Female Reproductive System and Breast III Flashcards
What is the likely diagnosis in a women age > 30 with a well-circumscribed, soft, mobile breast mass?
Breast cyst (benign)
breast cysts are soft and most common after age 30, versus a fibroadenoma, which is hard and most common before age 30

What is the likely diagnosis in a young sexually active woman that presents with multiple papular lesions around the vagina? Some lesions bleed with manipulation.
Condylomata acuminata (genital warts)
due to infection with HPV (strains 6 & 11); in contrast, condyloma lata (secondary syphilis) typically causes flat, velvety lesions
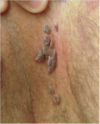
What is the likely diagnosis in a young woman that presents with a soft, mobile, well-circumscribed mass at the base of the labia majora?
Bartholin duct cysts
common in women age
What is the likely diagnosis in a young woman that presents with chronic pelvic pain, especially with exercise, and a homogenous cystic ovarian mass on ultrasound?
Ovarian endometrioma (secondary to endometriosis)
endometriomas are also associated with infertility, which improves with surgical resection of the endometrioma
What is the likely diagnosis in a young, sexually active woman that presents with fever, sore throat, and lower abdominal pain? Physical exam reveals erythematous tonsils without exudates and non-tender cervical lymphadenopathy.
Gonococcal pharyngitis with pelvic inflammatory disease
versus Epstein-Barr virus, which typically causes tender cervical lymphadenopathy and exudative pharyngitis
What is the likely diagnosis in an adolescent girl that presents with amenorrhea and cyclic lower abdominal pain with a bulging vaginal mass on physical exam?
Imperforate hymen
the bulging vaginal mass is a hematocolpos
What is the likely diagnosis in an adolescent girl with delayed puberty, clitoromegaly, and osteoporosis? Laboratory exam reveals undetectable estrogen and elevated testosterone levels.
Aromatase deficiency

What is the likely diagnosis in an afebrile middle-aged woman that presents with unilateral breast warmth, erythema, and swelling refractory to antibiotics?
Inflammatory breast carcinoma
lack of fever and no response to antibiotics help distinguish inflammatory breast cancer from mastitis; other distinguishing features include axillary lymphadenopathy and a peau d’orange appearance

What is the most accurate way to determine estimated gestational age?
ultrasound crown-rump measurement in the first trimester
last menstrual period may be used to estimate gestational age if the patient has normal menses and a reliable LMP

What is the most common gynecologic malignancy in the U.S?
Endometrial cancer

What is the most common side effect of combined oral contraceptives?
Breakthrough bleeding
other side effects include hypertension, increased risk of venous thromboembolism, and increased risk of cervical cancer

What is the most common side effect of tamoxifen?
Hot flashes (80%)
due to anti-estrogenic activity in the CNS which causes thermoregulatory dysfunction in the anterior hypothalamus

What is the most effective emergency contraceptive?
Copper intrauterine device (IUD)
contraindicated if the patient has acute cervicitis or PID; emergency contraceptive pills are less effective

What is the next step in diagnosis for a middle-aged woman that presents with “night sweats”, insomnia, and irregular menses? Pregnancy test is negative.
Measure serum TSH and FSH
these symptoms could be due to menopause or hyperthyroidism, thus both should be evaluated

What is the next step in diagnosis for a woman that presents with stress urinary incontinence with an irregularly enlarged uterus on physical exam?
Pelvic ultrasound
SUI due to direct pressure of fibroids on the bladder
What is the next step in management for a 14-year-old girl that presents with lack of menses? Breast and pubic hair are tanner stage 3.
Reassurance and re-evaluation
primary amenorrhea is not diagnosed until age > 15 with normal secondary sex characteristics (age > 13 without)

