Fallopian tube
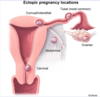
What is the most likely cause of postpartum hemorrhage in a patient that presents with profuse vaginal bleeding with a soft, enlarged uterus on pelvic examination? Ultrasound reveals a thin endometrial stripe.
Uterine atony
risk factors include prolonged labor, fetal weight > 4000g, induction of labor, and operative vaginal delivery
What is the next step in management after IV lines have been placed in a woman with uterine inversion with a retained placenta?
Manual replacement of the uterus
should be performed prior to placent



