Pharmacology Flashcards
What are the three major routes of drug administration?
Topical, Transdermal and Subcutaneous


What does the stratum corneum consist of?
Cornerocytes (hardened, dead keratinocytes), surrounded by intercellular lipids forming 10-30 sheets of tissue that are constantly shed (desquamated) and renewed


What is the differences between these routes and which is the principle route?

Principle route is intercellular

Why can steriods be stored in the Stratum Coneneum?
The “mortar” is highly lipophillic, allowing highly lipophillic drugs such as steriods to be stored
Describe the “brick and mortar” model
Brick: corneocytes suspended in aggegated keratin filaments embedded in a matrix of filagrin. Adjacent corneocytes are held together by corneodesmosomes
Mortar: Multiple bilayers of intercellular lipids (ceramides, cholesterol and free fatty acids). Highly hydrophobic and can act as a reservior for lipid soluble drugs (eg steriods).
What is the most effective way for drugs to enter across the stratum corneum both locally and systemically?
Via intercellular route, and normally only allows the diffusion of small, hydrophobic drugs.
What two factors dictate the choice of vehicle?
1) Physicochemical properties of the drug
2) The clincal condition
What is Fick’s law of diffusion?

What other factors does Kp, the permeability coefficient, take into account within Fick’s Law of Diffusion?

What is the concentration of the drug and the partition coefficient of the drug highly dependant on?
The vehicle
What are the important factors when considering the rate and extent of absorption of a topically applied drug?
- Solubility of the drug in vehicle (Cv)
- Maximising the movement (or partitioning) or the drug from vehicle to the stratum corneum (Km)
Comment on each of these stages of drug absorption

1) Lipophilic drug is good for absorption. If in a lipophillic base, likes to dissolve, therefore vehicle retains drug
2) Can expect good partitioning
3) Hydrophillic cannot diffuse rapidly through strateum corneum
What is the driving force for percutaneous absorption?
The concentration of soluble drug in the vehicle
How can percutaneous absorption be enhanced?
By increasing the concentration of soluble drug in the vehicle. To do this, an inclusion of excipients such as propylene glycol can enhance solubility.
Why are topically applied drugs generally poorly absorbed?
Because only a small fraction partitions into the stratum corneum
What are the physical and chemical conditions which can improve partitioning?
- Hydration of the skin by occlusion (prevention of water loss) by using ointments, creams or even cling film!
- Increase the solubilty of hydrophobic drugs by inclusion of excipients such as propylene glycol
Why should non specific prescribing be avoided, in particular reference to hydrocortisone?
Hydrocortisone comes in many forms and the salt can can vastly influence potency
What must be considered when prescribing?
Where is the drug being applied, skin thickness, hydration of the skin, intergrity of the epidermis, drug concentration, vehicle, the drug salt
What can glucocorticosteriod features vary with?
-Body site, state of skin, occlusion, vehicle, concentration of drug and form of drug
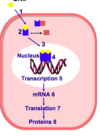
Explain the mechanism of glucocorticosteriods in relation to this diagram

Why is the skin an attractive route or drug administration for a systemic effect?

When is Transdermal drug delivery suitable and what are the advantages and disadvantages?



