Practical 1 Flashcards
What are examples of epithelial tissue?
blood vessel linings
digestive track lining
Where are epithelial tissue found?
Blood vessels
Digestive track lining
Explain the characteristics of epithelial tissue
simple squamous epithelium
allos material to diffuse in/out
Explain examples of connective tissue
Blood
bone
Explain location of connective tissue
Circulatory system
throughout body
Explain the characteristics of connective tissue
protect against infection
provide nutrients
provide support
rigid
Explain examples of muscular tissue
skeletal muscle
cardiac muscle
explain location of muscular tissue
throughout body
cardiovascular system (heart)
Explain the characteristics of muscular tissue
Skeletal = striated, voluntary
Cardiac = striated, involuntary
Explain examples of nervous tissue
peripheral nerves, brain
Explain the characteristics of nervous tissue
Peripheral nerves: roots and branches, sensory and motor outside spinal cord
Brain: information center, corticalization (wrinkled)
Explain the function and associated organs of the cardiovascular organ system
Function:
- Transport of nutrients
- Transport of oxygen
- Transport of hormones
Associated organs:
- Heart and blood vessels
Explain the function and associated organs of the lymphatic system
Function:
- Removal of interstitial fluid from tissue
- Absorbs and transports fatty acid and fats from digestive system
- Transports WBC to and from lymph nodes into the blood
Associated organs:
- Thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, ducts, cistenna chyli
Explain the function and associated organs of the Respiratory system
Function:
- Take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide
Associated organs:
- Lungs, airways, muscles of respiration
- (nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, branchi, brachioles)
Explain the function and associated organs of the Digestive system
Function:
- Digestion = breakdown food into small molecules
- absorbs nutrients
Associated organs:
- Digestive track = mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines and anus
Explain the function and associated organs of the Excretory system
Function:
- Discharge wastes produced by homeostasis
Associated organs:
- Kidneys, liver and large intestines
Explain the function and associated organs of the Reproductive system
Function:
- Produce gametes (egg or sperm cells)
- Protect and nourish offspring until birth
Associated Organs:
- Female: ovaries, fallopian tube, uterus, cervix, urithra
- Male: Testes, urithra, scrotum, spermatic ducts
Explain the function and associated organs of the Integumentary system
Function:
- Retain body fluids, protect against disease, eliminate waste products, regulate body temperature
Associated Function:
- Skin, hair, nails, glands and nerves
What type of blood cell is this?

neutrophil
Leukocyte, granulocyte
50-70%
What is the function of this blood cell type?

neutrophil
Leukocyte, granulocyte
Function:
- active phagocyte, very abundant
What type of blood cell is this?

Erythrocyte (RBC)
What type of blood cell is this?

Eosinophil
Leukocyte, granulocyte
2-4%
(large, deep red, hard to find)
What type of blood cell is this?

basophil
Leukocyte, granulocyte
<1%
What type of blood cell is this?

Lymphocyte
Leukocyte, agranulocytes
25-30%
small and large pink nuc
What type of blood cell is this?

Monocyte
3-8%
Leukocyte, agranulocytes
very large, mainly cytoplasm
What is the function of this blood cell?

Erythrocytes (RBC)
Function:
- carry oxygen throughout body
What is the function of this blood cell?

eosinophil
Leukocytes, granulocytes
larger, deep red
Function:
- Counterattack parasite worms
- allergy and asthma
- about same size as neutrophil
What is the function of this blood cell?

basophil
leukocytes, basophil
<1%
very purple blob
Function:
- Include histamine, a vasodilator that is discharged on exposure to antigens and helps mediate the inflammatory response
- Least abundant leukocyte
- Hepren = clotting agent
What is the function of this blood cell?

lymphocyte
leukocytes, agranulocytes
25-30%
small and large pink nuc
Function:
- B lymphocytes = produce antibodies released to blood
- T lymphocytes = regulatory rule and destroy grafts, tumors and virus - infected cells
- Immune response
What is the function of this blood cell?
monocyte
leukocytes, agranulocytes
3-8%
very large, mainly cytoplasm
Function:
- Convert to macrophages, active phagocytes (“long term clean up team”)
- Increased dramatically in number curing cronic infection
- Largest leukocytes (2x RBC)
What is this blood cell and state the function

