Pregnancy, Childbirth and Puerperium I Flashcards
A non-stress test is considered reactive (normal) if there are at least […] in 20 minutes.
A non-stress test is considered reactive (normal) if there are at least 2 accelerations in 20 minutes.
accelerations are increases in heart rate > 15 beats/min above baseline lasting for at least 15 seconds; due to fetal sympathetic nervous system activity, which develops around 26 - 28 weeks

A […] fetal fibronectin test prior to term is an indicator of high risk for preterm delivery.
A positive fetal fibronectin test prior to term is an indicator of high risk for preterm delivery.
typically performed in patients with contractions at < 34 weeks gestation; fetal fibronectin levels are high until 20 weeks gestation and thus are not a reliable marker of preterm delivery in early pregnancy

Adequate contractions are defined as generation of > […] Montevideo units (MVUs) in 10 minutes.
Adequate contractions are defined as generation of > 200 Montevideo units (MVUs) in 10 minutes.
measured via an intrauterine pressure catheter

After instructing the laboring patient to breath and not push, management of shoulder dystocia includes […] and application of suprapubic pressure.
After instructing the laboring patient to breath and not push, management of shoulder dystocia includes flexing the hips toward the abdomen (McRoberts manuever) and application of suprapubic pressure.

these maneuvers relieve ~50% of shoulder dystocias with no further intervention
After instructing the laboring patient to breath and not push, management of shoulder dystocia includes flexing the hips toward the abdomen (McRoberts manuever) and application of […].
After instructing the laboring patient to breath and not push, management of shoulder dystocia includes flexing the hips toward the abdomen (McRoberts manuever) and application of suprapubic pressure.
these maneuvers relieve ~50% of shoulder dystocias with no further intervention

All pregnant women should be screened for gestational diabetes mellitus at […] - […] weeks gestation.
All pregnant women should be screened for gestational diabetes mellitus at 24 - 28 weeks gestation.
placental hormones in the 2nd and 3rd trimester create increased maternal insulin resistance; patients with risk factors (e.g. obesity, previous GDM) should be screened earlier and re-screened at 24-28 weeks if negative

Amniocentesis may be performed between […] to […] weeks.
Amniocentesis may be performed between 15 to 22 weeks.
diagnostic for aneuploidies

Amphetamine abuse during pregnancy is associated with fetal […]. (size)
Amphetamine abuse during pregnancy is associated with fetal growth restriction. (size)
other complications include preterm delivery, preeclampsia, placental abruption, and intrauterine fetal demise

An abnormal biophysical profile score (0 - 4) is consistent with […] due to placental dysfunction.
An abnormal biophysical profile score (0 - 4) is consistent with fetal hypoxia due to placental dysfunction.

Antenatally diagnosed placenta accreta is delivered by planned […].
Antenatally diagnosed placenta accreta is delivered by planned cesarean hysterectomy.
Can a non-reactive non-stress test effectively rule in fetal acidemia?
No
a non-reactive NST has a low positive predictive value for fetal acidemia (high rate of false positives)
Can a reactive non-stress test effectively rule out fetal acidemia?
Yes
a reactive NST has a high negative predictive value for fetal acidemia

Cell-free fetal DNA testing can be ordered at > […] weeks gestation.
Cell-free fetal DNA testing can be ordered at > 10 weeks gestation.

Chorionic villus sampling may be performed between […] to […] weeks.
Chorionic villus sampling may be performed between 10 to 13 weeks.
earlier than amniocentesis, but higher risk of fetal loss; diagnostic for aneuploidies
Complications of inadequate weight gain during pregnancy include […] and preterm delivery.
Complications of inadequate weight gain during pregnancy include fetal growth restriction and preterm delivery.

Complications of oxytocin include […]-natremia, […]-tension, and uterine […].
Complications of oxytocin include hypo-natremia, hypo-tension, and uterine tachysystole.
uterine tachysystole is defined as > 5 contractions in 10 minutes; hyponatremia may occur due to structural similarities between oxytocin and ADH

During pregnancy, the size of the pituitary gland […], but blood supply does not change significantly.
During pregnancy, the size of the pituitary gland doubles, but blood supply does not change significantly.
thus increased risk of infarction (Sheehan syndrome)

During the surveillance period following removal of a hydatidiform mole, patients must take […] for 6 months.
During the surveillance period following removal of a hydatidiform mole, patients must take contraceptives for 6 months.
pregnancy during this time period would make it difficult to determine the significance of a rising beta-hCG

Eclampsia is defined as preeclampsia with new-onset […].
Eclampsia is defined as preeclampsia with new-onset seizures.
most common cause of new-onset seizures in pregnant patients with hypertension; maternal morbidity may result from placental abruption, DIC, and cardiopulmonary arrest

Evaluation of a newborn with fetal growth restriction at delivery includes histopathologic examination of the […] to assess for infection and/or infarction.
Evaluation of a newborn with fetal growth restriction at delivery includes histopathologic examination of the placenta to assess for infection and/or infarction.
urine toxicology, serology, and karyotype should be considered as well; additional management is dependent on symptoms (e.g. antibiotics for suspected sepsis, surfactant therapy for suspected NRDS, etc.)

