Pigmentations & Tissue Deposits Flashcards
What are the 4 main categories of pigments?
1) Hematogenous pigments
2) Melanin
3) Lipofuscin
4) Exogenous pigments
What are 4 types of Hematogenous pigments?
1) Hemoglobin
2) Hemosiderin
3) Bilirubin
4) Porphyrins
What are the 3 main categories of Tissue depositis?
1) Calcification
2) Amyloid
3) Uric Acid
What are 3 type of Calcification?
1) Dystrophic
2) Metastatic
3) Calcinosis cutis
What is the cause of the jaundice color that comes from RBC catabolism?
Bilirubin
What animal species do not have Biliverdin reductase so they accumulate Biliverdin instead of Bilirubin?
Birds
What is the end product of the breakdown of the Heme group?
Bilirubin
In Hemoglobin Catabolism, what are the 2 pathways that Conjugated bilirubin will go once in the bile duct?
1) Most will be secreted into the GI tract
2) Some will go back into the blood
Term used when too much bilirubin in the blood
Hyperbilirubinemia
Term used when Bilirubinemia >2mg/dl
Jaundice
Definition of Jaundice/Icterus
Increased bilirubin in tissues
What are 2 gross descriptions of Jaundice/Icterus
1) Yellow-green discoloration of tissue or fluid
2) Most prominent in mucous membranes, adventicial surfaces
What is the ONLY organ tissue that you DO see pigment in jaundiced tissues?
Cholestatic liver
What is a microscopic description of Jaundice/Icterus?
Yellow-brown intracellular (hepatocytes, kupffer cells) or extracellular pigment (bile canalliculi)
What are 3 types of hyperbilirubinemia and main characteristic of each one?
1) Pre-hepatic -> too much breakdown of RBCs
2) Hepatic -> Hepatocyte dysfunction
3) Post-Hepatic -> buildup of conjugated bilirubin in blood
In Prehepatic hyperbilirubinemia, what happens and what is the cause?
Bilirubin production exceeds hepatocellular uptake
Cause: Hemolysis (intravascular or extravascular)
In Hepatic hyperbilirubinemia, what are the 3 types of hepatocellular dysfunction and the cause of it all?
- Decreased bilirubin uptake
- Decreased conjugation
- Decreased secretion in bile
Causes: Hepatic insufficiency, hepatitis, hepatocellular degeneration
In Posthepatic hyperbilirubinemia, what happens and what causes it?
Reflux of conjugated bilirubin into blood
Causes: Biliary obstruction (cholestasis) or rupture
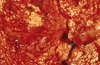
Which mechanism of jaundice is to blame with this sheep?

Prehepatic hyperbilirubinemia
What are 2 gross descriptions of Hemoglobinuria?
1) Red-brown coloration of kidney and urine
2) Pink serum

What is a microscopic description of Hemoglobinuria?
Red-orange material in renal tubules

What are 2 ways of hemoglobin catabolism?
1) Extravascular hemolysis
2) Intravascular hemolysis
What happens in Extravascular Hemolysis?

What happens in Intravascular Hemolysis?
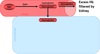
Extravascular and Intravascular hemolysis BOTH result in jaundice
True or False?
True
What are the 5 etiologies of Intravascular hemolysis?
1) Oxidative damage (most common)
2) Erythrocyte metabolic deficiency
3) Infectious
4) Immune-mediated
5) Direct membrane damage
Copper Toxicosis falls under which etiology of Intravascular hemolysis?
Oxidative damage
Neonatal Isoerythrolysis falls under which etiology of Intravascular hemolysis?
Immune-mediated
What is the end result of Acute Copper Toxicosis in small ruminants?
Hemoglobinuria