Pictures Week 2 Flashcards

polycythemia vera
hypercellular marrow, erythroid hyperplasia, increased megs

essential thrombocythemia
increased megs: large and weird, tend to cluster

early primary myelofibrosis: looks like ET
reticulin stain shows reticulin fibers

late primary myelofibrosis
increased megs; bizarre shapes, clustering, fibrosis

mastocytosis
aggregates of bland cells, round or spindle shaped, sometimes eosinophila

Refractory cytosine with unilineage dysplasia
weird looking precursors, binucleation or irregular nuclei; can show fibrosis, high or low cellularity; megaloblastoid features

refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts
ring sideroblasts, usually with dyspoietic features (in red cell series only)

MDS with isolated del(5q)
all megs monomuclear

refractory cytosine with multilineage dysplasia
granulocytes (if affected) don’t granulate normally; nuclei don’t lobulate normally

refractory anemia with excess blasts
blasts and dyspoeitic maturation

reactive follicular hyperplasia: bacterial abscess

Paracortical expansion: infectious mononucleosis (EBV or CMV): T cells and APCs
low power: normal architecture looks effaced
high power: polymorphic cell population in paracortex
also typical of: viruses and early HIV

activated T cells
huge reactive mononuclear cells: infectious mononucleosis
NOT cookie cutter: rules out malignancy

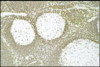
lupus lymphadenitis: necrosis (pale area)

HIV: lymphadenopathy: burned out follicles
rectangle: residual mantle zones
circle: histiocytes where germinal centers should be
normal germinal centers requiee CD4+ follicular helper cells

dermatopathic lymphadenopathy: aggregates of histiocytes
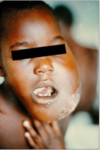
ex: eczema, psoriasis, pemphigus
normal small germinal centers with prominent mantle zones and large pale areas (cells with lots of cytoplasm)

dermatopathic lymphadenopathy: aggregates of histiocytes
pale: lots of cytoplasm

dermatopathic lymphadenopathy
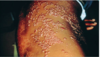
aggregates of histiocytes: lots of dark pigment is melanin from skin lesions

chronic lymphocytic leukemia/lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
pseudofollicular, effacement of normal architecture

chronic lymphocytic leukemia/lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
proliferation center: pseudofollicular, effacement of normal architecture
collections of larger cells undergoing DNA synthesis and mitosis

chronic lymphocytic leukemia/lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
small lymphocytes, little cytoplasm: smudge cells

mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
homogeneous effacement, starry sky: no proliferation center in lymph nodes
PB: small lymphocytes, little cytoplasm: smudge cells

mantle cell lymphoma (MCL)
Ki-67 immunostain

Burkitt lympohoma
cytology: variation in nucleus size and chape; intermediate size cells with basophilic, vacuolated cytoplasm; mitotic cell to far right
tissue: usually homogeneous effacement, high growth rate, starry sky