Pictures Flashcards

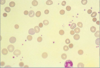
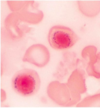
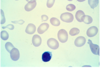
normal red blood cells

eosinophil

basophil

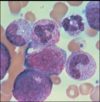
monocyte

lymphocyte

lymphocyte

reactive lymphocyte

large granular lymphocyte
(NK cell or cytotoxic T cell)

neutrophil
left shift: neutrophil variants
horseshoe nuclei: band
bean nuclei: metamyelocytes
round nuclei: myelocyte

neutrophil with toxic granulation

platelet

giant platelet
Describe RBC

normocytic, normochromic RBC
Describe RBC
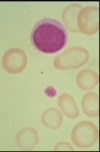
hypochromic RBC
Describe RBC

Hypochromia, anisocytosis, poikilocytosis

polychromasia

sickle cell

Bite cells and hemoglobin clumps

schistocytes

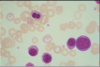
blast

promyelocyte

myelocyte

metamyelocyte

band
pronormoblast

basophilic erythroblast

polychromatophilic

normochromic erythroblast

immature megakaryocyte

mature megakaryocyte

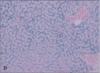
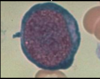
bone marrow core biopsy (5 year old)

bone marrow core biopsy (35 years old)

bone marrow core biopsy
top circle: erythroid
bottom circle: myeloid
arrow: megakaryoctye

normal bone marrow
Describe.
Name.
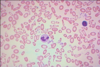
- microcytosis, hypochromia, anisocytosis, poikilocytosis
- Iron deficiency
Describe.
Name.

- microcytosis, hypochromia, target cells
- beta thalasemia
Describe.
Name.

- impaired nuclear maturation indicated by red nucleus, enhanced cytoplasm
- meagaloblastic RBCs
What is this and what causes it?

- megoblastic anemia
- impaired B12 uptake, folate deficiency, some drugs, bone marrow dysfunction
Describe.
Name.

- normocytic, iron
- anemia of chronic infection
Describe.
Name.

- spherocytes
- hereditary spherocytosis
Describe.
Name.
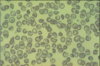
- hemoglobin crystals
- Hemoglobin C disease
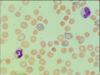
polychromasia (increased reticulocytes)
Describe.
Name.
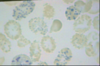
- heinz bodies
- G6PD deficiency

- cell that looks like it has a blister
- G6PD deficiency
- Left arrows
- Upper right arrows
What is this?

- merozoites
- gametocyte
- Plasmodium falciparum

Plasmodium vivax

babesia

Bartonella bacilliformis

Bartonella bacilliformis