What is the next step in management for a 45-year-old woman that presents with insomnia, fatigue, weight gain, ameorrhea, and an enlarged uterus?
measure hCG level
all women of reproductive age (~12 to 49) with amenorrhea and signs of pregnancy should be evaluated with an hCG level
What is the next step in management for a hemodynamically stable young woman with RLQ pain and a beta-hCG level of 1000 IU/L? Transvaginal ultrasound reveals no intrauterine or extrauterine pregnancy.
Repeat serum beta-hCG in 2 days
in a viable pregnancy, beta-hCG levels should double every 2 days (ectopic and non-viable pregnancies are associated with a slower rise); once beta-hCG is > 1500 IU/L, a TVUS should be repeated

What is the next step in management for a postmenopausal woman with a suspected granulosa cell tumor that presents with vaginal bleeding and a thickened endometrial stripe on ultrasound?
Endometrial biopsy
postmenopausal bleeding and thickened endometrium are concerning for endometrial hyperplasia/cancer; must be evaluated with endometrial biopsy, which is the gold standard test to rule out endometrial malignancy

What is the next step in management for a postmenopausal woman with an incidentally discovered ovarian cyst on ultrasound?
Measure CA-125 levels
an elevated CA-125 level in a postmenopausal patient is suspicious for malignancy, even if the ultrasound findings seem benign

What is the next step in management for a pregnant patient with high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion discovered on Pap testing?
Immediate colposcopy +/- biopsy (safe during pregnancy)
cervical excision is needed if invasive cancer is found; if the transformation zone (squamocolumnar junction) is not visualized during colposcopy, an endocervical curettage may be deferred until after pregnancy

What is the next step in management for a premenopausal woman with a palpable adnexal mass on physical exam?
Pelvic ultrasound
CA-125 levels are not as useful for initial evaluation of an ovarian mass in premenopausal women (in postmenopausal women, pelvic ultrasound and CA-125 are part of the initial workup)

What is the next step in management for a woman that presents with a thin, white plaque suspicious for lichen sclerosus?
Vulvar punch biopsy
necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out vulvar squamous cell carcinoma

What is the next step in management for a woman with bilateral, milky nipple discharge that is guaiac negative?
Serum prolactin, TSH, and pregnancy test
consider brain MRI in patients with elevated prolactin or signs of pituitary mass

What is the next step in management for a young woman that presents with diffuse periumbilical abdominal pain that then localizes to the right lower quadrant? Her LMP was one month ago.
Pregnancy test
should be administered to any woman of childbearing age before performing any diagnostic tests (e.g. X-ray, CT scan)
What is the next step in management for an afebrile woman that experiences relief of symptoms following aspiration of clear fluid from a simple breast cyst?
Repeat breast examination in 2 - 4 months
cystic fluid can reaccumulate; if no signs of recurrence, annual screening can be resumed

What is the next step in management for an elderly woman that presents with bloody, malodorous discharge and an irregular vaginal lesion?
Biopsy of the lesion
this patient likely has vaginal sqaumous cell carcinoma

What is the preferred adjuvant treatment for ER+ breast cancer in postmenopausal women?
Aromatase inhibitors (e.g. anastrozole)
What is the preferred adjuvant treatment for ER+ breast cancer in premenopausal women?
Tamoxifen

What is the preferred initial imaging modality for suspected gynecological tumors?
Pelvic ultrasound
high sensitivity for diagnosing uterine fibroids and ovarian pathology

What is the preferred method of contraception for patients with breast cancer?
Copper IUD
all hormone-containing contraceptives are contraindicated in patients with breast cancer (both estrogen and progesterone may have a proliferative effect on breast tissue)

What is the preferred test to diagnose Haemophilus ducreyi infection (chancroid)?
Bacterial culture

What is the preferred test to diagnose HSV infection?
PCR testing
more sensitive and specific than viral culture and Tzanck smear

What is the recommended contraceptive for a woman with a history of anemia and medication non-compliance?
Levonorgestrel IUD
typically causes amenorrhea, which is beneficial in patients with anemia (versus the copper IUD, which can cause heavy menstrual bleeding); less common side effects include mood changes, breast tenderness, and headache
What is the recommended follow-up following removal of a breast lesion found to be fat necrosis?
Routine follow-up

