Pharynx and oesophagus Flashcards
What is the function of the pharynx with regard to the GI system? The osephagus?
Pharynx: bypass the airway
Oesophagus: convey to stomach
What are the basilar (skull) attachments of the pharynx?
Attachment of the fibrous part of the pharynx is the red outline: sphenoid bone (pointy bone), auditory tube, temporal bone and occipital bone.

Explain each of these structures?
How do they lie?
The upper muscle has a common origin with ________.

Pharyngeal fascia is the first ‘cup’ and sits inside the superior constrictor muscle.
All of the constrictor muscles join posteriorly in a raphe and have a similar attachment posteriorly.
Superior constrictor sits outside the pharyngeal fascia but inside the middle constrictor and comes of a common origin with buccinator (circled in black).
Middle constrictor sits outside the superior constrictor but inside the inferior constrictor and comes off hyoid.
Inferior constrictor outside middle constrictor and comes off the hyoid and cricoid cartilage.
Deeper to these are the levators.

Where do each of these muscles come from?
What are the functions of these muscles?

Salpingopharyngeus: comes off the auditory tube and inserts into the pharynx.
Palatopharyngeus: comes off the soft palate
Stylopharyngeus: comes off the styloid process
These 3 muscles can pull the pharynx up and can also get constricted and pulled inward by the constrictor muscles.

Black lines and blue lines pointing to?


Tonsils and blue lines?


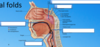

What are valleculae?
Clinical significance?
Valleculae is the recess before the epiglottis. The spot where the laryngoscope goes for intubation. It is also where bits of food get stuck and make you feel like you are going to choke.
Seat the laryngoscope in the valicular (key landmark): posterior to that is the epiglottis which is where you will chuck a tube down into the trachea.

Laterally and posterior to the epiglottis is the __________.
Piriform fossa.

What is each of the arrows pointing to?
Including the green arrows?


how long is the oesophagus?
25 cm long.
Explain stage 1 of swallowing?

Stage 2 of swallowing?

Stage 3 of swallowing?



