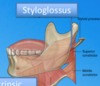
Oral cavity Flashcards



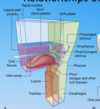
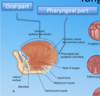
Where is the parotid duct opening?
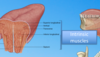
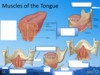
What part of the oral cavity is this?
Upper 2nd molar.
vestibule.
What are the two compartments of the oral cavity?
Vestibule: Outside the teeth but inside the lips.
Oral cavity proper: inside the arches of the teeth.
What is the other name for the opening of the mouth?
Oral fissure.
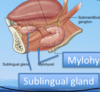
Which ducts open into the oral cavity proper?
Submandibular and sublingual.
What two tissues will help food stay in between the teeth for mastication?
Buccinator and tongue.

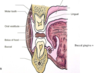

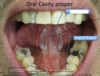
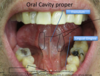
Roof, floor and exit of the oral cavity proper?

How much of the palate is hard vs soft?
Anterior 2/3 is hard. Posterior 1/3 is soft.


Which bones form the hard palate?
maxilla, palatine and sphenoid.

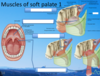
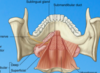
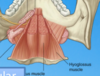
What are these two structures in the soft palate?


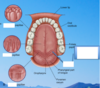
What is the purpose of palatine rugae? What happens as you travel more posterior from the rugae?
help keep the food in the mouth while it is being processed.
Travel more posterior it becomes softer and more slippery which helps it slide down