What is the recommended management for a patient with suspected endometriosis refractory to NSAIDs and OCPs?
Laparoscopy
allows for direct visualization, biopsy, and removal of endometriotic lesions

What is the recommended management for an adolescent that presents with fever and leukocytosis secondary to pelvic inflammatory disease?
Inpatient broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
hospitalization is recommended for those with severe presentation (e.g. fever, leukocytosis) and those with a higher risk of noncompliance (e.g. adolescents)

What is the recommended screening for asymptomatic patients at average-risk of ovarian cancer?
No screening recommended
What is the recommended treatment for a breastfeeding woman with a suspected breast abscess?
needle aspiration, antibiotics, and continued feeding
common antibiotics for mastitis include dicloxacillin and cephalexin; incision and drainage is typically reserved for abscesses that are not responsive to needle aspiration and antibiotics
What is the recommended treatment for a breastfeeding woman with acute mastitis?
analgesics, breastfeeding, and antibiotics

e.g. dicloxacillin or cephalexin; if high suspicion for MRSA, clindamycin, TMP-SMX, or vancomycin may be needed
What is the recommended treatment for a hemodynamically stable patient with a ruptured ovarian cyst?
Supportive (e.g. analgesics)
hemodynamically unstable patients require urgent surgical intervention

What is the recommended treatment for a patient with a painless genital ulcer and bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy? Serum RPR is negative.
Empiric penicillin treatment
patients with negative initial serologies and strong clinical evidence of primary syphilis should be treated empirically (non-treponemal testing has a high false negative rate in early infection)

What is the recommended treatment for a patient with ovarian torsion?
Urgent surgical detorsion and cystectomy

What is the recommended treatment for a symptomatic Bartholin duct cyst?
Incision and drainage, followed by Word catheter placement

What is the recommended treatment for advanced ovarian cancer?
Exploratory laparotomy followed by chemotherapy (e.g. cisplatin + paclitaxel)
the ovaries, uterus, omentum, and any visible cancerous lesion are removed and pelvic/aortic lymph nodes are dissected
What is the recommended treatment for an asymptomatic Bartholin duct cyst?
Observation
spontaneous drainage and resolution may occur; symptomatic cysts require incision & drainage, followed by placement of a Word catheter
What is the recommended treatment for atrophic vaginitis refractory to vaginal moisturizer and lubricant?
Topical vaginal estrogen

What is the recommended treatment for bacterial vaginosis (Gardnerella infection)?
metronidazole or clindamycin

What is the recommended treatment for Candida vaginitis?
Oral fluconazole

What is the recommended treatment for confirmed chlamydia infection?
Azithromycin

What is the recommended treatment for confirmed gonorrhea infection?
azithromycin + ceftriaxone

What is the recommended treatment for endometrial carcinoma?
Hysterectomy +/- chemo- or radiation therapy
endometrial hyperplasia may be managed with progestin therapy or hysterectomy, depending on if the patient desires future children

What is the recommended treatment for imperforate hymen?
Incision and drainage

What is the recommended treatment for non-pregnant women age > 25 with grade 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)?
Cervical conization
via cold knife conization or loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP)

What is the recommended treatment for symptomatic pelvic organ prolapse refractory to lifestyle modifications?
pessary or surgical management
conservate management with pessary placement is appropriate for poor surgical candidates

What is the recommended treatment for trichomoniasis (Trichomonas infection)?
metronidazole for both the patient and the sexual partner

What is typically the first sign of puberty in girls?
Breast development (thelarche)
remembered with the mnemonic “boobs, pubes, grow, flow”

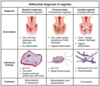
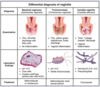
What microscopy finding is characteristic of bacterial vaginosis (Gardnerella infection)?
Clue cells (epithelial cells coated with bacteria)

