Phylogenetic reconstruction Flashcards
Cladistics vs Phenetics
Cladistics: regards combining characters (Apomorphies)
Phenetics: Regards numeric diferences (Distances)
Criterion and method cladistic methods
- Parsimony:
1. Maximum parsimony (MP) - Probabilistic: Likelihood-based:
- Maximum likelihood (ML)
- Bayesian inference (BI)
Parsimony
- Less number of steps
- We expect convergence and reversals
to occur less than synapomorphies - less homoplasy
- # sp = #trees
Advantages and disadvantages Parsimony
Advantages:
Is a simple method - easily understood operation
- Does not depend on an explicit model of evolution
- Gives both trees and associated hypotheses of character evolution
- Should give reliable results if the data is well structured
Disadvantages:
May give misleading results if homoplasy is common or concentrated in particular parts of the tree
Character evolution
History vs model
Observed topology
History: Hypothesis about the evolution of a particular character or a phylogeny
Model: Specifies probability of change between the start and end of each branch
Observed topology: Different scenarios
Assumptions about character evolution
BUT
- Unordered (Fitch Parsimony)
- Ordered (Wagner Parsimony)
- Irreversible (Camin-Sokal Parsimony)
- Dollo (Dollo Parsimony): The loss of function is more posible
BUT: there are distances that violate inequality
Compound coding probelms
- Create compound conditions
- each of such condition might legitimately be consider its own character
Multistate coding problems
Phylogenetic information can be lost to the tree search process
Non-additive binary coding problem
Non-additive binary coding makes the absence token (usually 0) correspond to a ‘nonspecified other’ variable: The ‘0’ taken becomes a catch-all for anything that isn’t scored as ‘1’
Search for a Parsimony tree
- Exhaustive search (exact)
- Branch-and-bound search (exact)
- Heuristic search methods (hopefully exact)
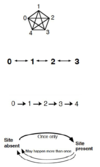
Exhaustive search for the Parsimony tree
- Adding 1 more taxon each time
- All posible trees
- Absourd t with more than 10 taxa
Branch and bound search for the Parsimony tree
Looking for short cuts (most likely trees)
- Also t consuming
Heuristic search for the Parsimony tree
- Create a starting tree
- Branch swapping (Randomize the data ser for every search):
- Multiple random search replicates
3. new starting point: change points until: less steps
4. re-start with different order.
Create a staring tree
- • A greedy method
- • Start with 3-taxon tree (Most parsimoniuos)
- • Add taxa one at a time.
- • Keep only the best tree found so far
- • No guarantee of optimality, but may provide good starting point for search
Branch swapping:
- Nearest-Neighbor Interchange (NNI)
- Subtree Pruning and Regrafting (SPR): cutting & pasting different parts of the tree
- Tree Bisection and Reconnection (TBR)
Criterion phenetic
Distance methods
Distance methods
Criterion
Advantages & Disadvantages
Minimum Evolution (ME)
The tree with the shortest sum of the
branch lengths
Advantages:
• Distances can be ‘corrected’ for unseen events.
• Usually faster than character-based methods.
• Can be used for some rate analyses.
-used at the beginning for checking the alignments
Disadvantages:
• Information lost when characters transformed to distances.
• Cannot be used for character analysis.
Examples for distances (ME)
- total number of differences
- p (= uncorrected) distances
- corrected distances following evolutionary models
p- distances = (total # differences)/total # characters
Distance methods tree reconstruction
Neighbor joining

Why Maximum Likelihood
- Multiple substitutions not detectable by parsimony or distance methods
- Observes the likelihood of every character state
in a phylogenetic tree
Parameters of Maximum Likelihood
- Substitution probabilities
- Base composition
Parameter substitution for ML
Transitions more frequent than transversion

Parameter Base composition in ML
- Amount of character states (ACGT)
- varies significantly en very organism
DNA substitutions models
- Jukes-Cantor (JC 1969)
- Kimura 2 parameters (K2P 1980)
- Felstein 1981 (F81)
- Hasegawa, Kishino, Yano (HKY 1985)
- General time reversible models ( GTR 1990)
- Nasty Model




