Physics 4: Light & Sound Flashcards
(46 cards)
Monochromatic light of a certain wavelength falls on a narrow slit. On a screen a certain distance away, the distance between the second minimum and the central maximum is 2cm. What would happen to the spacing between the two if the wavelength of the radiation were increased?
- a) It would depend on whether the new wavelength is an odd or even multiple of the old.
- b) It would remain unchanged
- c) It would decrease.
- d) it would increase.
D. It would increase.

Electromagnetic Spectrum
The following units are often used when quoting wavelengths:
- 1 mm = 10− 3m,
- 1 μ m = 10− 6 m,
- 1 nm = 10− 9 m, and
- 1 Å (angstrom) = 10− 10 m.
The full spectrum is broken up into many regions, which in descending order of wavelength are
- radio (109 m− 1 m),
- microwave (1 m− 1 mm),
- infrared (1 mm− 700 nm),
- visible light (700 nm− 400 nm),
- ultraviolet (400 nm− 50 nm),
- x-ray (50 nm− 10− 2 nm), and
- gamma rays (less than 10− 2 nm).
electromagnetic waves
speed of light
c=3 × 108m/s
c=fλ
blackbody
- used to describe an ideal radiator
- refers to the fact that such an object is also an ideal absorber and would appear totally black if it were at a lower temperature than its surroundings
rectilinear propagation
When light travels through a single homogeneous medium, it travels in a straight line
geometrical optics.
behavior of light at the boundary of a medium or interface between two media is described by this theory
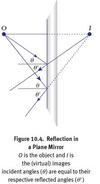
law of reflection
θ 1=θ<span>2</span>
where θ 1 is the incident angle and θ 2 is the reflected angle, both measured from the normal
real image
light actually converges at the position of the image
virtual image
light only appears to be coming from the position of the image but does not actually converge there.
- Because the light does not converge at all, plane mirrors always create virtual images
center of curvature (C)
a point on the optical axis located at a distance equal to the radius of curvature from the vertex of the mirror;
in other words, where the center of the mirrored sphere would be, were it a complete sphere.
radius of curvature (r)
a measure of the radius of the circular arc which best approximates the curve at that point
Focal length (for all spherical mirrors)
f=r/2
Key Variable Distances for Geometrical Optics
The focal length (f) is the distance between the focal point (F) and the mirror (for all spherical mirrors,
, where the radius of curvature (r) is the distance between C and the mirror); the distance of the object from the mirror is o; the distance of the image from the mirror is i

Mirror Equation
(1/o) + (1/i) = 1/f =1/f = 2/r
- _Plane mirrors_ can be thought of as infinitely large spherical mirrors.
- As such, for a plane mirror, r = f = ∞ , and the equation becomes: (1/o) + (1/i) = 0
- or : i= (-o)
magnification (m)
** dimensionless value that is the ratio of the image’s height to the object’s height**
m= -(i/o)
- A negative magnification signifies an inverted image, while
- a positive value means the image is upright.
- If |m| < 1, (“absolute value of m is less than 1”) the image is reduced; i
- f |m| > 1, the image is enlarged; and
- if |m| = 1, the image is the same size as the object.
Ray Diagrams for Concave Spherical Mirror at 3 Different Points
- In Figure 10.6a, the object is placed between F and C, and the image produced is real, inverted and magnified.
- In Figure 10.6b, the object is placed at F, and no image is formed because the reflected light rays are parallel to each other. In terms of the mirror equation, we say that the image distance i = ∞ here.
- Figure 10.6c, the object is placed between Fand the mirror, and the image produced is virtual, upright, and magnified.
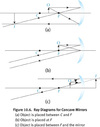
In general, there are three important rays to draw..
What are they?
- For a concave mirror, a ray that strikes the mirror parallel to the horizontal is reflected back through the focal point.
- A ray that passes through the focal point before reaching the mirror is reflected back parallel to the horizontal.
- A ray that strikes the mirror right where the normal intersects it gets reflected back with the same angle (measured from the normal).
Sign Chart for Single MIrrors
Symbol
Positive (+)
Negative (-)
o
Object is in front of the mirror (R-side)
Object is behind mirror (V-side)
i
Image is in front of mirror (R-side)
Image is behind mirror (V-side)
r
Concave mirrors
Convex mirrors
f
Concave mirrors
Convex mirrors
m
Image is upright (erect)
Image is inverted
Snell’s Law of Refraction
n1sin θ1= n2sin θ2
index of refraction of the medium.
n=c/v
- For air, n is essentially equal to 1 because v≈ c.
- But for all other materials on MCAT: ** v < c and n > 1.**
General Bending concepts moving between indecies of different n-values:
- when light enters a medium with a higher index of refraction (n2 > n1), it bends towards the normal so that θ 2 < θ 1
- if the light travels into a medium where the index of refraction is smaller (n2 < n1), the light will bend away from the normal so that θ 2 > θ 1.
Total internal reflection
all the light incident on a boundary is reflected back into the original material, results for any angle of incidence greater than the critical angle, θ c
sinθ c=n1/n2
THIN SPHERICAL LENSES
two surfaces that affect the light path
Because light can be coming from either side of a lens, a lens has two focal points (one on each side of the lens) and the focal length can be measured in either direction from its center


