Peripheral Nerves Flashcards
Axillary nerve (C5, 6)
Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, 6, 7)
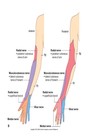
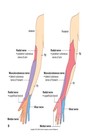
Axillary nerve (C5, 6)
- Motor: deltoid and teres minor - abduction from 15-90° (C5 myotome test)
- Sensory: capsule of the shoulder joint and skin superficial to the deltoid (regimental badge) (C5 dermatome test, specifically over deltoid)
Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, 6, 7)
- Motor: i. Biceps brachii (elbow flexion in supinated position – C6 myotomal test), ii. Brachialis (below the biceps, and flexes the elbow but does not pronate or supinate: therefore test with elbow flexion in a neutral position i.e. thumb superior) iii. Coracobrachialis (flex 120°and adduct 10° at the shoulder)
- Sensory: ends as the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve of the forearm - anterior lateral forearm
Median nerve C6-T1
Motor:
- Pronation of the arm: pronator teres (c6-7) and quadratus (c7-8)
- Flexion at thw wrist - myotome test
- Flex middle phalange, do finger flexion myotome test - C7
LOAF:
- Flex and extend digit 2 and 3
- Opponnens pollocis - thumb to pinky
- Abductor pollicis - thumb right angle on palm
- Flexor pollicis brevis - flex thumb at palm
Sensory:
- Palmar cutaneous nerve – palmar surface of lateral 3.5 fingers i.e. thenar eminence and lateral palm but not the digits. Takes its origin proximal to the flexor retinaculum of hand so not affected by carpal tunnel syndrome. b.
- Digital cutaneous branches – supplies the lateral 3.5 digits anteriorly, and dorsal tips of lateral 3 fingers
- For sensory loss: test pinprick over the hand – the palmar aspect of the thumb, index, middle and lateral half of the ring finger is often affected (C6, C7 dermatome test)
Radial Nerve (C5-8)

Motor:
- Triceps and anconeus (C6-8): extension of elbow in supinated position (C7 myotome test)
- Brachioradialis (C5-6) is an elbow flexor in the forearm posterior compartment: test with elbow flexion done in neutral (thumb up) position, as this muscle tends to move a pronation to a supination and vice-versa (variation of C6 myotome test)
- Extension of the wrist - c6 myotome
- finger extension - c7
Sensory
- Posterior arm and forearm
Ulnar Nerve (c7-T1)

Motor:
- Flexion of the wrist (c7 myotome)
- flex pinky to palm, flex pinky at MCP, abduct pinky, flex and extend pink and ring finger, finger abduction and adduction
- adduct thumb and flex
- Hold a peice of paper between thumb and forefinger
Sensory:
medial forearm and the dorsal plus anterior aspects of medial 1½ fingers and associated palm (C8, T1 dermatomes)
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (L2-3)
Femoral nerve (L2, 3, 4)

Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (L2-3)
i. A lesion is usually the result of entrapment between the inguinal ligament and anterior superior iliac spine.
ii. There is sensory loss over the lateral aspect of the thigh
iii. There is no motor loss
iv. If painful, it is called meralgia paraesthetica
Femoral nerve(L2, 3, 4)
- Hip Flex - L1/L2 myotome
- Extend the knee - L3 myotome
Sensory
Anterior femoral cutaneous nerve: anteromedial aspect of the thigh (about L3 dermatome but more medial)
Saphenous nerve: medial aspect of the leg (L4 dermatome test)
Obturator nerve (L2-4)
Sciatic nerve (L4, 5; S1,2, 3)
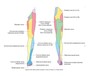
Obturator nerve (L2-4)
- Motor: obturator externus, adductors for adduction of the thigh (L2-3 myotome test)
- Sensory: terminal branch supplies the medial thigh (about L2 dermatome test)
Sciatic nerve (L4, 5; S1,2, 3)
Motor: hamstrings and adductor magnus: flexion of knee (L5-S1 myotome) and extension of hip (L5-S1myotome)
Sciatic - no sensation cos sensory is via femoral
Common Fibular Nerve (L4-S2)
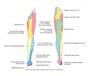
Superfical Fibular
- Motor - eversion 21 myotome
- Sensory - L5 anterior leg to middle toe
Deep fibular
- Motor - Dorsiflexion L4-L5 and inversion L4 myotomes, big tow extension, toes dorsifelxion and eversion, ankle and toe dorsiflex
- Sensory - between 1st and 2nd skin
Tibial nerve (L4-S3)
- Motor: supplies gastrocnemius, plantaris and soleus (plantar flexion S1 myotome, with the hamstrings L5-S1 myotome), popliteus (knee flexion, L5-S1), tibialis posterior (inversion L4, plantar flexion S1 and responsible for maintaining the medial arch of the foot), flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus (toe flexion, S2 myotome)
- .Branches in the foot are the medial plantar and lateral plantar nerves a. Medial plantar: abductor hallucis (abduction and flexion of big toe, S2 myotome), flexor digitorum brevis and flexor hallucis brevis (toe flexion, S2 myotome). Sensory is the skin over medial 2/3 of plantar surface of foot (S1 dermatome) b. Lateral plantar: supplies remaining muscles of foot. Sensory is the skin over lateral third of plantar surface of foot (S1 dermatome)

