Practical 3 Flashcards
What is feature A in the following figure?

Renal Cortex

What is feature B in the following figure? (region)

medulla
Renal pyramid

What is feature C in the following figure?

Renal capsule

What is feature D in the following figure?

minor calyx

What is feature E in the following figure?

major calyx

What is feature F in the following figure?

Renal column
What is feature G in the following figure?

renal pyramid

What is feature H in the following figure?

ureter

What is feature I in the following figure?

renal pelvis

What is feature J in the following figure?

renal papillae

What is feature D in the following figure?

renal vein

What is feature E in the following figure?

renal artery

What is the feature that makes up D, E and F?
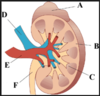
Hilum

Explain the renal artery flow through the kidneys

Renal artery (1)
segmental artery (2)
interlobar artery (3)
arcuate artery (4)
cortical radiate artery (5)

Explain the detailed arterial flow around the nephron
- afferent arterioles
- glomerulus
- efferent arterioles
- efferent arterioles
- peritubular capillaries
- vasa recta

explain the veinus flow through the kidneys
- cortical radiate vein
- arcuate vein
- interlobar veins
- renal vein

explain the overall arterial and vein flow through the renal system

Explain which of the following is the proximal and distal convoluted tubules

cloudy = proximal CT
open = distal CT
What is feature A in the following image?

urinary bladder

What is feature B in the following image?

vas deferens

What is feature D in the following image?

spongy urethra

What is feature E in the following image?

corpus cavernosa

What is feature G in the following image?

corpus spongiosum

What is feature H (region) in the following image?

glans penis

What is feature H (skin) in the following image?

prepuce (foreskin)

What is feature I in the following image?

scrotum

What is feature J in the following image?

Testis

What is feature K in the following image?

Epididymus

What is the feature that the line is pointing to just above K?

bulbourethral glands

What is the large feature above the bulbourethral glands

Prostate gland

What is the duct that is being pointed at in the prostate gland

Ejaculatory duct

What is the following feature?

seminal vesicles

What is the following feature?

spermatic cord

What is the region of the femail where hair grows?
mons pubis
What is feature M in the following image?

Labia majora

What is feature K in the following image?

labia minora

What is a space or cavity at the entrance to a canal, channel, tube, vessel
vestibule
What is the area between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx. (anus and urethra)
perineum
What is feature I in the following image?

clitoris

What is the fold capping the clitoris formed by union of the labia minora and the clitoris.

clitoral prepuce

What is the membrane that partially closes the opening of the vagina and whose presence is traditionally taken to be a mark of virginity.
hymen
What is the following feature?

greater vestibular glands

What is feature 1 in the following image?

vagina

What is feature 2 in the following image?

cervix

What is feature 4 and the feature right above that feature?

uterus (body and fundus)

What is feature 5 in the following image?

uterine (Fallopian) tubes

What is feature 6 in the following image?

fimbriae

What is the curved region of the Fallopian tubes? (Around feature 6)

infundibulum

Explain the structures of the testis

- Spermatogonia (2n): A large unspecialized germ cell that in spermatogenesis divides by mitosis to form primary spermatocytes
- Primary spermatocytes (2n): original large diploid cell into which a spermatogonium develops; it can later undergo the first meiotic division into the secondary spermatocyte
- Spermatids (n): haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte.
- Immature sperm (n): Sertoli cells form the walls of a seminiferous tubule. Sertoli cells nourish, support, and protect developing germ cells, which undergo cell division by meiosis to form spermatozoa (immature sperm).
- Sustentacular (nurse) cells: testicles that is part of a seminiferous tubule and helps in the process of spermatogenesis; that is, the production of sperm.
- Interstitial (Leydig) cells: also known as interstitial cells of Leydig, are found adjacent to the seminiferous tubules in the testicle. They produce testosterone in the presence of luteinizing hormone (LH).

Describe the structure of a sperm
Head
acrosome
body
tail

Explain the structures of the ovary slides


What is feature 4 in the following image?

primordial follicles
made of granulosa cells
(yellow dots on the model)

What is feature 1 on the following image?

primary follicle (2n)

What is feature 3 in the following image?

secondary oocytes (n)
(Released in the fallopian tube, pre ovulation)

What are the small haploid cell that is formed concomitantly as an egg cell during oogenesis, but which generally does not have the ability to be fertilized.

polar body

What is feature 5 in the following image?

tertiary (Graafian) follicle

What is feature 7 in the following image?

Corpus luteum

What is feature 6 in the following image?

corpus albicans

Explain the layers of the uterus

- Endometrial base layer:
- Endometrial functional layer (sluffs off)
- Myometrium: middle layer of the uterine wall
- Perimetrium (serosa)

Explain the innermost glandular layer and functions as a lining for the uterus, preventing adhesion between the opposed walls of the myometrium.
endometrial base layer

What is the layer that sluffs off during menstruation?
endometrial functional layer

What are the main layers of the uterus..

Explain the fertilized egg structure
corona radiata (ring of cells)
zona pellucida (hard outer layer)
prenuclei (#4 on model in class)

Explain the cleavage step of the fetal development
two-cell stage
eight-cell stage
mortula (ball of cells, model #9)

Explain the implantation stage model

blastocyst (blastula) = hollow sphere of cells - first differentiation
inner cell mass = cells piled inside
trophoblast - outer cell that forms placenta
gastrula = beginning of differentiation develemental stage

Explain the embryonic membrane structures

amnion = pink portion
amniotic cavity = hollow area around baby
yolk sac = little yellow sac
chorion = with amnion it makes up the amniotic sac
allantois = forms the umbillical chord

identify and name the germ layers

endoderm = innermost (gray on model)
mesoderm = middle (white on model)
ectoderm = outer layer (pink on model

Explain the placental blood exchange between mother and baby

umbilical arteries (deoxygenated = away from baby)
umbilical veins (oxygenated = to baby)
placenta = exchange
decidua basalis = vascular layer
chorionic villi = blood capillary exchange
maternal / fetal blood

What is feature C in the following image and what is the adult structure?

ductus venosus = in the liver (bypass)
adult = ligamentum venosum

What is feature A in the following image?

foramen ovale

What is feature F in the following image and what is the adult structure?

ductus arteriosus
Adult = ligamentum arteriosum

Explain the overall fetal circulation

Umbilical vein
ductus venosus
inferior vena cava
right atrium
foramen ovale (pulmonary trunk)
ductus arteriosum
aorta

What are the two cardiac shunts for the fetus?

faramen ovale
ductus arteriosus