Evidence of a retained placenta includes an echogenic mass or […] endometrial stripe on ultrasound.
Evidence of a retained placenta includes an echogenic mass or thickened endometrial stripe on ultrasound.
Examination findings consistent with uterine rupture include the presence of […] and/or the loss of […].

Examination findings consistent with uterine rupture include the presence of abdominally palpable fetal parts and/or the loss of fetal station.
loss of fetal station may be described as no presenting fetal parts vaginally or a “bulging bag” and is pathognomonic; other symptoms include abdominal pain and bleeding (vaginal or intra-abdominal)

Examination findings consistent with […] include the presence of abdominally palpable fetal parts and/or the loss of fetal station.
Examination findings consistent with uterine rupture include the presence of abdominally palpable fetal parts and/or the loss of fetal station.
loss of fetal station may be described as no presenting fetal parts vaginally or a “bulging bag” and is pathognomonic; other symptoms include abdominal pain and bleeding (vaginal or intra-abdominal)

External cephalic version can be attempted for breech presentations at > […] weeks gestation.
External cephalic version can be attempted for breech presentations at > 37 weeks gestation.
if the patient refuses ECV, cesarean delivery is typically performed at 39 weeks gestation
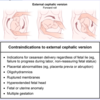
External cephalic version is relatively contraindicated in patients with […] amniotic fluid.
External cephalic version is relatively contraindicated in patients with decreased amniotic fluid.
i.e. oligohydramnios or ruptured membranes; also contraindicated if there are contraindications to vaginal delivery

Fetal anemia typically presents with a […] fetal heart tracing.
Fetal anemia typically presents with a sinusoidal fetal heart tracing.

Fetal complications of maternal hypertension include oligohydramnios, preterm delivery, and fetal […]. (size)
Fetal complications of maternal hypertension include oligohydramnios, preterm delivery, and fetal growth restriction. (size)
maternal complications include superimposed preeclampsia and placental abruption

Fetal complications of preeclampsia include oligohydramnios and […] due to chronic uteroplacental insufficiency.
Fetal complications of preeclampsia include oligohydramnios and fetal growth restriction due to chronic uteroplacental insufficiency.
pathophysiology of preeclampsia likely involves abnormal placental spiral artery development

Fetal growth restriction is an ultrasound-estimated fetal weight
Fetal growth restriction is an ultrasound-estimated fetal weight 10th percentile for gestational age.

Following suction curettage for a hydatidiform mole, […] levels are measured weekly until undetectable and then monthly for 6 months.
Following suction curettage for a hydatidiform mole, beta-hCG levels are measured weekly until undetectable and then monthly for 6 months.

Following suction curettage for a hydatidiform mole, beta-hCG levels are measured weekly until undetectable and then monthly for […].
Following suction curettage for a hydatidiform mole, beta-hCG levels are measured weekly until undetectable and then monthly for 6 months.

Gestational diabetes is a result of pancreatic beta-cell hyperplasia and increased […] secondary to elevated levels of human placental lactogen during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes is a result of pancreatic beta-cell hyperplasia and increased insulin resistance secondary to elevated levels of human placental lactogen during the third trimester of pregnancy.
hPL (a type of placental somatomammotropin) production ceases after delivery resulting in resolution of GDM
Gestational diabetes is a result of pancreatic beta-cell hyperplasia and increased insulin resistance secondary to elevated levels of […] during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Gestational diabetes is a result of pancreatic beta-cell hyperplasia and increased insulin resistance secondary to elevated levels of human placental lactogen during the third trimester of pregnancy.
hPL (a type of placental somatomammotropin) production ceases after delivery resulting in resolution of GDM
Healthy patients in preterm labor at < 34 weeks should receive […] to postpone delivery.
Healthy patients in preterm labor at < 34 weeks should receive tocolytics to postpone delivery.
e.g. indomethacin (preferred if given with magnesium), nifedipine; the risks of tocolytics do not outweigh the benefits after 34 weeks

Healthy patients in preterm labor at
Healthy patients in preterm labor at 34 weeks should receive tocolytics to postpone delivery.
e.g. indomethacin (preferred if given with magnesium), nifedipine; the risks of tocolytics do not outweigh the benefits after 34 weeks