Thrombocytes (platelets)
~1%
Function:
- assist with clotting
How can you tell the type of blood?
Using Anti-A, Anti-B and Anti-Rh(D),
if it agrogates than the blood is that blood type
For example +A blood type will agrogate with anti-A and Anti-Rh(D)
State the blood type chart for Type A blood
antigens present,
antibodies,
what can they recieve,
what can they donate to
Antigen = A
Antibodies = B
Can receive = A or O
Can donate = A, AB
State the blood type chart for Type B blood
antigens present,
antibodies,
what can they recieve,
what can they donate to
Antigens = B
Antibodies = A
Can receive = B or O
Can donate = B , AB
State the blood type chart for Type AB blood
antigens present,
antibodies,
what can they recieve,
what can they donate to
Antigens = A and B
Antibodies = none
Can receive = A, B, AB or O
Can donate = AB
State the blood type chart for Type O blood
antigens present,
antibodies,
what can they recieve,
what can they donate to
Antigens = none
Antibodies = A and B
Can receive = O
Can donate = A, B, AB, and O
What is this and state the function

Pericardial sac
Function:
- double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels

What is this and state the function (number 1)

epicardium
Function:
- a serous membrane that forms the innermost layer of the pericardium and the outer surface of the heart

What is this and state the function (number 6)

endocardium
Function:
- the thin, smooth membrane that lines the inside of the chambers of the heart and forms the surface of the falves

What is this and state the function (number 5)

myocardium
Function
- the muscular tissue of the heart. middle lining

What is the bottom point of the heart?
What is the function?
apex
Function:
- consisting of the left ventricle, is responsible for regulating ventricular contraction and sending and receiving signals from the heart’s atrial nodes
What are structures 3 and 8?
What are their functions?

left and right atrium
Function:
- Blood enters the heart through the two atria and exits through the two ventricles

What is this and what is the function?

auricle
Function:
- attached to each of the anterior surfaces of the outer-walls of the atria.
- Purpose is to increase the capacity of the atrium, and so also increased the volume of blood that is able to contain in the heart
What are 5 and 9 structures? What are their functions?

Left and right ventricle
Function:
- Pump blood to the lungs (right) or the body (left)

What is this groove and what is the function?

coronary sulcus
a groove on the outer surface of the heart marking the division between the atria and the ventricles.
Function:
- it contains the trunks of the blood vessels that are known as the “nutrient vessels of the heart”. it comprises of veins and arteries that supply blood to the cardiac muscles and also carries it from them
What is this and what is the function?

interatrial septum
Function:
- the upper chambers, the atria, are separated by this partition
What is this and what is the function?

interventricular septum
Function:
- Part of the structure of the heart and separates the left ventricle from the right
What is this and what is the function?
(number 4 in the picture)

tricuspid valve
Function:
- right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, between the right atrium and the right ventricle.
- The function of the valve is to prevent back flow of blood into the right atrium

What is the valve between the right atrium and ventricle?
bicuspid valve
mitral valve
What is this and what is the function?

chordae tendineae
Function:
- (tendinous chords), colloquially known as the heart strings, are cord-like tendons that connect the papillary muscles to the tricuspid valves and the mitral valve in the heart
What is the muscle in this picture? what is the function?

Papillary muscles
Function:
- muscles located in the ventricles of the heart. They attach to the cusps of the atrioventricular valves via the chordae tendineae
What is the following valve? what is the function?

pulmonary semilunar valve
Function:
- located at the connections between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle, and the aorta and the left ventricle. These valves allow the blood to be pumped forward into the arteries, but prevent backflow of blood from the arteries into the ventricles.
What is the following valve? What is the function? (number 10)

aortic semilunar valve
Function:
- prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle and keeps it moving towards the body

What is this feature inside the right atrium and what is the function?

fossa ovalis
Function:
- This enables respiration and circulation independent from the mother’s. With the child’s first breath, the lungs send oxygenated blood to the left atrium
what is feature 11 and what is the function?

Aorta
Function:
- Largest artery in the body, allows oxygenated blood flow to the rest of the body

What is the portion of heart prior to the split of feature 6?

pulmonary trunk (and arteries)
Function:
- carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. The blood here passes through capillaries adjacent to alveoli and becomes oxygenated as part of the process of respiration.