What microscopy finding is characteristic of Candida vaginitis?
pseudohyphae and/or budding yeast
What microscopy finding is characteristic of trichomoniasis (Trichomonas infection)?
Motile protozoa

What ovarian tumor is associated with estrogen secretion?
Granulosa cell tumor

What pelvic surgery complication is characterized by continuous involuntary loss of urine through the vagina in the absence of other urinary symptoms?
Vesicovaginal fistula
may present within a month after surgery; dye tests and/or cystourethroscopy can help identify small fistulas not seen on visual inspection

What pharmacologic agent may be used in the treatment of overflow incontinence?
Cholinergic agonists (e.g. bethanecol)

What pharmacologic agent may be used in the treatment of urgency incontinence?
Anti-muscarinic agents (e.g. oxybutynin)
first-line treatment should consist of lifestyle modifications and/or bladder training; a newer agent, mirabegron (beta3-adrenergic agonist) may be offered to patients who cannot take antimuscarinic drugs

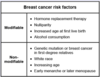
What race/ethnicity is associated with the highest risk of breast cancer?
White race
What serum marker is characteristically elevated in choriocarcinoma?
beta-hCG

What serum tumor marker is useful for monitoring treatment response and recurrence of ovarian neoplasms?
CA-125
may also be used as part of the initial workup for postmenopausal women with suspected ovarian cancer

What ultrasound finding is typical for an ovarian endometrioma?
Homogenous cystic mass

Which cause(s) of vaginitis are associated with a normal pH (3.4 - 4.5)?
candida vaginitis
Which cause(s) of vaginitis are associated with an elevated pH (> 4.5)?
bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis
Which genital infection is characterized by a single painless ulcer (chancre) often with non-tender bilateral lymphadenopathy?
Treponema pallidum (primary syphilis)
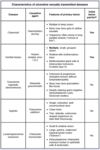
Which genital infection is characterized by extensive, painless ulcers without lymphadenopathy?
Klebsiella granulomatis (granuloma inguinale)
primarily seen in India, Guyana, and New Guinea (rare in the U.S)
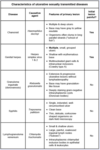
Which genital infection is characterized by small, painless ulcers that can progress to painful, fluctuant adenitis (buboes)?
Chlamydia trachomatis L1-L3 (lymphogranuloma venereum)

Which genital infection is characterized by tender, large ulcers with a grayish exudate and severe lymphadenopathy?
Haemophilus ducreyi (chancroid)
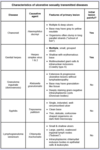
Which genital infection is characterized by tender, small ulcers with an erythematous base and mild lymphadenopathy?
Herpes simplex virus

Which selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) is preferred for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis?
Raloxifene
antagonist of estrogen in both breast and endometrium therefore no associated cancer risk

[…] consumption is a dose-dependent risk factor for breast cancer.
Alcohol consumption is a dose-dependent risk factor for breast cancer.

[…] is transient mid-cycle ovulatory pain that may mimic appendicitis.
Mittelschmerz is transient mid-cycle ovulatory pain that may mimic appendicitis.
e.g. on day 10-14 (corresponding with the time of ovulation)

Polycystic ovarian syndrome often presents in young, obese women with […] and symptoms of […] excess.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome often presents in young, obese women with oligo- or amenorrhea and symptoms of androgen excess.
laboratory findings include normal/elevated testosterone and estrogen levels with an imbalance of LH/FSH (often > 2:1 ratio of LH:FSH)

[…] often presents in young, obese women with oligo- or amenorrhea and symptoms of androgen excess.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome often presents in young, obese women with oligo- or amenorrhea and symptoms of androgen excess.
laboratory findings include normal/elevated testosterone and estrogen levels with an imbalance of LH/FSH (often > 2:1 ratio of LH:FSH)