HELLP syndrome is a potential manifestation of severe preeclampsia characterized by a triad of […], […], and […].
HELLP syndrome is a potential manifestation of severe preeclampsia characterized by a triad of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets.
this triad may present clinically as hypertension, anemia, RUQ pain, and bruising/bleeding

How do the following laboratory values change during normal pregnancy?
BUN: […]
Creatinine: […]
Renal protein excretion: […]
How do the following laboratory values change during normal pregnancy?
BUN: decrease
Creatinine: decrease
Renal protein excretion: increase
due to increased GFR and basement membrane permeability

How do the following laboratory values change during normal pregnancy?
Plasma volume: […]
RBC volume: […]
How do the following laboratory values change during normal pregnancy?
Plasma volume: 50% increase
RBC volume: 30% increase
this disparity results in a mild dilutional anemia, which is protective in the case of postpartum hemorrhage
Hyperemesis gravidarum is differentiated from typical vomiting of pregnancy by the presence of laboratory abnormalities, changes in volume status, and/or […] on urinalysis.
Hyperemesis gravidarum is differentiated from typical vomiting of pregnancy by the presence of laboratory abnormalities, changes in volume status, and/or ketones on urinalysis.
may also have weight loss of >5% of prepregnancy weight

Hyperemesis gravidarum is more common in patients with […], hydatidiform mole, or history of GERD.
Hyperemesis gravidarum is more common in patients with multiple gestation, hydatidiform mole, or history of GERD.
typically unresponsive to oral antiemetics

Hyperemesis gravidarum is more common in patients with multiple gestation, […], or history of GERD.
Hyperemesis gravidarum is more common in patients with multiple gestation, hydatidiform mole, or history of GERD.
typically unresponsive to oral antiemetics

Hypopituitarism may be caused by Sheehan syndrome, which is a pregnancy-related […] of the pituitary gland.
Hypopituitarism may be caused by Sheehan syndrome, which is a pregnancy-related infarction of the pituitary gland.
occurs as a complic

Indications for prophylactic administration of RhoGAM in Rh(D)- women include women at […] weeks gestation or within 72 hours of any procedure in which there is a possibility of feto-maternal blood mixing.
Indications for prophylactic administration of RhoGAM in Rh(D)- women include women at 28 - 32 weeks gestation or within 72 hours of any procedure in which there is a possibility of feto-maternal blood mixing.
e.g. spontaneous or induced abortion, amniocentesis, delivery

Initial treatment of postpartum hemorrhage includes bimanual massage and uterotonics (e.g. […]).
Initial treatment of postpartum hemorrhage includes bimanual massage and uterotonics (e.g. oxytocin).
oxytocin is a first-line agent; other agents, such as methylergonovine and carboprost may be administered if oxytocin fails

Intrapartum penicillin is indicated without routine screening in pregnant women with a history of GBS […] during current pregnancy or those with a prior delivery complicated by neonatal GBS infection.
Intrapartum penicillin is indicated without routine screening in pregnant women with a history of GBS bacteruria or UTI during current pregnancy or those with a prior delivery complicated by neonatal GBS infection.

Labor and vaginal delivery are contraindicated after a […] cesarean delivery or extensive myomectomy.
Labor and vaginal delivery are contraindicated after a classical cesarean delivery or extensive myomectomy.
due to significant risk of uterine rupture

Labor and vaginal delivery are contraindicated after a classical cesarean delivery or extensive […].
Labor and vaginal delivery are contraindicated after a classical cesarean delivery or extensive myomectomy.
due to significant risk of uterine rupture

Laboring patients at high risk of uterine rupture require urgent […].
Laboring patients at high risk of uterine rupture require urgent laparotomy and delivery.
e.g. patients with a history of extensive myomectomy or classical cesarean delivery
Late- and post-term pregnancies are commonly complicated by […]-hydramnios.
Late- and post-term pregnancies are commonly complicated by oligo-hydramnios.
the presence of oligohydramnios is an indication for delivery; aging placentas may have decreased fetal perfusion, which causes decreased renal perfusion and urinary output

Late- and post-term pregnancies require antenatal fetal surveillance beginning at 41 weeks with a […] to screen for fetal hypoxia.
Late- and post-term pregnancies require antenatal fetal surveillance beginning at 41 weeks with a biophysical profile to screen for fetal hypoxia.
late- and post-term pregnancies are at risk for uteroplacental insufficiency (e.g. oligohydramnios, late decelerations)

Leakage of CSF after epidural placement may result in postural headaches, which are worse with […] and better with […].
Leakage of CSF after epidural placement may result in postural headaches, which are worse with sitting up and better with lying down.
occurs if the dura is mistakenly punctured during epidural placement

Magnesium is solely excreted by the […].
Magnesium is solely excreted by the kidneys.
thus patients with renal insufficiency are at increased risk for toxicity