What is the feature shown by number 7?

pulmonary veins
Function:
- responsible for carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the left atrium of the heart

What is feature 1 in the figure and what is the function?

inferior vena cava
Function:
- large vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart

What is feature 2 in the figure and what is the function?

superior vena cava
Function:
- great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulationg to the right atrium of the heart

What is feature C in the following image and what is the function?

left coronary artery
supply blood to the myocardium itself

What is feature A in the following image and what is the function?

Right coronary artery
supply blood to the myocardium
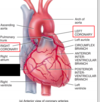
What is feature D in the following image and what is the function?

circumflex artery (circles heart)
Function:
- supply oxygenated blood to different parts of the heart

What is feature E in the following image and what is the fuction?

anterior interventricular artery
Function:
- a branch of the left coronary artery

What is the vein that follows feature E?

Great cardiac vein
Function:
- Large vein going down between the ventricles

What is the following feature and what is the function?

Coronary sinus
Function:
- Goes around the heart under the aorta going horizontal

What is the following feature?

- striations
- nucleus
- Intercalated disc

Explain the structures of this slide. What is it of?

Artery cross- section
A: tunica interna
B: tunica media
C: tunica externa

What do the sounds of the heart mean?
Lub = closure of the mitral (bicuspid) and the tricuspid valves, start of systole
Dub = closure of aortic and pulmonic valves, marking the end of the systole
What are palpation points on the body
superficial temporal
external maxillary
carotid
brachial
ulnar
radial
femoral
popliteal
posterior tibial
dorsalis pedis

What pulse points had have the greatest amplitude? the least?
Common carotid artery = greatest amplitude (close to aorta)
Dorsalis pedis = least amplitude (furthest from heart)

when taking the blood pressure, what is the large first number and what is the lower second number?
What units are they measured in
Systolic pressure = ______ mm Hg
(pressure in cuff = pressure in vessels)
Diastolic pressure = ______ mm Hg
(Pulse of low coming through vessel)
Pulse pressure = ______ mm Hg
How do you calculate the mean arterial pressure? and what is it for?
describe a notional average blood pressure in an individual. It is defined as the average arterial pressure during a single cardiac cycle.
MAP = diastolic pressure + (pulse pressure / 3)
you divide by 3 if in rest and 2 if being active
systol goes up during exercising, diastol goes down or stays the same.
how do you determine the index of physical fitness?
(duration of exercise in seconds x 100 )
/ (2 x sum of the three pulse counts during recovery)
What is feature D? What is the function?
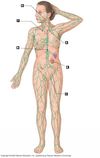
cervical lymph nodes (neck)
Function:
- Located in the neck region
- Filtering and draining your lymphatic fluid from the areas in your neck and head

What is feature F? What is the function?

right lymphatic duct
by the aorta
Function:
- much shorter than the thoracic duct, begins high in the right side of your chest. It collects lymph from the right side of the chest wall, your right arm, and the right side of your head and neck

What is feature A? What is the function?

Thoracic duct
(long white one above heart on left isde)
Function:
- reintroduce lymph to your blood stream through the large veins returning to your heart from your arms: the left and right subclavian veins

What is the bunch of lymphatic vessels in the armpit area called? What are their function?

axillary lymph nodes
Function:
- group of lymph nodes located in the axillary (or armpit) region of the body. They perform the vital functions of filtration and conduction of lymph from the upper limbs, pectoral region, and upper back

What is feature B? What is the function?

cisterna chyli
(white bulge by kidney/stomach)
Function:
- is a dialated sac at the lower end of the thoracic duct into which lymph from the intestinal trunk and two lumbar lymphatic trunks flow

What is feature C? What is the function?

Inguinal lymph nodes
(upper inner leg)
Function:
- Located in the femoral triangle of Scarpa, an area of the upper, inner thigh

What are the white vessels in the body that are involved with the lymphatic system and what are their functions?
lymphatic vessels
Function:
- Just like their neighboring blood capillaries, lympatic capillaries join into progressively large tubes called lymphatic vessels, which transport the fluid from your tissues (this fluid is now called lymph) toward the center of your body
What is feature E indicated in the figure and what is the function?

spleen
(L = left side)
Function:
- It acts as a filter for blood as part of the immune system. Old red blood cells are recycled in the spleen, and platelts and white blood cells are stored there. The spleen also helps fight certain kinds of bacteria that cause pneumonia and meningitis

What is the yellow structure indicated in this image and the function?

