Posterior Abdominal Wall Flashcards
1
Q
- What muscles make up the floor of the posterior abdominal wall?
A
- Psoas major and minor
- Iliacus
- Quadratus lumborum
- Diaphragm
2
Q
- Label the following structures

A
- Quadratus lumborum m.
- Diaphragm m.
- Psoas major m.
- Psoas minor m.
3
Q
- What is shown in the following image?
- What are signs and symptoms a patient with this condition would present with?
- What test can help you identify?
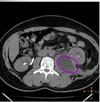
A
- Psoas abscess
- Back or flank pain
- Fever
- Inguinal mass
- Limp (lower abdominal pain exacerbated by extending limb)
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- Psoas sign would be positive
Side note: more common in populations with tuberculosis
4
Q
- What are the fascial components of the posterior abdominal wall?
A
- Median arcuate ligament
- Medial arcuate ligament
- Lateral arcuate ligament
5
Q
- Median arcuate ligament
A
- Tendinous arch of the crura of the diaphragm
6
Q
- Medial arcuate ligament
A
- Fascial thickening of psoas fascia
- Located lateral to the median arcuate ligament
7
Q
- Lateral arcuate ligament
A
Thickening of the fascia lining quadratus lumborum
8
Q
- What two fascial components of the posterior abdominal wall serve as attachment points for the diaphragm muscle?
A
- Medial arcuate ligament
- Lateral arcuate ligament
9
Q
- Identify the fascial components of the posterior abdominal wall

A
- From top to bottom:
- Median arcuate ligament
- Medial arcuate ligament
- Lateral arcuate ligament
10
Q
- What embryological structure gave rise to the muscular portion of the diaphragm?
- What are the parts of the muscular potion?
A
- Hypomere (mesoderm)
- Sternal part: attaches to xiphoid
- Costal part: attaches to inferior 6 costal cartilages
- Lumbar part: attaches to medial and lateral arcuate ligaments
11
Q
- What embryological structure gave rise to the central tendon of the diaphragm?
A
- Septum transversum
12
Q
- What embryological structure gave rise to the crura of the diaphragm?
- At what spinal levels are each crus located?
A
- Dorsal mesentary of the esophagus
- Right: L3-L4
- Left: L2-L3
13
Q
- What apertures are located in the diaphragm?
A
- Caval opening
- Esophageal hiatus
- Aortic hiatus
14
Q
- What runs through the caval opening of the diaphragm?
- What spinal level is it located?
A
- T8
- IVC and right phrenic nerve (remember that the left phrenic just pierces the diaphragm and does not go thru opening)
15
Q
- At what spinal level is the esophageal hiatus located?
- What runs through this hiatus?
A
- T10
- Esophagus
- Anterior and Posterior Vagal Trunks
16
Q
- At what spinal level is the aortic hiatus located?
- What structures run through it?
A
- T12
- Aorta
- Thoracic duct
- Sometimes azygos and hemi-azygos veins
17
Q
- Identify the apertures of the diaphragm

A
From top to bottom:
Caval opening
Esophageal hiatus
Aortic hiatus
18
Q
- Name the vascular relationships for the following:
- Aorta
- Celiac
- SMA
- Renals
- Gonadal
- IMA
- Bifurcation
A
- Aorta-T12-L4
- Celiac: T12
- SMA: L1 (anterior to left renal vein)
- Renals: L1/L2
- Gonadal: L2
- IMA: L3
- Bifurcation: L4

19
Q
- At what spinal levels are the following structures located:
- Body of pancreas and splenic vein
- Left renal vein
- Horizontal part of duodenum
A
- Body of pancreas and splenic vein: L1 and L2
- Left renal vein: L2
- Horizontal part of the duodenum: L3
20
Q
- Adrenal glands:
- Blood supply
- Innervation
- Covered in renal fascia attaching to _
A
- Blood supply
- Superior suprarenal a.
- Middle suprarenal a.
- Inferior suprarenal a.Innervation
- Preganglionic sympathetics from T6-L2
- Celiac plexus and splanchnic nerves
- Crura of the diaphragm

21
Q
- Relationships of the:
- Right adrenal gland
- Left adrenal gland
A
- Right
- Right crus of diaphragm superiorly
- Right kidney inferiorly
- IVC
- Liver anteromedially
- Left
- Left crus of the diaphragm superiorly
- Spleen
- Stomach
- Pancreas
- Left Kidney
22
Q
- Relationships of:
- Right kidney
- Left kidney
A
- Right kidney
- Right suprarenal gland superiorly
- Muscular floor of the posterior abdominal wall posteriorly (diaphragm, psoas major and minor, quadratus lumborum and transversus abdominis)
- Liver
- Duodenum
- Ascending colon
- Left kidney
- Left suprarenal gland superiorly
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Pancreas
- Jejunum
- Descending colon
- Posteriorly for both-muscular floor of posterior abdominal wall, L1 ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerves, subcostal nerves (T12)
23
Q
- Kidney anatomy
A

24
Q
- The ureters are POSTERIOR to _ in males and _ in females
- What are the three constriction points?
A
- Ductus deferens in males
- Uterine artery in females (careful of this during hysterectomy)
- Ureteropelvic junction
- Crossing external iliac artery and/or pelvic brim
- Uterer enters bladder wall
25
* Lymphatics
* _ lymph nodes drain foregut structures
* _ lymph nodes drain midgut structures
* _ lymph nodes drain hindgut structures
* Celiac
* Superior mesenteric
* Inferior mesenteric
26
* Lymph flow: Starting from deep inguinal
* Deep inguinal
* External iliac
* Internal iliac
* Common iliac
* Lumbar/aortic/caval
* Inferior mesenteric
* **Cisterna chyli (dilated sac structure at the end of the thoracic duct)**

27
* Important nerves of the lumbar plexus
* Iliohypogastric (L1)
* Ilio-inguinal (L1)
* Genitofemoral (L1-L2)
* Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (L2-L3)
* Obrutator nerve (L2-L4)
* Femoral nerve (L2-L4)

28
* Important nerves of the posterior abdominal wall