Maternal adaptations to pregnancy include a(n) […] cardiac output.
Maternal adaptations to pregnancy include a(n) increased cardiac output.
due to increased stroke volume (early pregnancy) or increased heart rate (late pregnancy); may be accompanied by a systolic ejection murmur

Maternal adaptations to pregnancy include a(n) […] tidal volume and […] respiratory rate.
Maternal adaptations to pregnancy include a(n) increased tidal volume and normal respiratory rate.
due to effects of progesterone; results in an increased minute ventilation (minute ventilation = tidal volume x respiratory rate)

Maternal complications associated with placental abruption include […] and hypovolemic shock.
Maternal complications associated with placental abruption include DIC and hypovolemic shock.
fetal complications include hypoxia and preterm delivery

Maternal complications associated with placental abruption include DIC and […].
Maternal complications associated with placental abruption include DIC and hypovolemic shock.
fetal complications include hypoxia and preterm delivery

Maternal contraindications to breastfeeding include active untreated tuberculosis or […] infection and herpetic breast lesions.
Maternal contraindications to breastfeeding include active untreated tuberculosis or varicella infection and herpetic breast lesions.
other contraindications include HIV infection in developed countries and active abuse of street drugs or alcohol

Maternal contraindications to breastfeeding include chemo- or radiation therapy and […] use.
Maternal contraindications to breastfeeding include chemo- or radiation therapy and illicit drug use.
e.g. alcohol, marijuana, cocaine, opioids

Maternal hypertensive crisis is defined as a SBP > […] or DBP > […] mmHg for > 15 minutes.
Maternal hypertensive crisis is defined as a SBP > 160 or DBP > 110 mmHg for > 15 minutes.

Newly detectable beta-hCG levels within 6 months following suction curettage for a hydatidiform mole is diagnostic for […].
Newly detectable beta-hCG levels within 6 months following suction curettage for a hydatidiform mole is diagnostic for gestational trophoblastic disease. (e.g. choriocarcinoma)

Normal postpartum changes include shivering, lochia, and a […] uterus. (relaxed or contracted)
Normal postpartum changes include shivering, lochia, and a contracted uterus. (relaxed or contracted)
the uterus should be palpable at or below the level of the umbilicus

Normal pregnancy is associated with a […]-coaguable state.
Normal pregnancy is associated with a hyper-coaguable state.
changes include increased fibrinogen and decreased protein C/S activity; protective against postpartum hemorrhage
Oligohydramnios is characterized by an amniotic fluid index
Oligohydramnios is characterized by an amniotic fluid index 5 cm or a single deepest pocket

Patients in preterm labor at < 37 weeks should receive […] to reduce risk of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
Patients in preterm labor at < 37 weeks should receive corticosteroids to reduce risk of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome.
e.g. betamethasone

Patients in preterm labor at < 32 weeks should receive […] for fetal neuroprotection.
Patients in preterm labor at < 32 weeks should receive magnesium sulfate for fetal neuroprotection.
decreases risk of neonatal neurological morbidities (e.g. cerebral palsy)

Patients in preterm labor at
Patients in preterm labor at 32 weeks should receive magnesium sulfate for fetal neuroprotection.
decreases risk of neonatal neurological morbidities (e.g. cerebral palsy)

Patients with HELLP syndrome may present with severe RUQ abdominal pain due to […].
Patients with HELLP syndrome may present with severe RUQ abdominal pain due to liver swelling with distention of the hepatic (Glisson’s) capsule.
pathogensis involves systemic inflammation with platelet consumption and activation of the coagulation cascade

Patients with placenta previa should be advised to avoid […].
Patients with placenta previa should be advised to avoid sexual intercourse.
digital vaginal examination is also contraindicated; both can cause trauma to the placenta and trigger massive hemorrhage

Physiologic changes during normal pregnancy include a(n) […] GFR and […] basement membrane permeability.
Physiologic changes during normal pregnancy include a(n) increased GFR and increased basement membrane permeability.
renal function increases graduallly in the first trimester, reaching 40-50% above the nonpregnant state by midpregnancy

Placenta accreta presents with no separation of the placenta after delivery and […].
Placenta accreta presents with no separation of the placenta after delivery and heavy post-partum bleeding.
usually caught on ultrasound prior to delivery
Placenta […] is the abnormal attachment of the placenta to the myometrium, without penetrating it.
Placenta accreta is the abnormal attachment of the placenta to the myometrium, without penetrating it.

Placenta […] is attachment of the placenta to the lower uterine segment over the internal cervical os.
Placenta previa is attachment of the placenta to the lower uterine segment over the internal cervical os.

Polyhydramnios is characterized by an amniotic fluid index > […] cm or a single deepest pocket > 8 cm.
Polyhydramnios is characterized by an amniotic fluid index > 24 cm or a single deepest pocket > 8 cm.