Thymus
(base of the throat)
Function:
- Serves a vital role in the training and development of T-lymphocytes or T cells, an extremely important type of white blood cells.

What is the following feature and what is the function?

Thoracic duct
(below the heart down the middle of body)
Function:
- It is also called the left lymphatic duct or the alimentary duct. A large portion of the body’s lymph is collected by this duct and then drained into the blood stream near the brachiocephalic vein between the internal jugular and the left subclavian vein

Explain the regions of the lymph node

Capsule = outside
Cortex = outer edge
Medulla = inside
Hilum = white dotted area by the efferent lymphatic vessel section

Describe the general flow of lymph from lymphatic capillaries through return to the circulatory system
- The lymphatic system begins at lymphatic capillaries
- Lymphatic capillaries convey lymph towards lymphatic vessels
- Lymph passes through lymph nodes, where it is filtered and monitored for pathogens
- Large lymphatic vessels (collecting ducts) ultimately return lymph to venous circulation

What is this feature and what is the function?

ascending aorta
Function:
- Sends blood from the heart to the aorta arch

What is the feature and what is the function?

aortic arch
Function:
- Blood from ascending aorta into artery branches off the heart

What is feature A and what is the function?

brachiocephalic artery
Function:
- Right large branch off of the aorta arch to the right arm, head and neck

What is feature E and what is the function?

left subclavian artery
Function:
- Furthest left branch off aorta arch to the arms

What is feature C and what is the function?

right subclavian artery
Function:
- Right branch off of brachiocephalic artery. To the arms

What is feature B and what is the function?

right common carotid artery
Function:
- Large carotid branch before splitting into external and internal carotid branch. To the head

What is feature D and what is the function?

left common carotid artery
Function:
- Large carotid branch before splitting into external and internal carotid branch. To the head

Explain the split of the carotid artery

External carotid artery = more forward
Internal carotid artery = closer to spine

What is this feature and what is the function?

Posterior intercostal arteries

What is this feature and what is the function?

axillary artery
by armpit (lower one down)
Function:
- Large branch from aorta that goes into clavicle region

What is this feature and what is the function?

brachial artery
top artery
Function:
- Runs along the brachial bone of the arm

What is this feature and what is the function?

Radial artery (+pressure pt)
(superficial)
Function:
- Runs along the radial bone of the wrist (thumb side)

What is this feature and what is the function?

Ulnar artery
(deep, cannot really see)
Function:
- Runs along the ulnar bone of wrist (pinky side)

What is this feature and what is the function?

Superficial palmar arch
Function:
- Artery in the palm of the hand that arches around

What is this feature and what is the function?

Azygos vein
(left up on right side - blue)
Function:
- vein running up the side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. Deoxygenated blood from the posterior walls of the thorax and abdomen

What is this feature and what is the function?

brachiocephalic vein
Function:
- Upper chest are formed by the union of each corresponding internal jugular vein and subclavian vein. Major veins returning blood to the superior vena cava

What is this feature and what is the function?
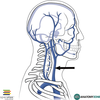
Jugular vein
Function:
- Blood from the face

what is this feature and what is the function?

subclavian vein
Function:
- Large vein from the arms

What is this feature and what is the function?

axillary vein
(big and blue by armpit)
Function:
- More medial branch of the subclavian vein. From the inner armpit

What is this feature and what is the function?

Brachial vein
(dives deep by clavical splits into radial and ulnar)
Function:
- Outside branch of the vein from the subclavian vein. Runs along the shoulder blade and down the brachial bone. Tow small branches off the cephalic vein

What is this feature and what is the function?

Basilic vein
(top vein)
Function:
- Vein on the medial side of the arm by the inner elbow

What is this feature and what is the function?

Cephalic vein
(very thin dangling vein)
Function:
- Outside vein of the arm on the radial side of the upper arm by brachial

What is this feature and what is the function?

Median cubital vein
(branch intersection)
Function:
- Vein that runs in the inner elbow region (across)

What is this feature and what is the function?

ulnar vein
(dives deep)
Function:
- Vein on the pinky side of the lower arm

What is this feature and what is the function?

Radial vein
(up top)
Function:
- Vein on the radial (thumb) side of the lower arm



